Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom - NTOU-Chem
... • The quantum-mechanical model explains the manner in which electrons exist and behave in atoms.量子力學模型解釋原子中電子的存在和行為? • It helps us understand and predict the properties of atoms that are directly related to the behavior of the electrons:它可以幫助我們了解和預測的原子的電子的行為有直接關係的屬性: – Why some elements are metals a ...
... • The quantum-mechanical model explains the manner in which electrons exist and behave in atoms.量子力學模型解釋原子中電子的存在和行為? • It helps us understand and predict the properties of atoms that are directly related to the behavior of the electrons:它可以幫助我們了解和預測的原子的電子的行為有直接關係的屬性: – Why some elements are metals a ...
Chapter 9
... This is the form in which Newton presented the Second Law It is a more general form than the one we used previously This form also allows for mass changes ...
... This is the form in which Newton presented the Second Law It is a more general form than the one we used previously This form also allows for mass changes ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... avoid the inconsistencies discussed above, related to Newton’s second law. These are typically collisions in which two or more particles interact for a very short time and in a very small region of space. Since the strength of the interaction is much higher than that of any other external force acti ...
... avoid the inconsistencies discussed above, related to Newton’s second law. These are typically collisions in which two or more particles interact for a very short time and in a very small region of space. Since the strength of the interaction is much higher than that of any other external force acti ...
Continuum modeling of hydrodynamic particle–particle
... calculation of the hydrodynamic interactions between many rigid spheres. A few years later, this method was extended by Ladd19,20 to allow for a higher number of particles to be considered in an efficient manner. In 1990, Ladd21 used the induced-force method in high-concentration suspensions to calc ...
... calculation of the hydrodynamic interactions between many rigid spheres. A few years later, this method was extended by Ladd19,20 to allow for a higher number of particles to be considered in an efficient manner. In 1990, Ladd21 used the induced-force method in high-concentration suspensions to calc ...
Hydrogenic Rydberg atoms in strong magnetic fields: Theoretical
... a mere inspection of the spect rum does not exhibit any perspicuous differences between thc structure of the spect rum below and above the critical energy. To find such differences it is necessary to look at more basic properties of the spectrum, e.g. the statis- ...
... a mere inspection of the spect rum does not exhibit any perspicuous differences between thc structure of the spect rum below and above the critical energy. To find such differences it is necessary to look at more basic properties of the spectrum, e.g. the statis- ...
Redox
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...
Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions
... Use standard enthalpies of formation from Table C-13 (attached) to calculate ΔHreaction for each of these reactions. a. 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) →2H2O(g) + 2SO2(g) CHAPTER 17 OBJECTIVES Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 50.0 g of NaCl per 0.6 L of solution. How many moles of solute are pres ...
... Use standard enthalpies of formation from Table C-13 (attached) to calculate ΔHreaction for each of these reactions. a. 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) →2H2O(g) + 2SO2(g) CHAPTER 17 OBJECTIVES Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 50.0 g of NaCl per 0.6 L of solution. How many moles of solute are pres ...
Inorganic Chemistry 412 / 512
... Ti(III) is a reducing agent, and can reduce water to H2. Ti is an early transition metal, the effective nuclear charge is relatively low. Cu is late TM (right-hand side of the d-block), and has a much greater Zeff. It therefore is more diffucult to oxidize, and Cu(III) is an oxidizing agent, capable ...
... Ti(III) is a reducing agent, and can reduce water to H2. Ti is an early transition metal, the effective nuclear charge is relatively low. Cu is late TM (right-hand side of the d-block), and has a much greater Zeff. It therefore is more diffucult to oxidize, and Cu(III) is an oxidizing agent, capable ...
******************Q***********Q*******Q****** Q***Q***Q***Q***Q***Q
... Maxwell's calculation (1859) of the distribution law of molecular velocities in thermal equilibrium can be considered as the starting point of statistical mechanics, the first time a macroscopic, thermodynamic concept such as temperature was quantitatively related to the microscopic dynamics. Boltzm ...
... Maxwell's calculation (1859) of the distribution law of molecular velocities in thermal equilibrium can be considered as the starting point of statistical mechanics, the first time a macroscopic, thermodynamic concept such as temperature was quantitatively related to the microscopic dynamics. Boltzm ...
2010 - SAASTA
... temperatures of almost 2000°C. Hot CO 2 rises up the furnace and reacts with additional carbon to form carbon monoxide. This is an endothermic reaction. Carbon monoxide reacts with iron oxides in the ore and reduces them to free metal. 14. Carbon has two common allotropes: graphite and diamond. Whic ...
... temperatures of almost 2000°C. Hot CO 2 rises up the furnace and reacts with additional carbon to form carbon monoxide. This is an endothermic reaction. Carbon monoxide reacts with iron oxides in the ore and reduces them to free metal. 14. Carbon has two common allotropes: graphite and diamond. Whic ...
pulsed laser atom probe characterization of silicon carbide
... high strength applications. Sintered or hot pressed silicon carbide ceramics are generally polycrystalline forms of a-SiC which contain relatively small amounts of aluminum'11 or boron'2' intentionally added as densification aids. Silicon carbide, grown in whisker form, is also used as a high streng ...
... high strength applications. Sintered or hot pressed silicon carbide ceramics are generally polycrystalline forms of a-SiC which contain relatively small amounts of aluminum'11 or boron'2' intentionally added as densification aids. Silicon carbide, grown in whisker form, is also used as a high streng ...
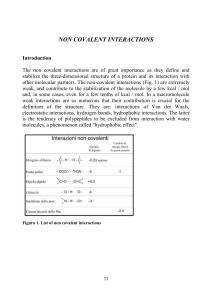
i principi di base - Structural Biology
... because 55 M is the concentration of water in liquid phase. The association constant indicates the tendency of two molecules to stay together and is given by: KAB= [AB] / [A] [ B] M-1 Two molecole, in order to associate one with another, must overcome an entropic barrier, reducing its degree of free ...
... because 55 M is the concentration of water in liquid phase. The association constant indicates the tendency of two molecules to stay together and is given by: KAB= [AB] / [A] [ B] M-1 Two molecole, in order to associate one with another, must overcome an entropic barrier, reducing its degree of free ...
Here - UiO
... the temperature of an electron gas, the electrons loose momentum and start to occupy the lowest possible momentum states, i.e. they all start to move towards the origin (0, 0, 0) in momentum space. But when all start to move towards the origin in momentum space (see again figure 3), all the boxes ar ...
... the temperature of an electron gas, the electrons loose momentum and start to occupy the lowest possible momentum states, i.e. they all start to move towards the origin (0, 0, 0) in momentum space. But when all start to move towards the origin in momentum space (see again figure 3), all the boxes ar ...
Atomic Polar Tensor Transferabllity and Atomic Charges kr the
... in ref 1. (RtY)represents the center of charge of the h brid orbital (pv),where p and v indicate orbitals of atom A, and R,,YB represents the bonding center of charge since p and v belong to different atoms, A and B, whether chemically bonded or not. These contributions in expression 1 are known, re ...
... in ref 1. (RtY)represents the center of charge of the h brid orbital (pv),where p and v indicate orbitals of atom A, and R,,YB represents the bonding center of charge since p and v belong to different atoms, A and B, whether chemically bonded or not. These contributions in expression 1 are known, re ...
Emergence, Effective Field Theory, Gravitation and Nuclei
... Theories are tested over some distance/energy scale -we know D.O.F. and interactions for that scale -can do calculations at that scale But, there likely are new particles and new interactions at higher energy -these do not propagate at low energy ...
... Theories are tested over some distance/energy scale -we know D.O.F. and interactions for that scale -can do calculations at that scale But, there likely are new particles and new interactions at higher energy -these do not propagate at low energy ...
Chem Curr - New Haven Science
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.