Chapter 42
... charged alpha particles hit and are scattered from a thin foil target Large deflections could not be explained by Thomson’s model ...
... charged alpha particles hit and are scattered from a thin foil target Large deflections could not be explained by Thomson’s model ...
chapter29
... charged alpha particles hit and are scattered from a thin foil target Large deflections could not be explained by Thomson’s model ...
... charged alpha particles hit and are scattered from a thin foil target Large deflections could not be explained by Thomson’s model ...
electron scattering (2)
... But the electron interacts with charge elements dQ inside the nucleus: ...
... But the electron interacts with charge elements dQ inside the nucleus: ...
Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field
... electrons are emitted from the cathode and are accelerated toward the anode. Many of these electrons (aka cathode rays), miss the anode and strike instead the glass wall of the tube, causing it to exhibit ...
... electrons are emitted from the cathode and are accelerated toward the anode. Many of these electrons (aka cathode rays), miss the anode and strike instead the glass wall of the tube, causing it to exhibit ...
chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
The Bohr Model of the Atom
... By 1911 Ernest Rutherford had solved the problem of alpha scattering investigated by Geiger and Marsden by developing a picture of the atom in which there is a small, dense positively charged nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space in which were sprinkled some electrons. In the spring of 1912, … a ...
... By 1911 Ernest Rutherford had solved the problem of alpha scattering investigated by Geiger and Marsden by developing a picture of the atom in which there is a small, dense positively charged nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space in which were sprinkled some electrons. In the spring of 1912, … a ...
Chemistry Cram Sheet
... John’s lab group compared the effect of different aged grass compost on bean plants. Because decomposition is necessary for release of nutrients, the group hypothesized that older grass compost would produce taller bean plants. Three flats of bean plants (25 plants/flat) were grown for five days. Th ...
... John’s lab group compared the effect of different aged grass compost on bean plants. Because decomposition is necessary for release of nutrients, the group hypothesized that older grass compost would produce taller bean plants. Three flats of bean plants (25 plants/flat) were grown for five days. Th ...
Besombes - International Conference on Quantum Dots (QD 2012)
... devices has dramatically reduced the number of atoms necessary to process and store one bit of information: An individual magnetic atom would represent the ultimate size limit for storing and processing information. With semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) doped with Mn atoms, the probing of a single a ...
... devices has dramatically reduced the number of atoms necessary to process and store one bit of information: An individual magnetic atom would represent the ultimate size limit for storing and processing information. With semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) doped with Mn atoms, the probing of a single a ...
Ch. 4: Electron Configuration
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
energy
... frequency (and also wavelength!) • Planck’s constant has a value of 6.626 x 10–34 J · s, where J is the symbol for the joule, the SI unit of energy. • Looking at the equation, you can see that the energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency, v (of “f”), ...
... frequency (and also wavelength!) • Planck’s constant has a value of 6.626 x 10–34 J · s, where J is the symbol for the joule, the SI unit of energy. • Looking at the equation, you can see that the energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency, v (of “f”), ...
the bohr-sommerfeld model of the atom
... any hydrogen-like ion that consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus containing more than one proton. Such a system is obtained by ionizing (removing) all but one electron from an initially neutral atom. Other two-particle systems can be composed of exotic particles such as pions, muons, posi ...
... any hydrogen-like ion that consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus containing more than one proton. Such a system is obtained by ionizing (removing) all but one electron from an initially neutral atom. Other two-particle systems can be composed of exotic particles such as pions, muons, posi ...
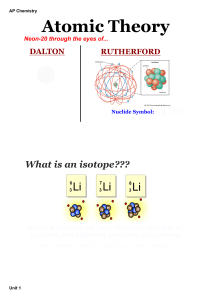
AP Chemistry
... Composed of molecules, all of which are alike Small! One billionth of a drop of water has 1 trillion molecules!!! ...
... Composed of molecules, all of which are alike Small! One billionth of a drop of water has 1 trillion molecules!!! ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.