Name - Madison County Schools
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled ...
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled ...
Document
... Chemistry 130 (Lecture VII-VIII) Answer 1. Which of the following statements is not consistent with a quantum mechanical view of nature? a. Matter can be thought of as waves b. Excited atoms can emit all possible energies c. Knowing the exact speed of an electron means we do not know anything about ...
... Chemistry 130 (Lecture VII-VIII) Answer 1. Which of the following statements is not consistent with a quantum mechanical view of nature? a. Matter can be thought of as waves b. Excited atoms can emit all possible energies c. Knowing the exact speed of an electron means we do not know anything about ...
Gas Behavior: Not Just Laws, It*sa Good Idea
... Je suis Jacques Charles! Je suis Joseph Gay-Lussac! ...
... Je suis Jacques Charles! Je suis Joseph Gay-Lussac! ...
Periodic Table, Bonding, Reactions, and Moles
... 6. Explain, in terms of electrons, why the ionic radius of a Group 2 element is smaller than its atomic radius. 7. What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bo ...
... 6. Explain, in terms of electrons, why the ionic radius of a Group 2 element is smaller than its atomic radius. 7. What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bo ...
Unit 2: Practice
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
Document
... positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero. The Crisscross Method or Swap N’ Drop Method can also work. 4) All compounds are neutral so the oxidation numbers should combine in ratios that will add up to zero. The number of ions combining in the compound will be written as subscripts in the fina ...
... positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero. The Crisscross Method or Swap N’ Drop Method can also work. 4) All compounds are neutral so the oxidation numbers should combine in ratios that will add up to zero. The number of ions combining in the compound will be written as subscripts in the fina ...
Hpsxray - Nucleonica
... accelerating charged particles to higher energies, but the cyclotron of Ernest Orlando Lawrence would prove to be the most important tool in high-energy physics. Lawrence conceived the idea for the cyclotron in 1929 after coming across an article by Rolf Wideroe. The article described an accelerator ...
... accelerating charged particles to higher energies, but the cyclotron of Ernest Orlando Lawrence would prove to be the most important tool in high-energy physics. Lawrence conceived the idea for the cyclotron in 1929 after coming across an article by Rolf Wideroe. The article described an accelerator ...
atomic structure
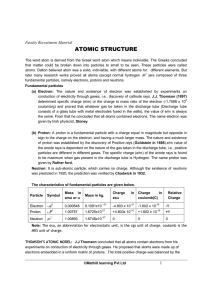
... the same. From that he concluded that all atoms contained electrons. The name electron was given by Irish physicist, Stoney (b) Proton: A proton is a fundamental particle with a charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge on the electron, and having a much larger mass. The nature an ...
... the same. From that he concluded that all atoms contained electrons. The name electron was given by Irish physicist, Stoney (b) Proton: A proton is a fundamental particle with a charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge on the electron, and having a much larger mass. The nature an ...
Aurora Reading
... accelerate along the magnetic field lines into the upper atmosphere, where they collide with gas atoms, causing the atoms to give off light. But why does that happen? To find the answer, we must look further away, to the Sun. The spectacular, "great" auroras in "What do they look like?" are powered ...
... accelerate along the magnetic field lines into the upper atmosphere, where they collide with gas atoms, causing the atoms to give off light. But why does that happen? To find the answer, we must look further away, to the Sun. The spectacular, "great" auroras in "What do they look like?" are powered ...
Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter A. How do chemists describe
... 31. You melted and burned paraffin wax in the Lab Investigating Matter. Write the chemical formula of paraffin wax given its model below. (Note: The carbon and hydrogen atoms are smaller than in the key so that this molecule can fit on the page.) ...
... 31. You melted and burned paraffin wax in the Lab Investigating Matter. Write the chemical formula of paraffin wax given its model below. (Note: The carbon and hydrogen atoms are smaller than in the key so that this molecule can fit on the page.) ...
Document
... Prediction – e– should emit light at whatever frequency f it orbits nucleus d sin θ = mλ ...
... Prediction – e– should emit light at whatever frequency f it orbits nucleus d sin θ = mλ ...
Student - Davison Chemistry Website
... b. The arrangement of electrons is discussed in terms of the _____________ of finding an electron in a certain location. ...
... b. The arrangement of electrons is discussed in terms of the _____________ of finding an electron in a certain location. ...
Charge of an Electron Worksheet Key
... Millikan adjusted the electric field so that the drop would move slowly upward in front of a grid in a microscope. The drops would move away from whichever plate had the same charge. He timed the rate of the moving droplet. Knowing the rate at which the drop was rising, the strength of the electric ...
... Millikan adjusted the electric field so that the drop would move slowly upward in front of a grid in a microscope. The drops would move away from whichever plate had the same charge. He timed the rate of the moving droplet. Knowing the rate at which the drop was rising, the strength of the electric ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... (partially!positively!charged).! ! The!hydrogen!is!taken!off!due!to!the!nucleophile!(the!carbons!in!the!double!bond!–!electron! rich!due!to!the!pie!orbitals!above!and!below!the!double!bond)!attacking!it!with!electrons.! These!electrons!then!attach!to!the!oxygen,!replacing!the!hydrogen!and!giving!the ...
... (partially!positively!charged).! ! The!hydrogen!is!taken!off!due!to!the!nucleophile!(the!carbons!in!the!double!bond!–!electron! rich!due!to!the!pie!orbitals!above!and!below!the!double!bond)!attacking!it!with!electrons.! These!electrons!then!attach!to!the!oxygen,!replacing!the!hydrogen!and!giving!the ...
Quantum Physics and Human Affairs
... quantized field is like water in a bucket that, for unknown reasons, must contain either exactly 1 gallon, or 2 gallons, or 3 gallons, etc. of water and never any intermediate amount such as 1.7 gallons. Such a "quantized bucket of water" could gain or lose water only in sudden 1-gallon increments o ...
... quantized field is like water in a bucket that, for unknown reasons, must contain either exactly 1 gallon, or 2 gallons, or 3 gallons, etc. of water and never any intermediate amount such as 1.7 gallons. Such a "quantized bucket of water" could gain or lose water only in sudden 1-gallon increments o ...
Joseph John Thomson 1856-1940
... accelerating charged particles to higher energies, but the cyclotron of Ernest Orlando Lawrence would prove to be the most important tool in high-energy physics. Lawrence conceived the idea for the cyclotron in 1929 after coming across an article by Rolf Wideroe. The article described an accelerator ...
... accelerating charged particles to higher energies, but the cyclotron of Ernest Orlando Lawrence would prove to be the most important tool in high-energy physics. Lawrence conceived the idea for the cyclotron in 1929 after coming across an article by Rolf Wideroe. The article described an accelerator ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed of protons and neutrons (I,D,M) More massive than ele ...
... That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed of protons and neutrons (I,D,M) More massive than ele ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not ...
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not ...
uncertainty: einstein, heisenberg, bohr, and the struggle for the soul
... conserved because the emission and absorp tion of energy ran according to rules of probability: it can disappear from one place and reappear somewhere else without the event being strictly connected by old fashioned cause and effect. Apparently the radiation field would account for any discrepanci ...
... conserved because the emission and absorp tion of energy ran according to rules of probability: it can disappear from one place and reappear somewhere else without the event being strictly connected by old fashioned cause and effect. Apparently the radiation field would account for any discrepanci ...
Figure 30-5 The Photoelectric Effect
... When electron fell back to ground state it would emit the energy that it had absorbed as a photon. ...
... When electron fell back to ground state it would emit the energy that it had absorbed as a photon. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.