* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
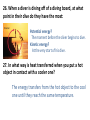
Final Exam Review Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed June 11 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 4 Chapter 9: Lesson 1 1. What is the formula for finding density? Density = mass / volume 2. Describe the steps to find the density of a cube. 1. Finding the mass of the object 2. Finding the volume of the object 3. Dividing the mass by the volume. Density = mass / volume 3. How does the density of an object determine whether or not it floats? If an object is more dense than water it will sink. If an object is less dense than water it will float. 4. What is the name of the instrument at the bottom of the page? Graduated Cylinder 5. What happens to the water level when a solid object is placed in the water? The water level rises. 6. What is this process for finding the volume of an irregularly-shaped object called? Water Displacement 7. What is the volume of the liquid shown in the instrument below? 21 mL Final Exam Review: Day 2 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed 8 – 14 Thurs 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed June 11 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 4 June 5 8. What physical change occurs at a substance’s melting point? The substance becomes a liquid. 9. Describe the movement of particles as they change phases (from a solid liquid gas) The particles start to move faster and spread out more at each phase. 10. Describe the physical properties (their volume and shape) of the states of matter: Solid: definite shape, definite volume Liquid: definite volume, not a definite shape - Liquids will take the shape of their container Gas: not a definite shape or volume - Gases change shape and volume to fill any container 11. A) 8 ounces of water will boil at 100°C. At what temperature will 1,800 ounces of water boil at? 100°C B) Why? Water will always boil at 100°C, regardless of the amount of water. 12. What happens to the amount of mass in an object when it goes from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas? The amount of mass does not change. (Matter is neither created or destroyed.) 13. Name some physical properties used to describe a rock. Any property that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance: Density, odor, hardness, color, shine, shape, texture 14. A) What is a physical change? Changing something without changing the substance B) Give an example of a physical change. Melting, Boiling, Freezing Final Exam Review: Day 3 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed June 4 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed June 11 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 6 Lesson 2 (pages E17-E29) 15. Explain what an element is. Purest substance; cannot be broken down any further. 16. Name some common elements: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Helium(anything from the periodic table). Lesson 3 (pages E31-E45) 17. A) What is a compound? A chemical combination of two or more elements. B) Give an example of a compound Iron and Oxygen combine to form the compound Rust 18. A) What is a chemical change? Chemically changing something into another substance. B) Give an example of a chemical change. Rust 19. What is a chemical formula? A way of using letters and numbers to show how much of an element is in a substance. 20. Carbonic acid is represented as H₂CO₃. A)How many different elements are in carbonic acid? 3 (H = Hydrogen; C = Carbon; O = Oxygen) B)Circle the correct ball-and-stick model for carbonic acid. 21. Know what a pure substance is: Definition: A pure substance is a sample of matter with both definite and constant composition with distinct chemical properties. Examples: water, diamond, gold, table salt (sodium chloride), ethanol Final Exam Review: Day 4 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed June 4 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed June 11 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 9 Chapter 10: Lesson 4 (pages E52-EE63) 22. When molecules are heated, how do they move? The molecules will speed up and move more freely. 23. How are kinetic energy and potential energy different? Kinetic Energy :the energy of any moving object Potential Energy : the energy stored in an object or material. 24.Describe the energy change when a child is sliding down a slide. The child has potential energy at the top of the slide. The energy changes to kinetic energy when the child moves down the slide. 25. Draw and label a diagram explaining how a golf ball changes from potential energy, to kinetic energy, back to potential energy. 26. When a diver is diving off of a diving board, at what point in their dive do they have the most: Potential energy? The moment before the diver begins to dive. Kinetic energy? At the very start of his dive. 27. In what way is heat transferred when you put a hot object in contact with a cooler one? The energy transfers from the hot object to the cool one until they reach the same temperature. 28. To make a liquid evaporate quicker or become more soluble what could you do to it? Heating a liquid will cause it to evaporate quicker or become more soluble. 29. What happens to the kinetic energy of an object when it A) Cools down: The molecules slow down – the kinetic energy decreases. B) Heats up: The molecules speed up – the kinetic energy increases. 30. Name the transfer of energy occurring in the picture above: A. Convection C. Radiation B. Conduction 31. Why does the liquid in the pot boil? How is it getting heated? The heat passes from the burner into the pot, heating the water at the bottom. Then, this hot water rises and cooler water moves down to replace it, causing a circular motion. Final Exam Review: Day 5 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed June 4 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues 39 – 45 Wed 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 10 June 11 Chapter 11: Lesson 7 (pages E97-E105) 32. The hair of a child sliding down a slide at the park is standing on end, why? The buildup of static electricity. The child is getting negative charges in their body from the slide, those charges move to the farthest part of the body which is the hair. Since all the hairs have the negative charges, each hair will be repelled from the other. 33. What will happen when two objects with the same charge come in contact? Objects with the opposite charges? Objects with the same charge will repel. Objects with opposite charges will attract. Lesson 8 (pages E107-E113) 34. What materials are good conductors of electricity? Metals, water (people) 35. What materials are good insulators (do not easily conduct electricity)? Rubber, plastic, wood 36. How do switches control whether a circuit is open or closed? • When a switch is on, the circuit is closed. • When a switch is off, the circuit is open. Lesson 9 (pages E117-E125) 37. What type of material do magnets attract? Metal objects made of iron, cobalt, and nickel; other magnets 38. In the bar magnet below, where is its magnetic field the strongest? At the poles. Final Exam Review: Day 6 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed June 4 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 June 11 Chapter 12 : Lesson 1 (pages F5-F15) 39. What is the formula for finding average speed? Average speed = distance / time 40. If a plane flies 2400 km in 3 hours, what is its average speed? 2400 km ÷ 3 hours = 800 km/h 41. If the plane from the above problem is traveling from New York to California, what is its velocity? 800 km/h, heading West 42. The graph below relates distance to time for a jogger on a morning run. What was the runner’s distance after 12 minutes? Show your work below. 2,000 m Lesson 2 (pages F17-F29) 43. What force makes a ball fall to the ground? Gravity 44. A child pushes a wagon forward with 100 N of force. Another child pushes back with 120 N. Which way will the wagon move, and why? The direction the child pushing back is pushing. This child is exerting more force on the wagon, therefore making the wagon move in the direction he is pushing. 45. What is Newton’s First Law of Motion? • An object at rest (velocity=0) will stay at rest. • An object in motion will stay in motion. - An object moving in a straight line at a constant speed (same velocity) will tend to keep moving that way. • An object’s velocity can only be changed after applying a force to the object. Final Exam Review: Day 7 Question numbers Due Day/Date 1–7 Wed June 4 8 – 14 Thurs June 5 15 – 21 Fri June 6 22 – 31 Mon June 9 32 – 38 Tues June 10 39 – 45 Wed June 11 46 – 51 Thurs June 12 46. What is friction? The force that opposes the motion of one object sliding over another. 47. Give examples for each of the types of friction discussed in your textbook. Sliding Friction – A worker moving a box across the floor. Static Friction – a book sliding down a ramp. Rolling Friction – A person rollerblading. 48. How does a spring scale work? As its name suggests, it has a spring inside. When the spring is connected to the wooden block, pulling on the spring scale’s handle causes the spring inside to stretch. As the spring stretches, it applies more and more force to the block. A pointer is attached to the spring, and its position gives the amount of force in newtons. Lab Skills: Reading a Ruler 49. What is the smallest unit of measurement on the ruler below? Millimeters (mm) Conducting an Experiment 50. A) When conducting an experiment to find the affect of light on the growth of a plant, what should be controlled? • • • • • Soil – type and how much; type of plant Water – type and how much; How often the plant gets watered Type of pot Temperature B) In the above experiment, what is the variable? Amount of light 51. What instrument would you use to find: A) Mass: Triple-beam balance B) Volume of a regularly-shaped object: Ruler (length x width x height) Of an irregularly-shaped object: Graduated Cylinder (water displacement) C) Length: Ruler D) Temperature: Thermometer E) Force: Spring Scale