Triple Science Physics P1,2,3
... Galileo observed 4 moons (1) orbiting Jupiter (1) and not Earth, therefore not everything orbits the Earth (1) Energy and information P-wave, ultrasound, infrasound, sound, P waves (each worth 1) All of the electromagnetic waves including light etc. and seismic S (secondary) waves. The direction of ...
... Galileo observed 4 moons (1) orbiting Jupiter (1) and not Earth, therefore not everything orbits the Earth (1) Energy and information P-wave, ultrasound, infrasound, sound, P waves (each worth 1) All of the electromagnetic waves including light etc. and seismic S (secondary) waves. The direction of ...
Final
... H = k ²k a†k ak + k ωk c†k ck + kk0 (Mkk0 ck0 −k a†k0 ak + Mkk 0 ck 0 −k ak ak 0 ) . (i) Write down some elementary Feynman diagrams. [3 mks] (ii) Consider the corrections in 2nd order perturbation theory (possibly diagrammatically) to the self-energy of the electron and phonon and simplify them to ...
... H = k ²k a†k ak + k ωk c†k ck + kk0 (Mkk0 ck0 −k a†k0 ak + Mkk 0 ck 0 −k ak ak 0 ) . (i) Write down some elementary Feynman diagrams. [3 mks] (ii) Consider the corrections in 2nd order perturbation theory (possibly diagrammatically) to the self-energy of the electron and phonon and simplify them to ...
Review
... Consider a particle moving in one-dimension characterized by the wavefunction (x,t). Write expressions for the following quantities: (a) probability of finding particle in some small interval dx (b) probability of finding particle between x=a and x=b (c) the normalization condition for the wavefunc ...
... Consider a particle moving in one-dimension characterized by the wavefunction (x,t). Write expressions for the following quantities: (a) probability of finding particle in some small interval dx (b) probability of finding particle between x=a and x=b (c) the normalization condition for the wavefunc ...
Unit - Pukekohe High School
... in the air, does it have kinetic or • What has more kinetic potential energy? energy, a bullet of 3 g flying at 900 kmh-1 or a cart with a • Do molecules with a high mass of 6 kg travelling at a temperature or low ...
... in the air, does it have kinetic or • What has more kinetic potential energy? energy, a bullet of 3 g flying at 900 kmh-1 or a cart with a • Do molecules with a high mass of 6 kg travelling at a temperature or low ...
BRIEF REPORTS
... large list of fruitful wave packet experiments, I will focus on electron wave packets. It must be remembered, though, that every aspect of this paper applies equally well to other types of time-dependent quantum measurements @11#.! In these studies, the initial state is a superposition of many diffe ...
... large list of fruitful wave packet experiments, I will focus on electron wave packets. It must be remembered, though, that every aspect of this paper applies equally well to other types of time-dependent quantum measurements @11#.! In these studies, the initial state is a superposition of many diffe ...
Classical-field description of the quantum effects
... for a description in natural way, in the framework of classical field theory with respect to the many observed phenomena that involve “electrons”, and it explains their properties which are considered to be paradoxical from the standpoint of classical mechanics. Thus, the Compton Effect, which is co ...
... for a description in natural way, in the framework of classical field theory with respect to the many observed phenomena that involve “electrons”, and it explains their properties which are considered to be paradoxical from the standpoint of classical mechanics. Thus, the Compton Effect, which is co ...
CHAPTER 4 | Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... e– + VO2+(aq) + 2 H+(aq) VO2+(aq) + H2O ( ) This reaction is a reduction. (d) As written, the reactant side has a charge of 0 and the product side has a charge of 10+. We need to add 10 electrons to the product side to balance the charge. I2(s) + 6 H2O ( ) 2 IO3–(aq) + 12 H+(aq) + 10 e– This rea ...
... e– + VO2+(aq) + 2 H+(aq) VO2+(aq) + H2O ( ) This reaction is a reduction. (d) As written, the reactant side has a charge of 0 and the product side has a charge of 10+. We need to add 10 electrons to the product side to balance the charge. I2(s) + 6 H2O ( ) 2 IO3–(aq) + 12 H+(aq) + 10 e– This rea ...
Impulse and Momentum
... B. If the impulse was triangular, rather than constant, what was the maximum force applied to the object? (see the F vs. t graph below) Force Fmax ...
... B. If the impulse was triangular, rather than constant, what was the maximum force applied to the object? (see the F vs. t graph below) Force Fmax ...
CMC Chapter 09 a
... • A few compounds form stable configurations with less than 8 electrons around the atom—a suboctet. • A group of compounds has central atoms with more than eight valence electrons, called an expanded octet. • Elements in period 3 or higher have a d-orbital and can form more than four ...
... • A few compounds form stable configurations with less than 8 electrons around the atom—a suboctet. • A group of compounds has central atoms with more than eight valence electrons, called an expanded octet. • Elements in period 3 or higher have a d-orbital and can form more than four ...
lewis dot diagrams (structures) for atoms and ions predicting
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
Document
... finding an s electron depends only on distance from the nucleus, not on direction. 2. Only one orientation of a sphere in space, ml = 0 3. Only one s orbital per shell. 4. The size of the s orbital is successively higher shells an electron in an outer-shell s orbital is farther from the nucleus on a ...
... finding an s electron depends only on distance from the nucleus, not on direction. 2. Only one orientation of a sphere in space, ml = 0 3. Only one s orbital per shell. 4. The size of the s orbital is successively higher shells an electron in an outer-shell s orbital is farther from the nucleus on a ...
The Paradoxes of Quantum Mechanics
... concepts of force, impulse, momentum, and energy. He or she may not be able to express these ideas mathematically, but in fact the equations only express in a quantitative mathematical way those things that every billiard player knows intuitively and physiologically. The physics of things that are v ...
... concepts of force, impulse, momentum, and energy. He or she may not be able to express these ideas mathematically, but in fact the equations only express in a quantitative mathematical way those things that every billiard player knows intuitively and physiologically. The physics of things that are v ...
Computational Modeling of Li Diffusion Using Molecular Dynamics
... Warshel’s computer program performed calculations on the π-electron vibrating spectra of carbon based materials.8 This program enabled combination of the advantages of classical and quantum methods to a hybrid technique so that complex chemical systems can be described. Warshel also collaborated wit ...
... Warshel’s computer program performed calculations on the π-electron vibrating spectra of carbon based materials.8 This program enabled combination of the advantages of classical and quantum methods to a hybrid technique so that complex chemical systems can be described. Warshel also collaborated wit ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... · Activity series is a listing of metallic elements in descending order of reactivity. Hydrogen is also included in the series since it behaves similar to metals. · Activity series tables are available in textbooks and other sources. · Elements listed higher will displace any elements listed be ...
... · Activity series is a listing of metallic elements in descending order of reactivity. Hydrogen is also included in the series since it behaves similar to metals. · Activity series tables are available in textbooks and other sources. · Elements listed higher will displace any elements listed be ...
08 PowerPoint
... reaction without being used up in the reaction) S or ppt or ↓ = precipitate (solid - only found on products side) ...
... reaction without being used up in the reaction) S or ppt or ↓ = precipitate (solid - only found on products side) ...
11 Two and many electron atoms - FU Berlin
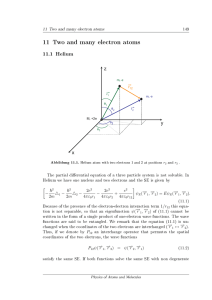
... state (1s)(2s) is metastable, since relaxation to (1s)2 is not possible upon light emission (intercombination lines are forbidden). Excitation of triplet states is possible upon collisions of atoms, spin-orbit coupling (which is very weak for helium) and magnetic dipole transitions. Interaction with ...
... state (1s)(2s) is metastable, since relaxation to (1s)2 is not possible upon light emission (intercombination lines are forbidden). Excitation of triplet states is possible upon collisions of atoms, spin-orbit coupling (which is very weak for helium) and magnetic dipole transitions. Interaction with ...
ENGPHY1 QUIZ 3 • Kinetic Energy and Work • Potential Energy and
... 13. A force on a particle is conservative if: A. its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle B. it obeys Newton’s second law C. it obeys Newton’s third law D. its work depends on the end points of every motion, not on the path between E. it is not a frictional force 14. Two part ...
... 13. A force on a particle is conservative if: A. its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle B. it obeys Newton’s second law C. it obeys Newton’s third law D. its work depends on the end points of every motion, not on the path between E. it is not a frictional force 14. Two part ...
Statistical Mechanics Lecture Notes 3 - Quantum statistics
... states correspond to the solutions of the Schrö equations. The second step is how the particles are distributed in these quantum states. This is where quantum statistics comes into the picture. This two steps also has to be consistent with each other since the quantum description of any entity (cal ...
... states correspond to the solutions of the Schrö equations. The second step is how the particles are distributed in these quantum states. This is where quantum statistics comes into the picture. This two steps also has to be consistent with each other since the quantum description of any entity (cal ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.