chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
... Example: Calculate the pH of a buffer system containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the sm ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus - Old Mill High School
... 1.) How would you predict products for reactions that occur in aqueous solution? 2.) How would you correlate solution concentration to stoichiometric calculations? 3.) How would you apply changes in oxidation states to balance chemical reactions? Essential Content Topics: Essential Content Topics: R ...
... 1.) How would you predict products for reactions that occur in aqueous solution? 2.) How would you correlate solution concentration to stoichiometric calculations? 3.) How would you apply changes in oxidation states to balance chemical reactions? Essential Content Topics: Essential Content Topics: R ...
2 - TestBankTop
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
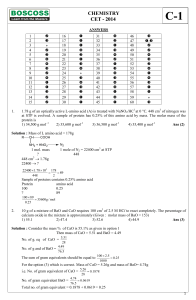
Exam
... B) NaOH, strong base C) HCl, weak acid D) H2 CO3 , strong acid E) Ca(OH)2 , weak base 10) Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because A) it is a dilute solution. B) it is only slightly soluble in water. C) it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. D) it dissociates only slightly in water. E) it is comp ...
... B) NaOH, strong base C) HCl, weak acid D) H2 CO3 , strong acid E) Ca(OH)2 , weak base 10) Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because A) it is a dilute solution. B) it is only slightly soluble in water. C) it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. D) it dissociates only slightly in water. E) it is comp ...
Chapter 4 Student Presentation
... • A metal in the activity series can only be oxidized by a metal ion below it. • For example: – If Cu + Ag1+ ions: – Cu2+ ions are formed because Cu is above Ag in the activity series: – Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Ag(s) • or – Cu(s) + 2 Ag1+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) ...
... • A metal in the activity series can only be oxidized by a metal ion below it. • For example: – If Cu + Ag1+ ions: – Cu2+ ions are formed because Cu is above Ag in the activity series: – Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Ag(s) • or – Cu(s) + 2 Ag1+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) ...
1 Solutions 4a (Chapter 4 problems) Chem151 [Kua]
... (c) The second two parts of this problem involve stoichiometric calculations. The problem gives information about the amounts of both starting materials, so this is a limiting reactant situation. We must calculate the number of moles of each species, construct a table of amounts, and use the result ...
... (c) The second two parts of this problem involve stoichiometric calculations. The problem gives information about the amounts of both starting materials, so this is a limiting reactant situation. We must calculate the number of moles of each species, construct a table of amounts, and use the result ...
File
... Equations must be balanced – have same number of each kind of atom in reactants and products, since atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass) 2 Na + 2 H2O 2NaOH + H2, balanced 2, 2, 2, (1) are stoichiometric coefficients - coefficients are relative numb ...
... Equations must be balanced – have same number of each kind of atom in reactants and products, since atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass) 2 Na + 2 H2O 2NaOH + H2, balanced 2, 2, 2, (1) are stoichiometric coefficients - coefficients are relative numb ...
Charge transfer reactions between gas
... to smaller sizes with increasing reaction delay. Fig. 2 shows the reaction kinetics and the nanocalorimetric fit for this experiment, for reaction delays up to 3 s. The kinetics clearly exhibits pseudofirst order behavior. A fit of the average cluster sizes and their difference with eqn (1) and (2) w ...
... to smaller sizes with increasing reaction delay. Fig. 2 shows the reaction kinetics and the nanocalorimetric fit for this experiment, for reaction delays up to 3 s. The kinetics clearly exhibits pseudofirst order behavior. A fit of the average cluster sizes and their difference with eqn (1) and (2) w ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... E) 20 million O2 molecules Since O2 is a diatomic gas, here we have 40 million O atoms, corresponding to 40 x 106/(6.022 x 1023) mol O atoms = 6.64 x 10-17 mol O atoms choice E 2. The element oxygen consists of three naturally occurring isotopes: 16O, 17O, and 18O. The average atomic mass of oxygen ...
... E) 20 million O2 molecules Since O2 is a diatomic gas, here we have 40 million O atoms, corresponding to 40 x 106/(6.022 x 1023) mol O atoms = 6.64 x 10-17 mol O atoms choice E 2. The element oxygen consists of three naturally occurring isotopes: 16O, 17O, and 18O. The average atomic mass of oxygen ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... Ethylene is produced from natural gas or crude oil (mixtures of hydrocarbons, containing mainly alkanes and cycloalkanes and smaller amounts of unsaturated including alkenes), which is called feedstock. The feedstock is refined by fractional distillation to obtain alkenes since alkanes are susceptib ...
... Ethylene is produced from natural gas or crude oil (mixtures of hydrocarbons, containing mainly alkanes and cycloalkanes and smaller amounts of unsaturated including alkenes), which is called feedstock. The feedstock is refined by fractional distillation to obtain alkenes since alkanes are susceptib ...
Class XI Physical Chemistry Short note
... Until 1920 an atom was supposed to consist of only 2 fundamental particles i.e. electrons and protons. Since electrons have negligible mass, the entire mass of the atom was regarded as the mass of the proton only. Each proton has a mass of 1.67x 10-24 g which is taken as 1 unit mass. In 1920, Ruther ...
... Until 1920 an atom was supposed to consist of only 2 fundamental particles i.e. electrons and protons. Since electrons have negligible mass, the entire mass of the atom was regarded as the mass of the proton only. Each proton has a mass of 1.67x 10-24 g which is taken as 1 unit mass. In 1920, Ruther ...
Table of Contents Pages Unit 1- Matter and Change 1
... ___________________ that traps the solid particles while the liquid passes through in a process called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. M ...
... ___________________ that traps the solid particles while the liquid passes through in a process called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. M ...
Mock Examination (2016/2017) CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 SECTION B
... The number of occupied electron shell is the same as metal A ion and bromide ion, The ratio between the electron to proton is larger in bromide ion than metal ion A. The metal ion A exert a large nuclear charge to electron in outermost shell than bromide, the greater the attraction, the smaller size ...
... The number of occupied electron shell is the same as metal A ion and bromide ion, The ratio between the electron to proton is larger in bromide ion than metal ion A. The metal ion A exert a large nuclear charge to electron in outermost shell than bromide, the greater the attraction, the smaller size ...
Chapter 5
... the magnitude of temperature changes are essential skills in working with energy and chemical systems. The following example shows how to perform both of these calculations. Example Problem 5.3.2 Use specific heat capacity. a. Determine the amount of heat energy that is associated with heating a 154 ...
... the magnitude of temperature changes are essential skills in working with energy and chemical systems. The following example shows how to perform both of these calculations. Example Problem 5.3.2 Use specific heat capacity. a. Determine the amount of heat energy that is associated with heating a 154 ...
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
... Because of the presence of a lone pair of electron on nitrogen atom in ammonia, it forms a number of complexes with cations involving dative or coordinate bond. It acts as a monodentate ligand. When ammonia is added to an aqueous solution containing copper(II) ions, a deep blue complex cation [Cu(NH ...
... Because of the presence of a lone pair of electron on nitrogen atom in ammonia, it forms a number of complexes with cations involving dative or coordinate bond. It acts as a monodentate ligand. When ammonia is added to an aqueous solution containing copper(II) ions, a deep blue complex cation [Cu(NH ...
Unit F325 - Equilibria, energetics and elements - High band
... candidate. The final answer should have been given to 3 significant figures as all values in the question are to this precision. The answer of 0.8 against the actual calculated value of 0.848 introduces a 6% rounding error. This is a basic error and loss of marks such as this could prove costly for ...
... candidate. The final answer should have been given to 3 significant figures as all values in the question are to this precision. The answer of 0.8 against the actual calculated value of 0.848 introduces a 6% rounding error. This is a basic error and loss of marks such as this could prove costly for ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.








![1 Solutions 4a (Chapter 4 problems) Chem151 [Kua]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002731518_1-574ec10e88e667508364281b6325aeef-300x300.png)