Dot plot
... • After you’ve got your primers, you must verify they will not hybridize anywhere except you intend them to hybridize. • e.g. primer sequences are not outside the gene you’re interested in • or primers do not resemble a frequent repeats in DNA ...
... • After you’ve got your primers, you must verify they will not hybridize anywhere except you intend them to hybridize. • e.g. primer sequences are not outside the gene you’re interested in • or primers do not resemble a frequent repeats in DNA ...
Sol. RUBISC - askIITians
... i) An enzyme is specific for a substrate &catalyses only a particular reaction. Because of the specific shape of active site & substrate. ii) Every enzyme requires an optimum temperature for its functioning. iii) The enzymes are sensitive to PH & each enzyme shows its maximum activity at a specific ...
... i) An enzyme is specific for a substrate &catalyses only a particular reaction. Because of the specific shape of active site & substrate. ii) Every enzyme requires an optimum temperature for its functioning. iii) The enzymes are sensitive to PH & each enzyme shows its maximum activity at a specific ...
Diapositiva 1
... followed by ligation of oligonucleotide adapters to the fragments and selective amplification by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). The PCR-primers consist of a core sequence (part of the adapter), a restriction enzyme specific sequence and 1-3 selective nucleotides. The AFLP-technique simultaneou ...
... followed by ligation of oligonucleotide adapters to the fragments and selective amplification by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). The PCR-primers consist of a core sequence (part of the adapter), a restriction enzyme specific sequence and 1-3 selective nucleotides. The AFLP-technique simultaneou ...
what is your dna alias
... bases together in a sequence on a DNA strand are called a ‘codon’. Because there are so many possible base sequences (i.e., codons), geneticists have developed a short-hand using our 26 letter alphabet. Remember that 3 bases together define a specific amino acid. And two or more amino acids make a p ...
... bases together in a sequence on a DNA strand are called a ‘codon’. Because there are so many possible base sequences (i.e., codons), geneticists have developed a short-hand using our 26 letter alphabet. Remember that 3 bases together define a specific amino acid. And two or more amino acids make a p ...
Chapter 17. Application of Recombinant DNA Technology in
... • In recombinant DNA, nucleotide sequences from two different sources, often two species, are combined in vitro into the same DNA molecule. • Methods for making recombinant DNA are central to genetic engineering, the direct manipulation of genes for practical ...
... • In recombinant DNA, nucleotide sequences from two different sources, often two species, are combined in vitro into the same DNA molecule. • Methods for making recombinant DNA are central to genetic engineering, the direct manipulation of genes for practical ...
Enzymes - Pearland ISD
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
Enzymes
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... A purine base that pairs with thymine A pyrimidine base that pairs with guanine The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in w ...
... A purine base that pairs with thymine A pyrimidine base that pairs with guanine The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in w ...
Review-Qs-for-modern-genetics
... 1. The main enzyme involved in DNA replication is RNA polymerase. FALSE – DNA polymerase. 2. To determine the amino acid, look up the three base anticodon on the genetic dictionary FALSE – codon. 3. Ligase joins DNA fragments of the lagging strand. TRUE 4. DNA polymerase lengthens the new strands fr ...
... 1. The main enzyme involved in DNA replication is RNA polymerase. FALSE – DNA polymerase. 2. To determine the amino acid, look up the three base anticodon on the genetic dictionary FALSE – codon. 3. Ligase joins DNA fragments of the lagging strand. TRUE 4. DNA polymerase lengthens the new strands fr ...
Details - Dundee Life Sciences
... To confirm the organisation of the stem loop cassette, use the sense fragment cloning restriction enzymes. In the above example, Acc65I will excise both fragments and lacz468, while BamHI will only release lacz468. We regularly use two sequencing primers to confirm correct insertion: Seq1 5’-AATAGTG ...
... To confirm the organisation of the stem loop cassette, use the sense fragment cloning restriction enzymes. In the above example, Acc65I will excise both fragments and lacz468, while BamHI will only release lacz468. We regularly use two sequencing primers to confirm correct insertion: Seq1 5’-AATAGTG ...
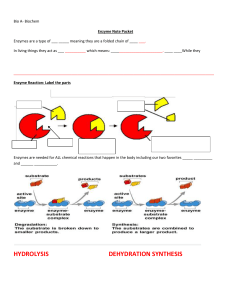
Bio A- Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of ___
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
Chapter 13( Sample questions)
... a. transgenic. b. polygenic. c. engineered. d. foreign. e. xenophobic. Goals of genetic engineering include all of the following EXCEPT a. to learn more about genetic inheritance. b. to learn more about genetic diseases. c. to learn more about bacterial inheritance. d. to provide economic and socia ...
... a. transgenic. b. polygenic. c. engineered. d. foreign. e. xenophobic. Goals of genetic engineering include all of the following EXCEPT a. to learn more about genetic inheritance. b. to learn more about genetic diseases. c. to learn more about bacterial inheritance. d. to provide economic and socia ...
SBI-4U1 Exam Review
... b. In which direction will fragments migrate? DNA is negatively charged. It will migrate away from the negative electrode, towards the ...
... b. In which direction will fragments migrate? DNA is negatively charged. It will migrate away from the negative electrode, towards the ...
Announcements DNA Invertebrates DNA DNA DNA Code
... • Made of four nucleotides strung together by two sugar-phosphate backbones (deoxyribose). • Strands are coupled by H-bonds between nucleotides (A-T G-C) . • Composed of two complimentary strands arranged in a helix. • DNA has direction - 5’ to 3’ • Stored as chromosomes in the nucleus. ...
... • Made of four nucleotides strung together by two sugar-phosphate backbones (deoxyribose). • Strands are coupled by H-bonds between nucleotides (A-T G-C) . • Composed of two complimentary strands arranged in a helix. • DNA has direction - 5’ to 3’ • Stored as chromosomes in the nucleus. ...
Enzyme
... Ribbon-diagram showing carbonic anhydrase II. The grey sphere is the zinc cofactor in the active site. Diagram drawn from PDB 1MOO. The activities of enzymes are determined by their three-dimensional structure.[9] Most enzymes are much larger than the substrates they act on, and only a very small po ...
... Ribbon-diagram showing carbonic anhydrase II. The grey sphere is the zinc cofactor in the active site. Diagram drawn from PDB 1MOO. The activities of enzymes are determined by their three-dimensional structure.[9] Most enzymes are much larger than the substrates they act on, and only a very small po ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... Biocatalyst—active site Proteins Substrate Reaction specificity Stereospecificity Coupled reactions Regulation ...
... Biocatalyst—active site Proteins Substrate Reaction specificity Stereospecificity Coupled reactions Regulation ...
Proteins, Enzymes, Nucleic Acids Proteins What are the buildi
... Describe the structure of DNA nucleotides (including the 4 types of nitrogenous bases) Phosphate group, Deoxyribose sugar, Nitrogenous Base (Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine) Describe the structure of a DNA molecule and draw a simple structure. (Specifically why is it a double helix?) DNA is ...
... Describe the structure of DNA nucleotides (including the 4 types of nitrogenous bases) Phosphate group, Deoxyribose sugar, Nitrogenous Base (Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine) Describe the structure of a DNA molecule and draw a simple structure. (Specifically why is it a double helix?) DNA is ...