chemistry paper 1
... The melting point of sodium chloride is much higher than that of methane because the ionic bonding in sodium chloride is much stronger than the covalent bonding in methane. ...
... The melting point of sodium chloride is much higher than that of methane because the ionic bonding in sodium chloride is much stronger than the covalent bonding in methane. ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Enzymes Enzymes are important biological macromolecules that do work in all living things. Plants, animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical ...
... Enzymes Enzymes are important biological macromolecules that do work in all living things. Plants, animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical ...
ExamView - 1984 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... (1) Test Questions are Copyright © 1984-2002 by College Entrance Examination Board, Princeton, NJ. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reproduce the questions. Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the Colle ...
... (1) Test Questions are Copyright © 1984-2002 by College Entrance Examination Board, Princeton, NJ. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reproduce the questions. Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the Colle ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... Q13. A solution has been prepared by dissolving 60g of methyl alcohol in 120g of water. What is the mole fraction of methyl alcohol and water? [XCH3OH= 0.22, XH20 =0.78] Q14. An organic compound on analysis gave the following percentage composition; C=57.8%, H=3.6% and the rest is oxygen. The molecu ...
... Q13. A solution has been prepared by dissolving 60g of methyl alcohol in 120g of water. What is the mole fraction of methyl alcohol and water? [XCH3OH= 0.22, XH20 =0.78] Q14. An organic compound on analysis gave the following percentage composition; C=57.8%, H=3.6% and the rest is oxygen. The molecu ...
Chapter One
... again and again and again. In theory, we should eventually end up with a single gold atom. If we tried to split this atom in half, we would end up with something that no longer retains any of the characteristics of the element. An atom is therefore the smallest particle that can be used to identify ...
... again and again and again. In theory, we should eventually end up with a single gold atom. If we tried to split this atom in half, we would end up with something that no longer retains any of the characteristics of the element. An atom is therefore the smallest particle that can be used to identify ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... (a) What is thermal decomposition? (2 marks) (b) Why is the porous pot included in the apparatus? (2 marks) (c) Complete the equation below for the cracking of the molecule C20H42. (1 mark) C20H42 C3H6 + _____________________ (d) What chemical test would you use to show that the gas, propene, was ...
... (a) What is thermal decomposition? (2 marks) (b) Why is the porous pot included in the apparatus? (2 marks) (c) Complete the equation below for the cracking of the molecule C20H42. (1 mark) C20H42 C3H6 + _____________________ (d) What chemical test would you use to show that the gas, propene, was ...
spontaneous change: entropy and free energy
... where S is the entropy, k is the Boltzmann constant, and W is the number of microstates. We can think of the Boltzmann constant as the gas constant per molecule; that is, k = R>NA . (Although we didn’t specifically introduce k in the discussion of kinetic–molecular theory, R>NA appears in equation 6 ...
... where S is the entropy, k is the Boltzmann constant, and W is the number of microstates. We can think of the Boltzmann constant as the gas constant per molecule; that is, k = R>NA . (Although we didn’t specifically introduce k in the discussion of kinetic–molecular theory, R>NA appears in equation 6 ...
Stoichiometry - Milton
... stoichiometry (which you studied in Chapter 3) deals with the mass relationships of elements in compounds. Reaction stoichiometry involves the mass relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Reaction stoichiometry is the subject of this chapter and it is based on chemical e ...
... stoichiometry (which you studied in Chapter 3) deals with the mass relationships of elements in compounds. Reaction stoichiometry involves the mass relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Reaction stoichiometry is the subject of this chapter and it is based on chemical e ...
CHEM 1412. Chapter 15. Chemical Equilibrium (Homework)
... B. Qc > Kc, the reaction proceeds from right to left to reach equilibrium C. Qc < Kc, the reaction proceeds from left to right to reach equilibrium D. Qc < Kc, the reaction proceeds from right to left to reach equilibrium E. Qc = Kc, the reaction is currently at equilibrium ...
... B. Qc > Kc, the reaction proceeds from right to left to reach equilibrium C. Qc < Kc, the reaction proceeds from left to right to reach equilibrium D. Qc < Kc, the reaction proceeds from right to left to reach equilibrium E. Qc = Kc, the reaction is currently at equilibrium ...
b - PianetaChimica
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
Chapter 2 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Note that the number 6.022 141 99 × 1023 without the units mol−1 is called Avogadro’s number, not the Avogadro constant. ...
... Note that the number 6.022 141 99 × 1023 without the units mol−1 is called Avogadro’s number, not the Avogadro constant. ...
CHAPTER TWO SOLID STATE REACTIONS 2.0 Introduction The
... The complex Fe(phen)(H2O)3SO4 (where phen is 1,10-phenanthroline) is reported to be produced from the solid state reaction of FeSO4.7H2O and 1,10-phenanthroline at 70 oC [57]. Solution reaction of the two reagents has often produced [Fe(phen)3][SO4]. The complex [Fe(phen)(H2O)3][SO4] resulting from ...
... The complex Fe(phen)(H2O)3SO4 (where phen is 1,10-phenanthroline) is reported to be produced from the solid state reaction of FeSO4.7H2O and 1,10-phenanthroline at 70 oC [57]. Solution reaction of the two reagents has often produced [Fe(phen)3][SO4]. The complex [Fe(phen)(H2O)3][SO4] resulting from ...
Material Equilibrium
... particular fixed composition, volume, energy, pressure, and temperature. While energy strives to be minimal, entropy strives to be maximal Entropy wants to grow. Energy wants to shrink. Together, they make a compromise. ...
... particular fixed composition, volume, energy, pressure, and temperature. While energy strives to be minimal, entropy strives to be maximal Entropy wants to grow. Energy wants to shrink. Together, they make a compromise. ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... to eliminate undesirable side effects. A16. Salicylic acid was used as a pain killer but found was to found to cause bleeding of the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) with ethanoic acid to form the ester, acetylsalicylic acid which while an effective pain ...
... to eliminate undesirable side effects. A16. Salicylic acid was used as a pain killer but found was to found to cause bleeding of the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) with ethanoic acid to form the ester, acetylsalicylic acid which while an effective pain ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet with blank pages. Only this "Blue Book" is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ...
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet with blank pages. Only this "Blue Book" is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ...
Stoichiometry

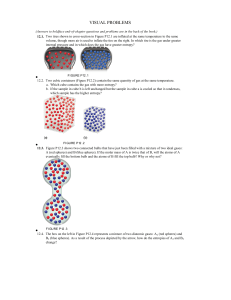
Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.