
Exam Review
... a. Calcium and Chlorine- CaCl2 b. Magnesium and oxygen- MgO c. Magnesium and phosphorus- Mg3P2 G) Write the formulas for the following compounds. ...
... a. Calcium and Chlorine- CaCl2 b. Magnesium and oxygen- MgO c. Magnesium and phosphorus- Mg3P2 G) Write the formulas for the following compounds. ...
Monday, March 3, 2014
... Importance of Bohr’s Model • Demonstrated the need for Plank’s constant in understanding the atomic structure • Assumption of quantized angular momentum which led to quantization of other quantities, r, v and E as ...
... Importance of Bohr’s Model • Demonstrated the need for Plank’s constant in understanding the atomic structure • Assumption of quantized angular momentum which led to quantization of other quantities, r, v and E as ...
cmc chapter 05 - Destiny High School
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
CMC Chapter 05
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
C. - Elliott County Schools
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
Exam 3 Review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
Chapter 1 Matter on the Atomic Scale
... Physical properties can be measured without changing the composition of a substance. ...
... Physical properties can be measured without changing the composition of a substance. ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... Are these correct Bohr models? • What errors are at the ...
... Are these correct Bohr models? • What errors are at the ...
Unit 3: Atomic Theory & Quantum Mechanics Section A.3
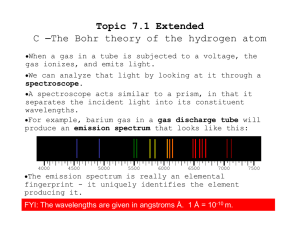
... individual lines of color corresponding to the frequencies of radiation emitted by the atoms of neon Note that it is NOT a continuous range of colors, such as the spectrum for sunlight (white light). Each element’s atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to identify an element or dete ...
... individual lines of color corresponding to the frequencies of radiation emitted by the atoms of neon Note that it is NOT a continuous range of colors, such as the spectrum for sunlight (white light). Each element’s atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to identify an element or dete ...
Intro to Quantum Mechanics
... marble reached the edge it would bounce back instead of dropping to the floor! Again, for something as large as a marble you'll probably never see something like that happen, but for photons (the massless particles of light) it is a very real ...
... marble reached the edge it would bounce back instead of dropping to the floor! Again, for something as large as a marble you'll probably never see something like that happen, but for photons (the massless particles of light) it is a very real ...
Lecture 18: Intro. to Quantum Mechanics
... • The idea behind wave mechanics was that the existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
... • The idea behind wave mechanics was that the existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. ...
Practice Exam for Final
... (a) Draw an energy level diagram for its electron states showing all states with principal quantum number n ≤ 3 . Indicate the energies, quantum numbers n and l , and degeneracies of the states. Draw arrows showing which transitions are permitted. Ignore ...
... (a) Draw an energy level diagram for its electron states showing all states with principal quantum number n ≤ 3 . Indicate the energies, quantum numbers n and l , and degeneracies of the states. Draw arrows showing which transitions are permitted. Ignore ...
Exam Review
... 21. Compared to the stability of the original atom, the stability of its ion that resembles a noble gas configuration would be a) identical b) sometimes less c) less d) greater 22. The formation of bonds between atoms depends on __. a) the electron configurations of the atoms involved c) both of the ...
... 21. Compared to the stability of the original atom, the stability of its ion that resembles a noble gas configuration would be a) identical b) sometimes less c) less d) greater 22. The formation of bonds between atoms depends on __. a) the electron configurations of the atoms involved c) both of the ...
ChemChapter_4[1]Light
... impossible to know both the exact position and the momentum (velocity) of a small particle at the same time. Schrodinger’s Wave Equation – describes the probability of finding an electron at some distance from the nucleus in terms of the wave function Y ...
... impossible to know both the exact position and the momentum (velocity) of a small particle at the same time. Schrodinger’s Wave Equation – describes the probability of finding an electron at some distance from the nucleus in terms of the wave function Y ...
Chapter 29: Light Waves Interference Constructive Interference
... energy (now called photons) • Each photon carries a certain amount of energy that depends on the frequency of the light – Each photon gives ALL of its energy to the electrons, not part – Higher intensity just means more photons, NOT higher energy photons! ...
... energy (now called photons) • Each photon carries a certain amount of energy that depends on the frequency of the light – Each photon gives ALL of its energy to the electrons, not part – Higher intensity just means more photons, NOT higher energy photons! ...
Chemistry in Biology
... which is located outside the nucleus in energy levels (electron clouds). -first energy level holds 2 electrons -second holds 8 electrons • Electrons have a negative charge. • Number of protons is balanced by an equal number of electrons therefore there is no charge of the atom. • All atoms have this ...
... which is located outside the nucleus in energy levels (electron clouds). -first energy level holds 2 electrons -second holds 8 electrons • Electrons have a negative charge. • Number of protons is balanced by an equal number of electrons therefore there is no charge of the atom. • All atoms have this ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.

















![ChemChapter_4[1]Light](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001894151_1-323884b777914f52c04d2bb917d4088a-300x300.png)


