Notes -- Unit 5 -- Reactions and Stoichiometry
... Analyze the Problem Develop a plan for solving the problem Solve the problem Check the solution ...
... Analyze the Problem Develop a plan for solving the problem Solve the problem Check the solution ...
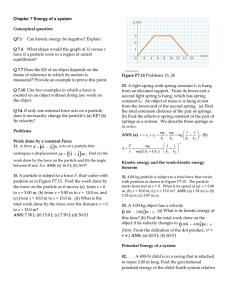
Chapter 7 Energy of a system Conceptual question Q7.1 Can kinetic
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
AP Chem – Unit 1 Part 2 AP Chemistry 2016-‐2017 Unit 1
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
Chapter 7 Energy of a system Conceptual question Q7.1 Can kinetic
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
110 exam i material
... A. Atoms are the smallest units/particles that can exist that will have the characteristics of the element. ...
... A. Atoms are the smallest units/particles that can exist that will have the characteristics of the element. ...
Energy Spectra for Fractional Quantum Hall
... many electrons; that energy is linearly dependent on 1/ν. The residual binding energies are also evaluated. The electron pair in nearest Landau-orbitals is more affected via Coulomb transition than an electron pair in non-nearest orbitals. Each nearest electron pair can transfer to some empty orbita ...
... many electrons; that energy is linearly dependent on 1/ν. The residual binding energies are also evaluated. The electron pair in nearest Landau-orbitals is more affected via Coulomb transition than an electron pair in non-nearest orbitals. Each nearest electron pair can transfer to some empty orbita ...
x - UW Canvas
... The probability per unit length of finding the particle as a function of position is n2(x). The particle is most likely to be found near the maxima. The particle cannot be found where 2 = 0. For very large values of n, the maxima and minima are so closely spaced that 2 cannot be distinguished fro ...
... The probability per unit length of finding the particle as a function of position is n2(x). The particle is most likely to be found near the maxima. The particle cannot be found where 2 = 0. For very large values of n, the maxima and minima are so closely spaced that 2 cannot be distinguished fro ...
Ultra cold atoms and Bose-Einstein condensation for quantum
... application of atom cooling, since Doppler-free lines become observable. Freezing the atomic motion is an essential tool in modern frequency-time metrology, in atomic fountains as well as in optical clocks [2–4]. Reaching temperatures of one microkelvin or less gives also access to experimental quan ...
... application of atom cooling, since Doppler-free lines become observable. Freezing the atomic motion is an essential tool in modern frequency-time metrology, in atomic fountains as well as in optical clocks [2–4]. Reaching temperatures of one microkelvin or less gives also access to experimental quan ...
1 of 52
... Key: Both compounds have C2H6O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. ...
... Key: Both compounds have C2H6O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. ...
"Effects of quantum chemistry models for bound electrons on positron annihilation spectra for atoms and small molecules" New J. Phys. , 14 , 085022 (2012). F. Wang, X. Ma, L. Selvam, G. F. Gribakin, and C. M Surko (PDF)
... 8% for some molecular orbitals. These results indicate that the predicted positron annihilation spectra for molecules are generally more sensitive to inclusion of electron correlation energies in the quantum chemistry model than the spectra for atoms are. Contents ...
... 8% for some molecular orbitals. These results indicate that the predicted positron annihilation spectra for molecules are generally more sensitive to inclusion of electron correlation energies in the quantum chemistry model than the spectra for atoms are. Contents ...
From Gravitons to Galaxies (A New View of the Universe)
... over the span of 12 years. No such decay was detected. Thus, even if a proton has a half-life, that half-life has to be 10^34 years at a minimum. This time span exceeds the “lifespan” of all macroscopic entities in the Universe – such as great walls of galaxies. Therefore, for all realistic purposes ...
... over the span of 12 years. No such decay was detected. Thus, even if a proton has a half-life, that half-life has to be 10^34 years at a minimum. This time span exceeds the “lifespan” of all macroscopic entities in the Universe – such as great walls of galaxies. Therefore, for all realistic purposes ...
"A Pint-ized System for Detecting Bioagents."
... year, with funding from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. The goal, notes Cotter, is to reach the point where "we could put in different biology agents -- bacteria or viruses or spores -and ultimately identify which bioagent it was." When a bacteria, virus, or spore is analyzed by a mas ...
... year, with funding from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. The goal, notes Cotter, is to reach the point where "we could put in different biology agents -- bacteria or viruses or spores -and ultimately identify which bioagent it was." When a bacteria, virus, or spore is analyzed by a mas ...
How and Why Inertial Mass and Gravitational Mass
... the non-existence of before the origin of the universe. Clearly, it must be the medium itself, the only non-nothing material reality, that is the cause of µ0 and ε0 . The amount of medium at a particular location determines, the value of µ0 and ε0 at that location. That quantity, the medium amount i ...
... the non-existence of before the origin of the universe. Clearly, it must be the medium itself, the only non-nothing material reality, that is the cause of µ0 and ε0 . The amount of medium at a particular location determines, the value of µ0 and ε0 at that location. That quantity, the medium amount i ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.