atomic structure and interatomic bonding
... 2) (a) Give the electron configurations of Ti; Ti2+, Cu; Cu+, F-, Ca, Ca2+ (b) Calcium Floride (CaF 2 ) exhibits predominantly ionic bonding. The Ca2+ and F- ions have electron structures that are identical to which inert gases? Atomic numbers(Z); Ti=22, Cu=29, F=9, Ca=20) ...
... 2) (a) Give the electron configurations of Ti; Ti2+, Cu; Cu+, F-, Ca, Ca2+ (b) Calcium Floride (CaF 2 ) exhibits predominantly ionic bonding. The Ca2+ and F- ions have electron structures that are identical to which inert gases? Atomic numbers(Z); Ti=22, Cu=29, F=9, Ca=20) ...
Liquid-drop model of electron and atom
... of atom. The idea of the Bohr orbits of electron in the atom thus was born. This idea assumes that the electrons revolve around the positively charged nucleus, being found in specific orbits. Passage from one orbit to another is accompanied by the emission of the quanta of the electromagnetic radiat ...
... of atom. The idea of the Bohr orbits of electron in the atom thus was born. This idea assumes that the electrons revolve around the positively charged nucleus, being found in specific orbits. Passage from one orbit to another is accompanied by the emission of the quanta of the electromagnetic radiat ...
m - Egloos
... (a) The ionization energy of potassium is 4.34 eV and the electron affinity of chlorine is 3.61 eV. The Madelung constant for the KCl structure is 1.748 and the distance between ions of opposite sign is 0.314 nm. On the basis of these data only, compute the cohesive energy of KCl. (b) The observed c ...
... (a) The ionization energy of potassium is 4.34 eV and the electron affinity of chlorine is 3.61 eV. The Madelung constant for the KCl structure is 1.748 and the distance between ions of opposite sign is 0.314 nm. On the basis of these data only, compute the cohesive energy of KCl. (b) The observed c ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... 19. Compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) on the other end are known as _______________ (Hint: They are the building blocks of proteins). A. nucleic acids B. amino acids C. carbohydrates D. lipids 20. ________________ are macromolecules that contain carbon, hyd ...
... 19. Compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) on the other end are known as _______________ (Hint: They are the building blocks of proteins). A. nucleic acids B. amino acids C. carbohydrates D. lipids 20. ________________ are macromolecules that contain carbon, hyd ...
Topic 2: Molecular Dynamics of Lennard
... using periodic boundary conditions. According to the ergodic hypothesis, if the initial state of the system is chosen sufficiently carefully, then the successive states of the system as a function of time can be used to compute the thermal averages of various observables such as temperature and pres ...
... using periodic boundary conditions. According to the ergodic hypothesis, if the initial state of the system is chosen sufficiently carefully, then the successive states of the system as a function of time can be used to compute the thermal averages of various observables such as temperature and pres ...
Hilbert-space partitioning of the molecular one
... [6]. Most methods are restricted to the partitioning of the electron density, but not all properties of a quantum mechanical object can be explicitly expressed in terms of the electron density. A more fundamental approach to the AIM should be based on density matrices[7]. Because of the inherent non ...
... [6]. Most methods are restricted to the partitioning of the electron density, but not all properties of a quantum mechanical object can be explicitly expressed in terms of the electron density. A more fundamental approach to the AIM should be based on density matrices[7]. Because of the inherent non ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
QM_2_particles_ver2
... 1921 uses quantum numbers to explain periodic table (Pauli’s contribution is that each state has 2 electrons in it, another quantum number) ...
... 1921 uses quantum numbers to explain periodic table (Pauli’s contribution is that each state has 2 electrons in it, another quantum number) ...
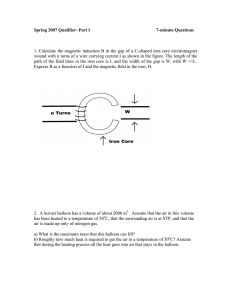
Spring 2007 Qualifier- Part I 7-minute Questions
... 20. A bead of mass m moves without friction on a table with a circular orbit of radius r as shown in figure. It is connected to a string that passes through a hole in the center of the table. Someone pulls down on the string such that the string remains taut and the circular orbit's radius is halve ...
... 20. A bead of mass m moves without friction on a table with a circular orbit of radius r as shown in figure. It is connected to a string that passes through a hole in the center of the table. Someone pulls down on the string such that the string remains taut and the circular orbit's radius is halve ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...
... are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...
Quantum Many-Body Culling: Production of a Definite
... where direct access to individual sites has not been accomplished and appears very difficult. A completely different approach was taken in a recent experiment where number squeezing was created and observed by direct atom counting [9]. Motivated by this work, we have studied theoretically the questi ...
... where direct access to individual sites has not been accomplished and appears very difficult. A completely different approach was taken in a recent experiment where number squeezing was created and observed by direct atom counting [9]. Motivated by this work, we have studied theoretically the questi ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react with chemically. Understanding the organization and plan of the periodic table will help you obtain basic informati ...
... For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react with chemically. Understanding the organization and plan of the periodic table will help you obtain basic informati ...
Lecture 3 : Atoms and the Atomic Theory Early Chemical
... Caption: (a) Deflection of cathode rays in an electric field. The beam of cathode rays is deflected as it travels from left to right in the field of the electrically charged condenser plates (E). The deflection corresponds to that expected of negatively charged particles - away from the negatively c ...
... Caption: (a) Deflection of cathode rays in an electric field. The beam of cathode rays is deflected as it travels from left to right in the field of the electrically charged condenser plates (E). The deflection corresponds to that expected of negatively charged particles - away from the negatively c ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... Section B will consist of five compulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each section carries equal marks. The minimum mathematical requirements of the syllabus are the same as those for the SEC examination in Chemistry. Questions wi ...
... Section B will consist of five compulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each section carries equal marks. The minimum mathematical requirements of the syllabus are the same as those for the SEC examination in Chemistry. Questions wi ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.