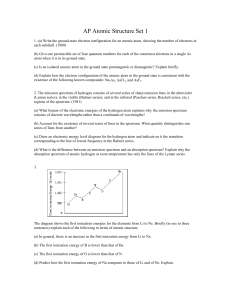
GHSGT Science Review
... amount of solute has been dissolved unsaturated solution = a solution in which an amount of solute less than the max amount has been dissolved supersaturated solution = a solution in which an amount of solute more than the max amount has been dissolved due to an increase in temp. ...
... amount of solute has been dissolved unsaturated solution = a solution in which an amount of solute less than the max amount has been dissolved supersaturated solution = a solution in which an amount of solute more than the max amount has been dissolved due to an increase in temp. ...
10 ≥ t 137 ≈ e cħ He re − mp vm E 2 2 1
... considerable interest for more than half a century. We have only 92 naturally occurring elements on the earth. Hydrogen, the lightest element, has one proton in its nucleus and uranium the heaviest naturally occurring element has ninety two protons. Towards the end of 1945 all these ninety two eleme ...
... considerable interest for more than half a century. We have only 92 naturally occurring elements on the earth. Hydrogen, the lightest element, has one proton in its nucleus and uranium the heaviest naturally occurring element has ninety two protons. Towards the end of 1945 all these ninety two eleme ...
Oops !Power Point File of Physics 2D lecture for Today should have
... If both are in the same quantum state a=b & aa (r1 ,r2 )= bb (r1 ,r2 )=0... Pauli Exclusion principle General Principles for Atomic Structure for n-electron system: 1. n-electron system is stable when its total energy is minimum 2.Only one electron can exist in a particular quantum state in an ...
... If both are in the same quantum state a=b & aa (r1 ,r2 )= bb (r1 ,r2 )=0... Pauli Exclusion principle General Principles for Atomic Structure for n-electron system: 1. n-electron system is stable when its total energy is minimum 2.Only one electron can exist in a particular quantum state in an ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... of an atom was a) in the electrons. b) concentrated in the nucleus. c) evenly spread throughout d) in rings around the atom. the atom 18. A nuclear particle that has about the same mass as a proton, but with no electrical charge, is called a(n) a) nuclide. b) neutron. c) electron. d) isotope. ...
... of an atom was a) in the electrons. b) concentrated in the nucleus. c) evenly spread throughout d) in rings around the atom. the atom 18. A nuclear particle that has about the same mass as a proton, but with no electrical charge, is called a(n) a) nuclide. b) neutron. c) electron. d) isotope. ...
CHEM 121
... 20. Give at least two reasons why Bohr's model is no longer used. 1. Bohr's model only works for the hydrogen atom and ions with one electron outside the nucleus. 2. Bohr's model ascribes definite orbits to electrons, contrary to the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. ...
... 20. Give at least two reasons why Bohr's model is no longer used. 1. Bohr's model only works for the hydrogen atom and ions with one electron outside the nucleus. 2. Bohr's model ascribes definite orbits to electrons, contrary to the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. ...
Forces between atoms and molecules
... Dispersion interaction potential: ~1/r6 Repulsion between electronic clouds at short distance: ~1/r12. ...
... Dispersion interaction potential: ~1/r6 Repulsion between electronic clouds at short distance: ~1/r12. ...
CHAPTER 4: ARRANGEMENT OF ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... In 1905, Albert Einstein expands on Planck’s idea about quanta. Einstein proposes that EMR has a wave-particle duality. Since light and other forms of EMR can be thought of as waves, then EMR can also be thought of as a stream of particles. These particles are called photons ...
... In 1905, Albert Einstein expands on Planck’s idea about quanta. Einstein proposes that EMR has a wave-particle duality. Since light and other forms of EMR can be thought of as waves, then EMR can also be thought of as a stream of particles. These particles are called photons ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Moves matter Potential, kinetic Ability to do work Conversions Sound, light, heat ...
... Moves matter Potential, kinetic Ability to do work Conversions Sound, light, heat ...
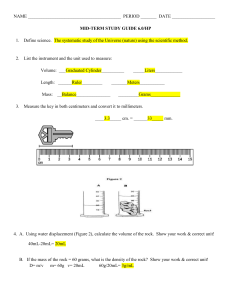
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE 6.0/HP
... The mass number equals: # of protons & Neutrons added together (# of particles in the nucleus) 7. Given a periodic table: How do you find the number of protons in an element? Atomic # How do you find the number of neutrons? Atomic mass – Atomic # How do you find the number of electrons? Equals the a ...
... The mass number equals: # of protons & Neutrons added together (# of particles in the nucleus) 7. Given a periodic table: How do you find the number of protons in an element? Atomic # How do you find the number of neutrons? Atomic mass – Atomic # How do you find the number of electrons? Equals the a ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... abundant, what is the averaged isotopic mass for chlorine? ...
... abundant, what is the averaged isotopic mass for chlorine? ...
EP-307 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... First breakthru came with radiations emitted by a black body ...
... First breakthru came with radiations emitted by a black body ...
Orbitals and energy levels
... The n represents the principle energy level The values for “n” are the same as the period numbers. Notice the s block has 2 columns because s can hold 2 electrons. The d block has 10 columns because d can hold up to 10 electrons The p block has 6 columns because p can hold up to 6 electrons ...
... The n represents the principle energy level The values for “n” are the same as the period numbers. Notice the s block has 2 columns because s can hold 2 electrons. The d block has 10 columns because d can hold up to 10 electrons The p block has 6 columns because p can hold up to 6 electrons ...
Element Symbol
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
Department of Physics, UCC PY 1054: Astronomy: Problem Set 7 In
... (a) The age of our Galaxy can be estimated by the radioactive decay of Uranium. Uranium is produced in Supernovae explosions, which result in the generation of two isotopes U235 and U236 , with an initial relative abundance ratio of 1.65 (i.e. number of U235 atoms divided by the number of U236 atoms ...
... (a) The age of our Galaxy can be estimated by the radioactive decay of Uranium. Uranium is produced in Supernovae explosions, which result in the generation of two isotopes U235 and U236 , with an initial relative abundance ratio of 1.65 (i.e. number of U235 atoms divided by the number of U236 atoms ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... Ion = an atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of 1 or more electrons. Ionic bond: attraction of opposite charges, fairly strong, most common, found in metals and salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ...
... Ion = an atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of 1 or more electrons. Ionic bond: attraction of opposite charges, fairly strong, most common, found in metals and salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ...
763628S CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS Problem Set 6 Spring
... general expression for the period in a magnetic field reduces to the free electron result. Effective mass tensor ...
... general expression for the period in a magnetic field reduces to the free electron result. Effective mass tensor ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.