Exercises in Statistical Mechanics (2004)
... 001 Random variables (distance between two particles in a box) 002 Random variables (length of chain molecule) 003 Random variables (fluctuations in number of particles) 005 Random variable x=cos(theta) 006 Microcanonical state of oscillator 007 The ergodic density rho(x) 008 Spreading of free parti ...
... 001 Random variables (distance between two particles in a box) 002 Random variables (length of chain molecule) 003 Random variables (fluctuations in number of particles) 005 Random variable x=cos(theta) 006 Microcanonical state of oscillator 007 The ergodic density rho(x) 008 Spreading of free parti ...
2nd Semester final review
... 37. What is the difference between a solute, a solvent, and a solution? Solute is the substance being dissolved (often solid) Solvent is the substance doing dissolving (usually liquid) Solution is the mixture of the two 38. Why do equations have to be balanced in the first place? Atoms can’t be crea ...
... 37. What is the difference between a solute, a solvent, and a solution? Solute is the substance being dissolved (often solid) Solvent is the substance doing dissolving (usually liquid) Solution is the mixture of the two 38. Why do equations have to be balanced in the first place? Atoms can’t be crea ...
Mathcad - MerminBohmEPRBell
... The switches on the detectors are set randomly so that all nine possible settings of the two detectors occur with equal frequency. Local realism holds that objects have properties independent of measurement and that measurements at one location on a particle cannot influence measurements of another ...
... The switches on the detectors are set randomly so that all nine possible settings of the two detectors occur with equal frequency. Local realism holds that objects have properties independent of measurement and that measurements at one location on a particle cannot influence measurements of another ...
Dynamics of Entanglement for Two-Electron Atoms
... continuous degrees of freedom. The ”bipartite” quantum system consists of two electrons interacting with each other and with a fixed center. The Hamiltonian for the system is given ...
... continuous degrees of freedom. The ”bipartite” quantum system consists of two electrons interacting with each other and with a fixed center. The Hamiltonian for the system is given ...
Module P8.3 Multi
... negatively charged electrons. It is known from experiments, particularly from observations of atomic spectra of the kind described elsewhere in FLAP, that the energy of each atomic electron cannot take arbitrary values, but is restricted to certain definite, fixed values determined by the nature of ...
... negatively charged electrons. It is known from experiments, particularly from observations of atomic spectra of the kind described elsewhere in FLAP, that the energy of each atomic electron cannot take arbitrary values, but is restricted to certain definite, fixed values determined by the nature of ...
Higher Chemistry - Mobile Resource
... It can also be shown that rates of reactions are very slow compared to the number of collisions actually happening. (This makes sense because if all collisions were successful and led to a reaction happening then there would be no slow reactions). So if 2 colliding molecules are moving slowly they w ...
... It can also be shown that rates of reactions are very slow compared to the number of collisions actually happening. (This makes sense because if all collisions were successful and led to a reaction happening then there would be no slow reactions). So if 2 colliding molecules are moving slowly they w ...
In the beginning - North Allegheny School District
... In the real world cats can't be both living and dead. So what is it that forces them to choose? IN the quantum world, measurements are what make things happen. When a measurement is made, one definite answer emerges from of a range of possibilities. Without measurements, evidently, the whole Univer ...
... In the real world cats can't be both living and dead. So what is it that forces them to choose? IN the quantum world, measurements are what make things happen. When a measurement is made, one definite answer emerges from of a range of possibilities. Without measurements, evidently, the whole Univer ...
l - coercingmolecules
... Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. ...
... Silberberg, M. 2010. Principles of General Chemistry. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. ...
BLACK HOLES AT CERN
... We speculate that strong gravity exists only on or within a new type of horizon formed in the “endpoint” of black hole evaporation. 1) Why is gravity seen at all from stars and planets, everyday objects and (presumably) from fundamental particles? Why would the basic underpinnings of cosmology (GR) ...
... We speculate that strong gravity exists only on or within a new type of horizon formed in the “endpoint” of black hole evaporation. 1) Why is gravity seen at all from stars and planets, everyday objects and (presumably) from fundamental particles? Why would the basic underpinnings of cosmology (GR) ...
Effects of antioxidants for the degradation of flame
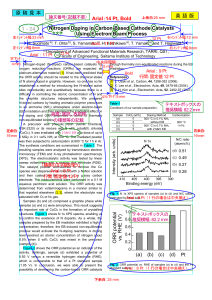
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
Chapter Summary
... The momentum of the system is conserved when the external forces are zero Conservation of Momentum can be applied when the collision force between the particles is much larger than the external forces Sketch the problem Make a sketch of the system Show the coordinate axes Show the initia ...
... The momentum of the system is conserved when the external forces are zero Conservation of Momentum can be applied when the collision force between the particles is much larger than the external forces Sketch the problem Make a sketch of the system Show the coordinate axes Show the initia ...
First Law of Thermodynamics Control Mass (Closed System)
... – Q (kJ ) amount of heat transfer – Q̇ (kW ) rate of heat transfer (power) – q (kJ/kg) - heat transfer per unit mass – q̇ (kW/kg) - power per unit mass • modes of heat transfer: – conduction: diffusion of heat in a stationary medium (Chapters 8 & 9) – convection: it is common to include convective h ...
... – Q (kJ ) amount of heat transfer – Q̇ (kW ) rate of heat transfer (power) – q (kJ/kg) - heat transfer per unit mass – q̇ (kW/kg) - power per unit mass • modes of heat transfer: – conduction: diffusion of heat in a stationary medium (Chapters 8 & 9) – convection: it is common to include convective h ...
Organic Structure Determination Analytical Chemistry
... DIRECTION OF THE BOND DIPOLE MOMENT the field can "pull" the atoms apart (if the frequency is matched) and thus increase the amplitude of the vibration (the atoms separate more), in this way the IR energy is absorbed into the molecule, the energy is "used" to make the bind vibrate with a larger ampl ...
... DIRECTION OF THE BOND DIPOLE MOMENT the field can "pull" the atoms apart (if the frequency is matched) and thus increase the amplitude of the vibration (the atoms separate more), in this way the IR energy is absorbed into the molecule, the energy is "used" to make the bind vibrate with a larger ampl ...
web 9-14
... resistance to brittle fracture in presence of a crack - resistance to crack propagation under load ...
... resistance to brittle fracture in presence of a crack - resistance to crack propagation under load ...
Module P10.2 A wave model for matter
... some features of the so-called photoelectric effect1—1the emission of electrons from a metal surface when illuminated by electromagnetic radiation. We need not go into the details of these observations here, as they are covered elsewhere in FLAP. ☞ It is sufficient to say that Einstein showed that t ...
... some features of the so-called photoelectric effect1—1the emission of electrons from a metal surface when illuminated by electromagnetic radiation. We need not go into the details of these observations here, as they are covered elsewhere in FLAP. ☞ It is sufficient to say that Einstein showed that t ...
Quantum Tweezer for Atoms
... condensate. The last panel shows the evolution for an even larger speed. In this case, the LZ tunneling takes place only partially and the outcome corresponds to a superposition of number states. One important point illustrated clearly in this figure is that there is no definite number of atoms in t ...
... condensate. The last panel shows the evolution for an even larger speed. In this case, the LZ tunneling takes place only partially and the outcome corresponds to a superposition of number states. One important point illustrated clearly in this figure is that there is no definite number of atoms in t ...
- Philsci
... Jauch’s criterion seems to suggest that, to obtain a wider theory, one should treat some intrinsic properties of the particle as extrinsic. But this would be in vain unless it had a surplus of physical meaning. De Muynck (1975) remarks on Jauch’s criterion, ”an intrinsic property may show up dynamic ...
... Jauch’s criterion seems to suggest that, to obtain a wider theory, one should treat some intrinsic properties of the particle as extrinsic. But this would be in vain unless it had a surplus of physical meaning. De Muynck (1975) remarks on Jauch’s criterion, ”an intrinsic property may show up dynamic ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom - NTOU-Chem
... • The quantum-mechanical model explains the manner in which electrons exist and behave in atoms.量子力學模型解釋原子中電子的存在和行為? • It helps us understand and predict the properties of atoms that are directly related to the behavior of the electrons:它可以幫助我們了解和預測的原子的電子的行為有直接關係的屬性: – Why some elements are metals a ...
... • The quantum-mechanical model explains the manner in which electrons exist and behave in atoms.量子力學模型解釋原子中電子的存在和行為? • It helps us understand and predict the properties of atoms that are directly related to the behavior of the electrons:它可以幫助我們了解和預測的原子的電子的行為有直接關係的屬性: – Why some elements are metals a ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.