king saud university - KSU Faculty Member websites
... c. Wears or damages surfaces rubbing against each other. Advantages of frictional force: * In the absence of friction ( = 0) humans will not walk because of absence of (traction). * Friction must be maximized when useful, and reduced when harmful. For example, in clinical applications such as (inse ...
... c. Wears or damages surfaces rubbing against each other. Advantages of frictional force: * In the absence of friction ( = 0) humans will not walk because of absence of (traction). * Friction must be maximized when useful, and reduced when harmful. For example, in clinical applications such as (inse ...
PH-102 (Modern Physics) (Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, Bose
... assumption that the temperature is so low that the probability of occupancy of levels is not altered from the one at oK. Calculate numerically the value of this fraction for copper at (ε F = 7.04 eV) 300 K and 1360 K (approximate melting point of Cu). This fraction is of interest because it is a rou ...
... assumption that the temperature is so low that the probability of occupancy of levels is not altered from the one at oK. Calculate numerically the value of this fraction for copper at (ε F = 7.04 eV) 300 K and 1360 K (approximate melting point of Cu). This fraction is of interest because it is a rou ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
Worksheets for Chapter 7
... Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum ...
... Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum ...
Snímek 1
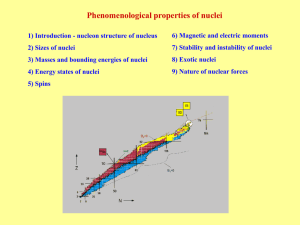
... Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capture of electron from atomic cloud Gamma decay → nucleus is not changed, only deexcitation by photon or converse electron irradiation Spontaneous fission → fission of very heavy nu ...
... Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capture of electron from atomic cloud Gamma decay → nucleus is not changed, only deexcitation by photon or converse electron irradiation Spontaneous fission → fission of very heavy nu ...
WELCOME TO AP CHEMISTRY
... 33. How many grams are there in 0.36 moles of cobalt (III) acetate (Co(C2H3O2)3)? How many grams of cobalt are in this sample? How many atoms of cobalt? ...
... 33. How many grams are there in 0.36 moles of cobalt (III) acetate (Co(C2H3O2)3)? How many grams of cobalt are in this sample? How many atoms of cobalt? ...
ch14
... Zeff increases for the larger 3A elements due to poor shielding by d and f electrons. The larger 3A elements have smaller atomic radii and larger ionization energies than electronegativities than expected. These properties influence the physical and chemical behavior of these elements. ...
... Zeff increases for the larger 3A elements due to poor shielding by d and f electrons. The larger 3A elements have smaller atomic radii and larger ionization energies than electronegativities than expected. These properties influence the physical and chemical behavior of these elements. ...
Sample Exercise 2.1 Illustrating the Size of an Atom
... Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+, and the anion is SO42–. (If you thought the ...
... Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+, and the anion is SO42–. (If you thought the ...
Study Guide - Flagler County Schools
... chemical energy into heat energy; chemical energy into light energy; mechanical energy to thermal energy) Know how the formula for power relates to work and time. Identify how temperature relates to k ...
... chemical energy into heat energy; chemical energy into light energy; mechanical energy to thermal energy) Know how the formula for power relates to work and time. Identify how temperature relates to k ...
Physics 9 Fall 2009 - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... The sun is powered by fusion, with four protons fusing together to form a helium nucleus (two of the protons turn into neutrons) and, in the process, releasing a large amount of thermal energy. The process happens in several steps, not all at once. In one step, two protons fuse together, with one pr ...
... The sun is powered by fusion, with four protons fusing together to form a helium nucleus (two of the protons turn into neutrons) and, in the process, releasing a large amount of thermal energy. The process happens in several steps, not all at once. In one step, two protons fuse together, with one pr ...
(c) In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization
... 2. What is the energy of a quantum of light with a frequency of 7.39 x 1014 Hz? What is the wavelength of the quantum of this light? 3. A certain red light has a wavelength of 680 nm. What is the frequency of the light? What is the energy of a quantum of this light? ...
... 2. What is the energy of a quantum of light with a frequency of 7.39 x 1014 Hz? What is the wavelength of the quantum of this light? 3. A certain red light has a wavelength of 680 nm. What is the frequency of the light? What is the energy of a quantum of this light? ...
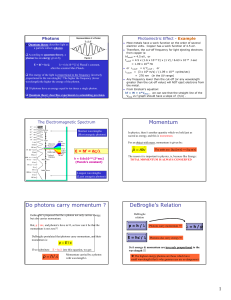
Momentum Do photons carry momentum ? DeBroglie`s Relation
... The energy of the light is proportional to the frequency (inversely proportional to the wavelength) ! The higher the frequency (lower wavelength) the higher the energy of the photon. 10 photons have an energy equal to ten times a single photon. Quantum theory describes experiments to astonishi ...
... The energy of the light is proportional to the frequency (inversely proportional to the wavelength) ! The higher the frequency (lower wavelength) the higher the energy of the photon. 10 photons have an energy equal to ten times a single photon. Quantum theory describes experiments to astonishi ...
Chemical Bonds ch6 p.161
... Higher melting point Higher boiling point Many dissolve in water, +ion and -ion break apart in water so will conduct electricity in water. Some do not dissolve because the pull between the charges are greater than the attraction of H2O molecule ...
... Higher melting point Higher boiling point Many dissolve in water, +ion and -ion break apart in water so will conduct electricity in water. Some do not dissolve because the pull between the charges are greater than the attraction of H2O molecule ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... 2. In the figure, a solid cylinder starts from rest and rolls without slipping a distance L = 6.0 m down a roof that is inclined at the angle θ = 30°. Use conservation of energy and find the linear speed of cylinder as it leaves the roof? ...
... 2. In the figure, a solid cylinder starts from rest and rolls without slipping a distance L = 6.0 m down a roof that is inclined at the angle θ = 30°. Use conservation of energy and find the linear speed of cylinder as it leaves the roof? ...
PowerPoint for Cornell Notes
... in a reaction at the beginning (reactants) and at the end (products), the amount of matter in a system does not change. ...
... in a reaction at the beginning (reactants) and at the end (products), the amount of matter in a system does not change. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.