Gen Chem Final--review problems Fall 2006
... Determine the total volume of gas produced when 50.0 g of C6H12 is completely combusted at 110° C and 1.0 atm pressure. C6H12(l) + 9 O2(g) Î 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) ...
... Determine the total volume of gas produced when 50.0 g of C6H12 is completely combusted at 110° C and 1.0 atm pressure. C6H12(l) + 9 O2(g) Î 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) ...
Quantum information processing with atoms and ions
... In a lattice loaded with many atoms a single movement will entangle in parallel all qubits. For three atoms this produces a maximally entangled GHZ-state, and for 2-dimensional lattices this allows the generation of a cluster state, which is the basic resource for universal quantum computing in Bri ...
... In a lattice loaded with many atoms a single movement will entangle in parallel all qubits. For three atoms this produces a maximally entangled GHZ-state, and for 2-dimensional lattices this allows the generation of a cluster state, which is the basic resource for universal quantum computing in Bri ...
Introduction to Quantum Physics - DigitalCommons@University of
... where Planck's constant h = 6.63 x 10 -34 J s. These discrete amounts of energy and momentum are called guanta; the quantum of electromagnetic radiation is called a photon. When the frequency is low and the number of photons involved very large, we use the language of classical waves. If the number ...
... where Planck's constant h = 6.63 x 10 -34 J s. These discrete amounts of energy and momentum are called guanta; the quantum of electromagnetic radiation is called a photon. When the frequency is low and the number of photons involved very large, we use the language of classical waves. If the number ...
Document
... Classical Lewis Structure provides a useful method for simple e configuration in molecules, however, it cannot explain: ...
... Classical Lewis Structure provides a useful method for simple e configuration in molecules, however, it cannot explain: ...
76, 023605 (2007).
... with two hyperfine ground states 兩 ↓ 典 ⬅ 兩F = 1 , mF = −1典 and 兩 ↑ 典 ⬅ 兩F = 2 , mF = −2典 chosen as the spin of each atom. Here the atomic dynamics in the z direction are frozen out by high frequency optical traps 关22兴. However, the scheme can be directly applied to three-dimensional optical lattices ...
... with two hyperfine ground states 兩 ↓ 典 ⬅ 兩F = 1 , mF = −1典 and 兩 ↑ 典 ⬅ 兩F = 2 , mF = −2典 chosen as the spin of each atom. Here the atomic dynamics in the z direction are frozen out by high frequency optical traps 关22兴. However, the scheme can be directly applied to three-dimensional optical lattices ...
Support material for lesson planning – AS content
... (c) calculations of empirical and molecular formulae, from composition by mass or percentage compositions by mass and relative molecular mass (d) the terms anhydrous, hydrated and water of crystallisation and calculation of the formula of a hydrated salt from given percentage composition, mass compo ...
... (c) calculations of empirical and molecular formulae, from composition by mass or percentage compositions by mass and relative molecular mass (d) the terms anhydrous, hydrated and water of crystallisation and calculation of the formula of a hydrated salt from given percentage composition, mass compo ...
Field around CCl4
... interaction point. The results obtained in the present study show that the electrostatic potential and electric field around the molecule and the molecular quadrupole moment are reasonably explained by introducing atomic quadrupoles on the chlorine atoms, and suggest that this is not special to HCl ...
... interaction point. The results obtained in the present study show that the electrostatic potential and electric field around the molecule and the molecular quadrupole moment are reasonably explained by introducing atomic quadrupoles on the chlorine atoms, and suggest that this is not special to HCl ...
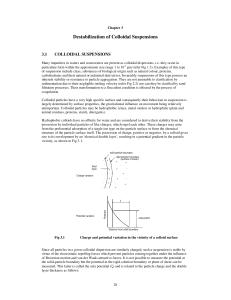
Destabilisation of colloidal suspensions
... Colloidal particles have a very high specific surface and consequently their behaviour in suspension is largely determined by surface properties, the gravitational influence on movement being relatively unimportant. Colloidal particles may be hydrophobic (clays, metal oxides) or hydrophilic (plant a ...
... Colloidal particles have a very high specific surface and consequently their behaviour in suspension is largely determined by surface properties, the gravitational influence on movement being relatively unimportant. Colloidal particles may be hydrophobic (clays, metal oxides) or hydrophilic (plant a ...
M for Moles - Shop
... involving atoms rearrangement. The total number of atoms at the left is always the same as that on the right. Virtually all simple gas molecules are made of two-atom pairs. They are called diatomics. For example, H2, Cl2, N2 and F2. The exceptions are those belong to Group 0. These are called inert ...
... involving atoms rearrangement. The total number of atoms at the left is always the same as that on the right. Virtually all simple gas molecules are made of two-atom pairs. They are called diatomics. For example, H2, Cl2, N2 and F2. The exceptions are those belong to Group 0. These are called inert ...
Atomic Mass: The atomic mass of an element is the mass average of
... Determine the molar mass of NaOH? NaOH contains one Na atom + one oxygen atom + one hydrogen atom Molar mass = 1 x mass of Na atom + 1 x mass of O atom + 1 x mass of H ...
... Determine the molar mass of NaOH? NaOH contains one Na atom + one oxygen atom + one hydrogen atom Molar mass = 1 x mass of Na atom + 1 x mass of O atom + 1 x mass of H ...
2_Quantum theory_ techniques and applications
... The larger n , the more uniform 2n(x): the situation is close to the example of a ball bouncing between two walls, for which there is no preferred position between the two walls. ...
... The larger n , the more uniform 2n(x): the situation is close to the example of a ball bouncing between two walls, for which there is no preferred position between the two walls. ...
Oxygen - Matheson
... oxidizing agent. A variety of process (liquor) streams show enhanced physical properties after treatment with oxygen; plant operating costs also improve. Similarly, oxygen enhances the combustion process in industries that manufacture glass, aluminum, copper, gold, lead, and cement, or that are invo ...
... oxidizing agent. A variety of process (liquor) streams show enhanced physical properties after treatment with oxygen; plant operating costs also improve. Similarly, oxygen enhances the combustion process in industries that manufacture glass, aluminum, copper, gold, lead, and cement, or that are invo ...
Entanglement via the Quantum Zeno Effect, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100
... 87036 Arcavacata di Rende (CS) Italy email: [email protected] ...
... 87036 Arcavacata di Rende (CS) Italy email: [email protected] ...
7.1 Electronic states of helium atom 7.2 The Variation Method
... Therefore, the latter operators trivially commute with ̂ . Hence the state functions of an atom must be eigenfunctions of ̂ and ̂ ; and as a result, can be labeled by the spin quantum numbers S and MS, in addition to L and ML. Similar to the case with the orbital angular momentum, the total electron ...
... Therefore, the latter operators trivially commute with ̂ . Hence the state functions of an atom must be eigenfunctions of ̂ and ̂ ; and as a result, can be labeled by the spin quantum numbers S and MS, in addition to L and ML. Similar to the case with the orbital angular momentum, the total electron ...
Final Exam Review
... matter with both definite and constant composition with distinct chemical properties. Examples: water, diamond, gold, table salt ...
... matter with both definite and constant composition with distinct chemical properties. Examples: water, diamond, gold, table salt ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.