4-cervical spines2016-12-18 11:173.3 MB
... It acts as a pivot for the rotation of the atlas (and the skull) above. It has a large upright peg-like odontoid process, or dens, which projects upward from the superior surface of the body. Actually it represents the body of the atlas that has fused with the axis. Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem ...
... It acts as a pivot for the rotation of the atlas (and the skull) above. It has a large upright peg-like odontoid process, or dens, which projects upward from the superior surface of the body. Actually it represents the body of the atlas that has fused with the axis. Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem ...
Document
... There are portions of the frontal bone that make the roof of the eye,underneath them we have the eye,between these portions we have a protrusion of the ethmoid bone (crista galli ) lateral to crista galli there is the cribriform plate where the; perpendicular plate (forms the superior portion of the ...
... There are portions of the frontal bone that make the roof of the eye,underneath them we have the eye,between these portions we have a protrusion of the ethmoid bone (crista galli ) lateral to crista galli there is the cribriform plate where the; perpendicular plate (forms the superior portion of the ...
Virtual Assessment of the Endocranial Morphology of the Early
... To obtain an approximation of the total endocranial volume, missing parts of the cranial base were virtually reconstructed by using a modern human cranium as reference. We determined the reference by carrying out a generalized Procrustes analysis (GPA) and a subsequent principal components analysis ...
... To obtain an approximation of the total endocranial volume, missing parts of the cranial base were virtually reconstructed by using a modern human cranium as reference. We determined the reference by carrying out a generalized Procrustes analysis (GPA) and a subsequent principal components analysis ...
He1. A 72-year-old man presents in the emergency room with
... patient to draw a vertical line that bisected a horizontal line drawn by the physician. The patient drew a vertical line on the right side of the line. When the physician waved his hand in front of the temporal visual field of the left eye or the nasal visual field of the right side, the patient did ...
... patient to draw a vertical line that bisected a horizontal line drawn by the physician. The patient drew a vertical line on the right side of the line. When the physician waved his hand in front of the temporal visual field of the left eye or the nasal visual field of the right side, the patient did ...
Special Senses
... Result of damage to the visual cortex on one side only. The person is unable to see things past the middle of his/her visual field on either the right or left side. ...
... Result of damage to the visual cortex on one side only. The person is unable to see things past the middle of his/her visual field on either the right or left side. ...
Sample
... Page Ref: Sec. 2.2 45) The circulatory system has two major fluid transportation systems: the cardiovascular and the lymphatic. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: Sec. 2.3 46) The elimination of body wastes is a function of the digestive system. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: Sec. 2.3 47) Blunt or penetrating injury to ...
... Page Ref: Sec. 2.2 45) The circulatory system has two major fluid transportation systems: the cardiovascular and the lymphatic. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: Sec. 2.3 46) The elimination of body wastes is a function of the digestive system. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: Sec. 2.3 47) Blunt or penetrating injury to ...
Name: Period:______ EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE CRAYFISH
... 1. Place the crayfish in the dissecting pan on its belly (dorsal side up – back is up). 2. Insert the point of the scissors under the top of the carapace at the back of the cephalothorax and cut up towards the eyes, stopping when you are between the eyes. 3. Cut across the carapace behind the eyes, ...
... 1. Place the crayfish in the dissecting pan on its belly (dorsal side up – back is up). 2. Insert the point of the scissors under the top of the carapace at the back of the cephalothorax and cut up towards the eyes, stopping when you are between the eyes. 3. Cut across the carapace behind the eyes, ...
Shoulder Injury Mechanisms and Integrative Medicine Therapies
... to move easily. This allows a wide range of movements for the humerus, which include adduction, abduction, extension, flexion, internal rotation, external rotation, horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction, and circumduction. The two main ligaments of this joint are the glenohumeral ligaments (sup ...
... to move easily. This allows a wide range of movements for the humerus, which include adduction, abduction, extension, flexion, internal rotation, external rotation, horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction, and circumduction. The two main ligaments of this joint are the glenohumeral ligaments (sup ...
The Skeletal System - Bio-Guru
... marrow. The color of yellow marrow is due to the much higher number of adipocytes. Both types of bone marrow contain numerous blood vessels and capillaries. • At birth, all bone marrow is red. With age, more and more of it is converted to the yellow type. Adults have on average about 2.6 kg of bone ...
... marrow. The color of yellow marrow is due to the much higher number of adipocytes. Both types of bone marrow contain numerous blood vessels and capillaries. • At birth, all bone marrow is red. With age, more and more of it is converted to the yellow type. Adults have on average about 2.6 kg of bone ...
Digestive System
... • The tongue is a muscular organ located in the oral cavity. The core of the tongue consists of connective tissue and interlacing bundles of skeletal muscle fibers. • The distribution and random orientation of individual skeletal muscle fibers in the tongue allows for increased movement during chewi ...
... • The tongue is a muscular organ located in the oral cavity. The core of the tongue consists of connective tissue and interlacing bundles of skeletal muscle fibers. • The distribution and random orientation of individual skeletal muscle fibers in the tongue allows for increased movement during chewi ...
Terminal Branch of Recurrent Human Laryngeal Nerve
... Hiroto et al. [24] found two to three branches, and Winckler [31] mentioned two branches. The origin of these branches was in the lower third (44.1%) or the middle third (49.2%) of the lateral margin of the cricoid cartilage. Eller et al. [39] found an average of three to four branches to the muscle ...
... Hiroto et al. [24] found two to three branches, and Winckler [31] mentioned two branches. The origin of these branches was in the lower third (44.1%) or the middle third (49.2%) of the lateral margin of the cricoid cartilage. Eller et al. [39] found an average of three to four branches to the muscle ...
Anterior & Lateral comp. of leg
... medial cuneiform bone and the adjoining base of the first metatarsal bone. ...
... medial cuneiform bone and the adjoining base of the first metatarsal bone. ...
A case of middle turbinate absence
... of the last three turbinates is a process induced by active intramural pneumatization of the lateral nasal wall during fetal life. Middle turbinate constitutes the superior and medial limits of middle nasal meatus, an air space in which maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid cells, and frontal sinus drai ...
... of the last three turbinates is a process induced by active intramural pneumatization of the lateral nasal wall during fetal life. Middle turbinate constitutes the superior and medial limits of middle nasal meatus, an air space in which maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid cells, and frontal sinus drai ...
Lesson 4 - Maryville University
... - lateral border, distal forearm, just proximal to wrist - from under lateral border of brachioradialis - innervates skin on lateral dorsum of hand, thumb, proximal 2/3 of 1st 2-3 fingers (lateral side of middle or ring finger) • (A) 9. Posterior cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve: - medial border, ...
... - lateral border, distal forearm, just proximal to wrist - from under lateral border of brachioradialis - innervates skin on lateral dorsum of hand, thumb, proximal 2/3 of 1st 2-3 fingers (lateral side of middle or ring finger) • (A) 9. Posterior cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve: - medial border, ...
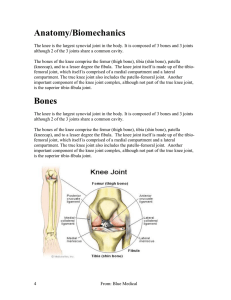
29-Reading - Blue Medical
... symptomatic instability but they may be associated with chronic pain. Significant ...
... symptomatic instability but they may be associated with chronic pain. Significant ...
Thoracic Wall - Dr. Sholley
... The sternal (also called parasternal or internal thoracic) nodes (Grant's Atlas: 11 th Ed. Fig. 1.8; 12 th Ed. Fig. 1.8) are present along the upper part of the internal thoracic artery, one or two in each of the upper four or five intercostal spaces. They receive lymphatic ...
... The sternal (also called parasternal or internal thoracic) nodes (Grant's Atlas: 11 th Ed. Fig. 1.8; 12 th Ed. Fig. 1.8) are present along the upper part of the internal thoracic artery, one or two in each of the upper four or five intercostal spaces. They receive lymphatic ...
A Case Report - International Journal of Health Sciences and
... Background: Orbital - facial manifestations are relatively rare in neurofibromatosis 1. Encephalocoeles are defined as herniation of meninges with brain matter. Absence of sphenoidal wing leads to Spheno orbital encephalocoele due to protrusion of brain tissue and meninges through superior orbital f ...
... Background: Orbital - facial manifestations are relatively rare in neurofibromatosis 1. Encephalocoeles are defined as herniation of meninges with brain matter. Absence of sphenoidal wing leads to Spheno orbital encephalocoele due to protrusion of brain tissue and meninges through superior orbital f ...
Hip Diseases
... Made up of the externus and internus obturators, the piriformis, the superior and inferior gemelli, and the quadratus femoris. Originate at or below the acetabulum of the ilium and insert on or near the greater trochantor. Aid lateral rotation of the hip. ...
... Made up of the externus and internus obturators, the piriformis, the superior and inferior gemelli, and the quadratus femoris. Originate at or below the acetabulum of the ilium and insert on or near the greater trochantor. Aid lateral rotation of the hip. ...
Brachial muscles in the chick embryo: the fate of
... wing-associated muscles of the shoulder and thorax. These muscles can be considered as a group, since they all develop from myogenic masses that form in the wing bud and subsequently divide into individual muscle primordia (Sullivan, 1962). The grafting of multiple somites from quail to chick embryo ...
... wing-associated muscles of the shoulder and thorax. These muscles can be considered as a group, since they all develop from myogenic masses that form in the wing bud and subsequently divide into individual muscle primordia (Sullivan, 1962). The grafting of multiple somites from quail to chick embryo ...
Congenital Temporal Bone Anomalies: An
... patient with hemifacial microsomia. This disease is thought to be due to an early vascular insult affecting branchial arch development and is the second most common facial developmental anomaly after facial clefts. There is dysplasia of the right mandibular condyle (*) with absence of the madibular ...
... patient with hemifacial microsomia. This disease is thought to be due to an early vascular insult affecting branchial arch development and is the second most common facial developmental anomaly after facial clefts. There is dysplasia of the right mandibular condyle (*) with absence of the madibular ...
Anatomy and histology of apical support: a literature review
... cross-sectional biopsies from the lateral third of the USL and CL of patients undergoing radical versus simple hysterectomy. Quantitative immunohistochemistry was used to demonstrate and quantify nerve content. They found that the ligaments contain autonomic nerves and ganglia, presumed to be extens ...
... cross-sectional biopsies from the lateral third of the USL and CL of patients undergoing radical versus simple hysterectomy. Quantitative immunohistochemistry was used to demonstrate and quantify nerve content. They found that the ligaments contain autonomic nerves and ganglia, presumed to be extens ...
A Rare Anatomical Variation in Medial Root of Azygos Vein with its
... the level of L3 and passing cranially to bifurcate quickly at the level of L2.Each of the branches then continues obliquely cranially and laterally, the right to terminates in the beginning of the azygos vein (medial azygos root), left in the hemiazygos (medial hemiazygos root). The right branch in ...
... the level of L3 and passing cranially to bifurcate quickly at the level of L2.Each of the branches then continues obliquely cranially and laterally, the right to terminates in the beginning of the azygos vein (medial azygos root), left in the hemiazygos (medial hemiazygos root). The right branch in ...
Hip Evaluation
... ♦ Position: Patient is supine, with the injured knee flexed at 90º and the hip flexed at 90º ♦ Hand placement: One hand is placed at the lateral femoral condyle and the other hand at the leg or the heel to move the leg ♦ Procedure: Apply pressure at the lateral femoral condyle while extending the kn ...
... ♦ Position: Patient is supine, with the injured knee flexed at 90º and the hip flexed at 90º ♦ Hand placement: One hand is placed at the lateral femoral condyle and the other hand at the leg or the heel to move the leg ♦ Procedure: Apply pressure at the lateral femoral condyle while extending the kn ...
HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY 213 CRANIAL NERVES
... 6. Pharyngeal branches to pharyngeal plexus (SVE Palate & pharynx) 7. Superior laryngeal branch Internal laryngeal nerve (GVA Supraglottic mucosa) External laryngeal nerve (SVE cricothyroid muscle) 8. Sinus nerve (GVA – arterial blood pressure & [O2] & [CO2]) 9. Recurrent laryngeal nerve ...
... 6. Pharyngeal branches to pharyngeal plexus (SVE Palate & pharynx) 7. Superior laryngeal branch Internal laryngeal nerve (GVA Supraglottic mucosa) External laryngeal nerve (SVE cricothyroid muscle) 8. Sinus nerve (GVA – arterial blood pressure & [O2] & [CO2]) 9. Recurrent laryngeal nerve ...
Interesting Case Series Review of Facial Nerve Anatomy
... facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranium at the stylomastoid foramen just inferior and posterior to the auricle. It has the longest path within a bony canal of any nerve in the body. Upon its exit of the cranium, the nerve courses within the parotid gland in a superior medial direction. It i ...
... facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranium at the stylomastoid foramen just inferior and posterior to the auricle. It has the longest path within a bony canal of any nerve in the body. Upon its exit of the cranium, the nerve courses within the parotid gland in a superior medial direction. It i ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.