SOL Essential Knowledge
... 2. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most easily held electron. 3. Elements with low ionization energy form ions easily. F. Recognize that transition metals can have multiple oxidation states. G. Summarize the following concepts about covalent bonding: 1. Covalent bonds involve ...
... 2. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most easily held electron. 3. Elements with low ionization energy form ions easily. F. Recognize that transition metals can have multiple oxidation states. G. Summarize the following concepts about covalent bonding: 1. Covalent bonds involve ...
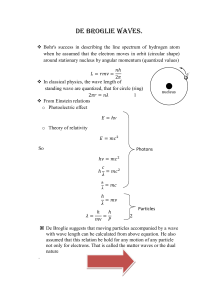
De Broglie Waves.
... Solution of Schrodinger equation (SWE) The solution of the equation means that we must know the Hamiltonian operator to get the wave function and total energy The wave functions contain all the dynamical information about systems they describe (position, momentum, angular momentum, ...
... Solution of Schrodinger equation (SWE) The solution of the equation means that we must know the Hamiltonian operator to get the wave function and total energy The wave functions contain all the dynamical information about systems they describe (position, momentum, angular momentum, ...
Chemistry
... to nucleus) to a higher energy level (farther from nucleus) by absorbing energy in discrete packets. The energy content of the packets is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. These electron transitions will produce unique absorption spectra for each element. When the electron ret ...
... to nucleus) to a higher energy level (farther from nucleus) by absorbing energy in discrete packets. The energy content of the packets is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. These electron transitions will produce unique absorption spectra for each element. When the electron ret ...
Quantum numbers
... This site shows how a particle such as an electron can have wave-like functions. http://www.chemtopics.com/lectures/unit04/lectu re3/l3u4.htm This site demonstrates wave like qualities of orbitals. ...
... This site shows how a particle such as an electron can have wave-like functions. http://www.chemtopics.com/lectures/unit04/lectu re3/l3u4.htm This site demonstrates wave like qualities of orbitals. ...
EMR and the Bohr Model of the Atom
... Model Model of the Atom 1. Bohr’s model of the atom worked very well for the hydrogen atom and the He+, but failed when applied to multielectron atoms. 2. Bohr’s model could not explain why the electron could not exist between orbits. ...
... Model Model of the Atom 1. Bohr’s model of the atom worked very well for the hydrogen atom and the He+, but failed when applied to multielectron atoms. 2. Bohr’s model could not explain why the electron could not exist between orbits. ...
De Broglie waves
... • In an electron microscope, current-carrying coils produce magnetic fields that act as lenses to focus an electron beam on a specimen. A magnification of over 1,000,000 can be reached. ...
... • In an electron microscope, current-carrying coils produce magnetic fields that act as lenses to focus an electron beam on a specimen. A magnification of over 1,000,000 can be reached. ...
Objective 6: TSW explain how the quantum
... electron waves and the electron wave characteristics were directly related to the probability of the location of an electron • The location of an electron was represented as a cloud (hence the reason the quantum mechanical model is sometimes referred to as the “electron cloud model”) • These probabi ...
... electron waves and the electron wave characteristics were directly related to the probability of the location of an electron • The location of an electron was represented as a cloud (hence the reason the quantum mechanical model is sometimes referred to as the “electron cloud model”) • These probabi ...
Problem set #1 - U.C.C. Physics Department
... the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assuming (1) that the electrons move around the nucleus in discrete orbits; and ( ...
... the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assuming (1) that the electrons move around the nucleus in discrete orbits; and ( ...
lec30
... field due to the trio, at a point on the positive y axis. The person determines the distance r that each particle is from the point on the y axis in question and kq then calculates the value of E 2 for each of the ...
... field due to the trio, at a point on the positive y axis. The person determines the distance r that each particle is from the point on the y axis in question and kq then calculates the value of E 2 for each of the ...
Lecture28
... • Yet another quantum number was introduced when it was discovered that the spectral lines of a gas are actually split into two closely spaced lines (fine structure) even without a strong magnetic field due to spinning of electrons. Spin magnetic quantum number ms : ms =-1/2,+1/2 Number of allowed ...
... • Yet another quantum number was introduced when it was discovered that the spectral lines of a gas are actually split into two closely spaced lines (fine structure) even without a strong magnetic field due to spinning of electrons. Spin magnetic quantum number ms : ms =-1/2,+1/2 Number of allowed ...
Chapter 7_01042016
... Pauli exclusion principle In a given atom no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms). ...
... Pauli exclusion principle In a given atom no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms). ...
Chapter 30: Quantum Physics Chapter 31: Atomic Physics Chapter
... Classically, it should be possible to eject electrons with light of any frequency—all that is required is to increase the intensity of the beam of light sufficiently. The fact that this is not the case means that the classical picture is incorrect. In addition, the fact that there is a lowest freque ...
... Classically, it should be possible to eject electrons with light of any frequency—all that is required is to increase the intensity of the beam of light sufficiently. The fact that this is not the case means that the classical picture is incorrect. In addition, the fact that there is a lowest freque ...
Name
... Numbered outward from the nucleus, each energy level is assigned a principal quantum number, n, which is also the number of sublevels. Each energy sublevel differs in shape and orientation and contains orbitals, each of which can contain up to two electrons. Each energy level contains a maximum of 2 ...
... Numbered outward from the nucleus, each energy level is assigned a principal quantum number, n, which is also the number of sublevels. Each energy sublevel differs in shape and orientation and contains orbitals, each of which can contain up to two electrons. Each energy level contains a maximum of 2 ...
CVB101 – Lecture 3 Chemical Bonding • Chemical bonding
... A molecule can contain atoms of the same element or atoms of two or more elements which are in a fixed ratio law of definite proportions Polyatomic molecules contain more than two atoms Empirical formula Empirical formula – an expression with the smallest whole numbers giving the correct rat ...
... A molecule can contain atoms of the same element or atoms of two or more elements which are in a fixed ratio law of definite proportions Polyatomic molecules contain more than two atoms Empirical formula Empirical formula – an expression with the smallest whole numbers giving the correct rat ...
Prelab notes
... • If energy has dual nature, why not matter? • De Broglie thought so. – Matter Waves – the wavelike behavior of waves. – Didn’t stand without experimental proof ...
... • If energy has dual nature, why not matter? • De Broglie thought so. – Matter Waves – the wavelike behavior of waves. – Didn’t stand without experimental proof ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the different weights of one element that combine with the same weight of the other element are in a simple ratio of whole numbers. What this means at the particulate level is that when elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole ...
... When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the different weights of one element that combine with the same weight of the other element are in a simple ratio of whole numbers. What this means at the particulate level is that when elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole ...
Electron Configuration
... • If energy has dual nature, why not matter? • De Broglie thought so. – Matter Waves – the wavelike behavior of waves. – Didn’t stand without experimental proof ...
... • If energy has dual nature, why not matter? • De Broglie thought so. – Matter Waves – the wavelike behavior of waves. – Didn’t stand without experimental proof ...
Practice MSL Multiple Choice 1. Compared to the charge and mass
... released, only neither released nor absorbed both released and absorbed ...
... released, only neither released nor absorbed both released and absorbed ...
Particle on a Sphere
... Designated by letters: s, p, d, f, … Specifies the shape of an orbital Magnetic quantum number = ml Determines the z component of orbital angular momentum Z component = ml restricted to values: Specifies orientation of orbital in space ...
... Designated by letters: s, p, d, f, … Specifies the shape of an orbital Magnetic quantum number = ml Determines the z component of orbital angular momentum Z component = ml restricted to values: Specifies orientation of orbital in space ...
Unit 3 – Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... state, energy is given off in the form of light. • Bohr used Planck’s equation, E = hv, to verify this theory for hydrogen. ...
... state, energy is given off in the form of light. • Bohr used Planck’s equation, E = hv, to verify this theory for hydrogen. ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Naming Simple Covalent Compounds Prefixes are used before the atom name to indicate the number of atoms in the molecule. ...
... Naming Simple Covalent Compounds Prefixes are used before the atom name to indicate the number of atoms in the molecule. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.