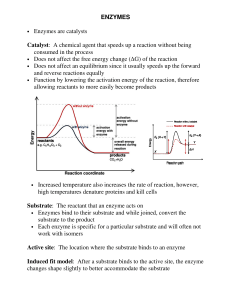
ENZYMES • Enzymes are catalysts Catalyst: A chemical agent that
... Enzymes lower the activation energy by binding substrates together in the correct orientation and by applying stress to the substrate’s bonds, reducing the amount of thermal energy that must be absorbed to achieve transition state Active sites can also provide suitable microenvironments for particul ...
... Enzymes lower the activation energy by binding substrates together in the correct orientation and by applying stress to the substrate’s bonds, reducing the amount of thermal energy that must be absorbed to achieve transition state Active sites can also provide suitable microenvironments for particul ...
Aims of lecture
... 3. An elevated level of triglycerides and a low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) — the "good" cholesterol 4. Resistance to insulin ...
... 3. An elevated level of triglycerides and a low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) — the "good" cholesterol 4. Resistance to insulin ...
Bio 181 Weekly Internet
... efficiency. These tools exploit bacterial or viral site-specific recombinases like the bacteriophage P1 Cre, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae FLP or the bacteriophage lambda integrase. These enzymes catalyze a reciprocal double-stranded DNA exchange between two specific DNA sites. Gateway (Invitrogen) i ...
... efficiency. These tools exploit bacterial or viral site-specific recombinases like the bacteriophage P1 Cre, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae FLP or the bacteriophage lambda integrase. These enzymes catalyze a reciprocal double-stranded DNA exchange between two specific DNA sites. Gateway (Invitrogen) i ...
4 1. agribiotechnology 2. genetically modified organisms
... 33. The biochemical property of lectins that is the basis for most of their biological effects is their ability to bind to: (A) amphipathic molecules. (B) hydrophobic molecules. (C) specific lipids. (D) specific oligosaccharides. (E) specific peptides. 34. Inhibitors against this viral enzyme have ...
... 33. The biochemical property of lectins that is the basis for most of their biological effects is their ability to bind to: (A) amphipathic molecules. (B) hydrophobic molecules. (C) specific lipids. (D) specific oligosaccharides. (E) specific peptides. 34. Inhibitors against this viral enzyme have ...
Chapter 2-ROLE OF ENZYMES
... together as shown in the diagram? 12. What happens to the active site of an enzyme at high temperatures? 13. What pH does pepsin enzyme work best at in the stomach? 14. What word is used to describe the best set of conditions that an enzyme can work at? 15. What happens to the rate of reaction if th ...
... together as shown in the diagram? 12. What happens to the active site of an enzyme at high temperatures? 13. What pH does pepsin enzyme work best at in the stomach? 14. What word is used to describe the best set of conditions that an enzyme can work at? 15. What happens to the rate of reaction if th ...
8/27/08 Transcript I
... vitamin portion of the enzyme and just uses the ADP. Used in DNA repair, especially when you have a mutated base, it is taken out of DNA and a new one is put in its place to repair DNA. 5. Methylation: deals with Glu Phosphorylation ...
... vitamin portion of the enzyme and just uses the ADP. Used in DNA repair, especially when you have a mutated base, it is taken out of DNA and a new one is put in its place to repair DNA. 5. Methylation: deals with Glu Phosphorylation ...
Enzymes for Pharma Applications
... fats, which is then acted upon by the lipase in pancreatin secreted by pancreas. Bile salts are either glyvine or taurine conjugates of polyhydroxy steroidal acid. Ox bile is the most important commercial source of these acids and contains primarily cholic acid with less amount of deoxycholic acid. ...
... fats, which is then acted upon by the lipase in pancreatin secreted by pancreas. Bile salts are either glyvine or taurine conjugates of polyhydroxy steroidal acid. Ox bile is the most important commercial source of these acids and contains primarily cholic acid with less amount of deoxycholic acid. ...
Enzyme Vs. Extremozyme -32
... salt-links, 10 hydrogen bonds and 74 Van der Waals interactions are established to thermostabilize lysozyme. The thermostability of a-amylase, glucoamylase and subtilisin have also been increased substantially by this approach. Organic Solvents 4: Usually enzymes do not function in organic solvents. ...
... salt-links, 10 hydrogen bonds and 74 Van der Waals interactions are established to thermostabilize lysozyme. The thermostability of a-amylase, glucoamylase and subtilisin have also been increased substantially by this approach. Organic Solvents 4: Usually enzymes do not function in organic solvents. ...
Name: Date: Block: ______ Objective: IWBAT summarize how
... In that reaction, lactase is the enzyme. Enzymes are proteins made by cells that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by reducing the required activation energy, which is the amount of energy needed to start the reaction. The following graph shows this: ...
... In that reaction, lactase is the enzyme. Enzymes are proteins made by cells that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by reducing the required activation energy, which is the amount of energy needed to start the reaction. The following graph shows this: ...
Enzyme
... Human saliva contains an enzyme called amylase. This enzyme helps to turn starch into a sugar called maltose. When you swallow a mouthful of food, the amylase stops working because it is much too acid in the stomach pH 2. Amyalse works best in neutral or slightly alkaline conditions, i.e. at about p ...
... Human saliva contains an enzyme called amylase. This enzyme helps to turn starch into a sugar called maltose. When you swallow a mouthful of food, the amylase stops working because it is much too acid in the stomach pH 2. Amyalse works best in neutral or slightly alkaline conditions, i.e. at about p ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Summary
... added to the growth media, including vitamins and fatty acids. Culture conditions include sterility to eliminate any effects of contaminating microorganisms, control of temperature, control of oxygen levels by aeration and control of pH by buffers or the addition of acid or alkali. (b) Phases of mic ...
... added to the growth media, including vitamins and fatty acids. Culture conditions include sterility to eliminate any effects of contaminating microorganisms, control of temperature, control of oxygen levels by aeration and control of pH by buffers or the addition of acid or alkali. (b) Phases of mic ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Summary
... vitamins and fatty acids. Culture conditions include sterility to eliminate any effects of contaminating microorganisms, control of temperature, control of oxygen levels by aeration and control of pH by buffers or the addition of acid or alkali. (b) Phases of microbe growth to include lag (enzymes i ...
... vitamins and fatty acids. Culture conditions include sterility to eliminate any effects of contaminating microorganisms, control of temperature, control of oxygen levels by aeration and control of pH by buffers or the addition of acid or alkali. (b) Phases of microbe growth to include lag (enzymes i ...























