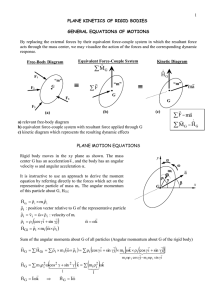
practice final examination
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
the problem book
... A particle of mass m and charge q enters a region with the vertically upward oriented homogeneous ~ = Bêz with the horizontal velocity ~v = vêx . magnetic field B [5 pt] ...
... A particle of mass m and charge q enters a region with the vertically upward oriented homogeneous ~ = Bêz with the horizontal velocity ~v = vêx . magnetic field B [5 pt] ...
Exam 1 - UF Physics
... (1) Code your test number on your answer sheet (use 76–80 for the 5-digit number). Code your name on your answer sheet. Darken circles completely (errors can occur if too light). Code your student number on your answer sheet. (2) Print your name on this sheet and sign it also. (3) Do all scratch wor ...
... (1) Code your test number on your answer sheet (use 76–80 for the 5-digit number). Code your name on your answer sheet. Darken circles completely (errors can occur if too light). Code your student number on your answer sheet. (2) Print your name on this sheet and sign it also. (3) Do all scratch wor ...
original Word doc (no figures)
... V. Discussion Although the variational calculations presented above are admittedly crude and are restricted to two-electron atomic ground states, it is reasonable to suppose that they present qualitatively correct patterns. In particular they lead to the proposition that the Møller-Plesset series fo ...
... V. Discussion Although the variational calculations presented above are admittedly crude and are restricted to two-electron atomic ground states, it is reasonable to suppose that they present qualitatively correct patterns. In particular they lead to the proposition that the Møller-Plesset series fo ...
Electronic structure of correlated electron systems
... to exactly one electron per atom but the wave function would be a single Slater determinant of one electron Bloch waves and not a single Slater determinant of atomic site localized s orbitals with one electron at each site. In the DFT case there would be two electrons with opposite spin in each k st ...
... to exactly one electron per atom but the wave function would be a single Slater determinant of one electron Bloch waves and not a single Slater determinant of atomic site localized s orbitals with one electron at each site. In the DFT case there would be two electrons with opposite spin in each k st ...
CHEM1611 Worksheet 2: Atomic Accountancy Model 1: Atomic
... Throughout history, the model of the atom and how/where the electrons exist and move has changed as our scientific knowledge has increased. The current model describes the motions of electrons using atomic orbitals. Orbitals gives us information about the probability of an electron being in a partic ...
... Throughout history, the model of the atom and how/where the electrons exist and move has changed as our scientific knowledge has increased. The current model describes the motions of electrons using atomic orbitals. Orbitals gives us information about the probability of an electron being in a partic ...
No Slide Title
... do a rigorous quantum mechanical derivation. Some of the phenomena are a black box for the classical NMR model... ...
... do a rigorous quantum mechanical derivation. Some of the phenomena are a black box for the classical NMR model... ...
O_4 Theory (III) QUANTUM MECHANICAL STUDY OF THE FLEISCHMANN-PONS EFFECT
... to reconsider the quantum mechanics of electrons and deuterons in such host lattices.” The goal of this paper is to predict possible changes in the probability of d-d fusion, caused by perturbations to the energy barriers or positive interference caused by the effects of adjacent atoms in a lattice. ...
... to reconsider the quantum mechanics of electrons and deuterons in such host lattices.” The goal of this paper is to predict possible changes in the probability of d-d fusion, caused by perturbations to the energy barriers or positive interference caused by the effects of adjacent atoms in a lattice. ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
Hands-On Chemistry Unit
... same no matter how they are rearranged, then their total mass stays the same. Explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed but only changed from one form into another. Describe how heat* can be transferred through materials by the collision of atoms, or across space by radiation*, or if the ma ...
... same no matter how they are rearranged, then their total mass stays the same. Explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed but only changed from one form into another. Describe how heat* can be transferred through materials by the collision of atoms, or across space by radiation*, or if the ma ...
The Electric Force Electric Charge Electric Fields Electron Beams
... • Same 1/r2 dependence; charge takes place of mass. • Does this mean electricity is product of geometry, just like gravity (general relativity)? – No, because gravity as geometry accounts for the fact that all masses accelerate the same. – This depends on applied force being proportional to inertial ...
... • Same 1/r2 dependence; charge takes place of mass. • Does this mean electricity is product of geometry, just like gravity (general relativity)? – No, because gravity as geometry accounts for the fact that all masses accelerate the same. – This depends on applied force being proportional to inertial ...
Chapter 7 (Lecture 10) Hydrogen Atom The explanation of
... particles. All elementary particles of a given kind have the same spin quantum number, an important part of a particle's quantum state. When combined with the spinstatistics theorem, the spin of electrons results in the Pauli exclusion principle, which in turn underlies the periodic table of chemica ...
... particles. All elementary particles of a given kind have the same spin quantum number, an important part of a particle's quantum state. When combined with the spinstatistics theorem, the spin of electrons results in the Pauli exclusion principle, which in turn underlies the periodic table of chemica ...
STOICHIOMETRY (I) Molecular Mass: The sum of the masses of the
... Ex: An 0.0989 g sample of an alcohol is burned in oxygen to yield 0.2160 g CO2 and 0.1194 g H2O. Calculate the mass percent composition and the empirical formula for the compound. (VI) Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations: Reactants → Products (g) = gas (l) = liquid (s) = solid (aq) = aqueous Co ...
... Ex: An 0.0989 g sample of an alcohol is burned in oxygen to yield 0.2160 g CO2 and 0.1194 g H2O. Calculate the mass percent composition and the empirical formula for the compound. (VI) Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations: Reactants → Products (g) = gas (l) = liquid (s) = solid (aq) = aqueous Co ...
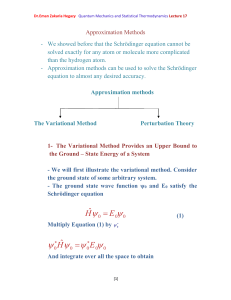
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... the Ground – State Energy of a System - We will first illustrate the variational method. Consider the ground state of some arbitrary system. - The ground state wave function ψ0 and E0 satisfy the Schrödinger equation ...
... the Ground – State Energy of a System - We will first illustrate the variational method. Consider the ground state of some arbitrary system. - The ground state wave function ψ0 and E0 satisfy the Schrödinger equation ...
Fall 2008 Blank Final Exam
... Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card, a calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of th ...
... Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card, a calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of th ...
CH 27 – Quantum Physics
... Quantum Physics Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with systems at the atomic level. Some of the consequences of quantum mechanics are that energy is quantized, particles have wave-like characteristics, and there are inherent uncertainties with which we can determine the position, ...
... Quantum Physics Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with systems at the atomic level. Some of the consequences of quantum mechanics are that energy is quantized, particles have wave-like characteristics, and there are inherent uncertainties with which we can determine the position, ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.