* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
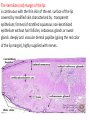
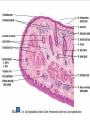
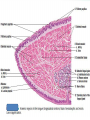
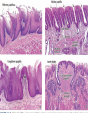
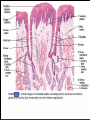
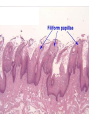
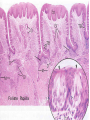
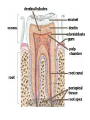
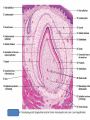
Digestive System Zahraa Ahmed Buthaina Al-Ezzi The digestive system • The digestive system is a long hollow tube or tract that starts at the oral cavity and terminates at the anus. • The system consists of the oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anal canal. • The oral cavity consists of the mouth and its structures, which include the tongue, teeth and major and minor salivary glands, and tonsils. Major functions of the digestive system include 1.transport of ingested water and food along the alimentary canal 2.secretion of fluids, electrolytes, and digestive enzymes 3.digestion and absorption of digested products; and excretion of indigestible remains. In the oral cavity, food is ingested, masticated (chewed), and lubricated by saliva for swallowing. Because food is physically broken down in the oral cavity, this region is lined by a protective, non keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium, The Lips • The oral cavity is formed, by (the lips and cheeks.) The lips are lined by a very thin skin covered by a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. Blood vessels are close to the lip surface, imparting a red color to the lips. The outer surface of the lip contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. The lips also contain skeletal muscle called orbicularis oris M • the outer lining changes to a thicker, stratified squamous non keratinized oral epithelium. Beneath the oral epithelium are found mucus-secreting labial glands. The lip structure: 1- The external surface 2- The internal surface 3- the vermilion margin (red margin) The external surface of the lip: is covered with thin skin formed of epidermis and dermis with the associated hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. underbeneath the skin, bundles of circular skeletal muscle of the orbicularis oris m. The internal surface of The lip: Lines by mucous membrane which is formed of: stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium (thicker than that of epidermis of the external surface) lamina propria : formed C.T. contain; Blood vessels, lymphatic Vessels , nerves and group of labial minor salivary glands (mucous acini) The Vermilion (red) margin of the lip: is continuous with the thin skin of the ext. surface of the lip covered by modified skin characterized by : transparent epithelium; formed of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium without hair follicles, sebaceous glands or sweat glands. deeply and vascular dermal papillae (giving the red color of the lip margin), highly supplied with nerves. The Tongue • The tongue is a muscular organ located in the oral cavity. The core of the tongue consists of connective tissue and interlacing bundles of skeletal muscle fibers. • The distribution and random orientation of individual skeletal muscle fibers in the tongue allows for increased movement during chewing, swallowing, and speaking. Papillae • The epithelium on the dorsal surface of the tongue is irregular or rough owing to numerous elevations or projections called papillae. • All papillae on the tongue are covered by stratified squamous epithelium that shows partial or incomplete keratinization. In contrast, the epithelium on the ventral surface of the tongue is smooth. • There are four types of papillae on the tongue: filiform, fungiform, circumvallate, and foliate. Taste Buds • Located in the epithelium of the foliate and fungiform papillae, and on the lateral sides of the circumvallate papillae, are barrel-shaped structures called the taste buds. • The free surface of each taste bud contains an opening called the taste pore • The main functions of the tongue during food processing are to perceive taste and to assist with mastication (chewing) and swallowing of the food mass, called a bolus. Papillae 1. Filiform The most numerous and smallest papillae on the surface of the tongue are the narrow, conical shaped filiform papillae. They cover the entire dorsal surface of the tongue. 2. Fungiform Papillae: Less numerous but larger, broader, and taller than the filiform papillae are the fungiform papillae. • These papillae exhibit a mushroom-like shape and are more prevalent in the anterior region of the tongue. 3.Circumvallate papillae are much larger than the fungiform or filiform papillae. Eight to 12 circumvallate papillae are located in the posterior region of the tongue. • These papillae are characterized by furrows that completely encircle them. Numerous excretory ducts from underlying serous (von Ebner’s) glands, located in the connective tissue, 4. Foliate Papillae are well developed in some animals but are rudimentary or poorly developed in humans.. Teeth are a major component of the oral cavity and are essential for the beginning of the digestive process. Teeth are embedded in and attached to the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible. Teeth are made up of three specialized tissues: • Enamel a hard, thin, translucent layer of acellular mineralized tissue that covers the crown of the tooth. Dentin, it lies deep to the enamel in the crown and cementum in the root. Its unique tubular structure and biochemical composition support the more rigid enamel and cementum overlying the surface of the tooth. • Cementum, a thin, pale-yellowish layer of bonelike calcified tissue covering the dentin of the root of the teeth. Cementum is softer and more permeable than dentin and is easily removed by abrasion when the root surface is exposed to the oral environment Dental pulp The dental pulp (also called "the nerve" of the tooth) is the central part of the tooth and is filled with soft connective tissue that contains blood vessels and nerves.