Characteristics of the Roman World Timeline There are three distinct
... which ran from 753 B.C. to about A.D. 476, or more than 1,000 years. Some dates for the beginning and ending of periods are controversial among historians, but most experts agree with the approximations. The first period, from 753 B.C. to 509 B.C., is when Rome was founded. Romans believed that the ...
... which ran from 753 B.C. to about A.D. 476, or more than 1,000 years. Some dates for the beginning and ending of periods are controversial among historians, but most experts agree with the approximations. The first period, from 753 B.C. to 509 B.C., is when Rome was founded. Romans believed that the ...
Early People of Italy
... 5. To stop or reject the actions of another. ______________ 6. A plebeian official who could attend meetings of the assembly in ancient Rome. ________________ 7. A loose group of governments working together. _______________ 8. A descendant of Rome’s earliest settlers. _______________ Applications: ...
... 5. To stop or reject the actions of another. ______________ 6. A plebeian official who could attend meetings of the assembly in ancient Rome. ________________ 7. A loose group of governments working together. _______________ 8. A descendant of Rome’s earliest settlers. _______________ Applications: ...
WHCH_51 - Teacherpage
... Republic • Romans defeated the Etruscans and drove them away in 509 B.C. • Republic – “res publica” that which belongs to the people • People chose some of the officials • Romans believed this would stop an individual from gaining to much power ...
... Republic • Romans defeated the Etruscans and drove them away in 509 B.C. • Republic – “res publica” that which belongs to the people • People chose some of the officials • Romans believed this would stop an individual from gaining to much power ...
Chapter 11: THE ROMAN EMPIRE AND CHRISTIANITY Notes
... 7. Christians believe that ______________ is the ___________________, which means “God’s anointed one.” Romans _______________________ Christians, even forcing them to fight gladiators and wild animals in the Coliseum! 8. However, the first Roman Emperor to _______________, or change religions, to C ...
... 7. Christians believe that ______________ is the ___________________, which means “God’s anointed one.” Romans _______________________ Christians, even forcing them to fight gladiators and wild animals in the Coliseum! 8. However, the first Roman Emperor to _______________, or change religions, to C ...
earlymid2v2
... Human settlements must always be near a source of fresh water, whether a river or a spring. While Rome was just a small state within Latium, its source was the River Tiber. By the late fourth century B.C., when the Romans were fighting the second Samnite War, an alternative source of water was urgen ...
... Human settlements must always be near a source of fresh water, whether a river or a spring. While Rome was just a small state within Latium, its source was the River Tiber. By the late fourth century B.C., when the Romans were fighting the second Samnite War, an alternative source of water was urgen ...
3. Rise and fall of roman empire
... Result of splitting the Empire • two rulers would issue all laws together. • very negative effect on Rome. • It was no longer the capital of the empire or the centre of power. • Roman Senate lost all of its power. • The rule of these two parts of the Roman Empire broke down when 7 different ...
... Result of splitting the Empire • two rulers would issue all laws together. • very negative effect on Rome. • It was no longer the capital of the empire or the centre of power. • Roman Senate lost all of its power. • The rule of these two parts of the Roman Empire broke down when 7 different ...
Chapter 11 The Roman Republic
... This was a council of wealthy and powerful Romans that advise the city’s leaders. It was originally created to advise Rome’s kings. They gained control of financial ...
... This was a council of wealthy and powerful Romans that advise the city’s leaders. It was originally created to advise Rome’s kings. They gained control of financial ...
Tiberius Caesar Augustus
... He had Two children Drusus, who became a prominent military commander, and Nero Claudius, who became a Roman Consult. However the Heir to the throne went to Gaius Caligula his adoptive son and grand-nephew ...
... He had Two children Drusus, who became a prominent military commander, and Nero Claudius, who became a Roman Consult. However the Heir to the throne went to Gaius Caligula his adoptive son and grand-nephew ...
Intro to Rome
... a wall around his village. When his brother leapt over the wall, Romulus was upset, and killed him. This legend further says that Romulus then stated that a similar fate would befall anyone who ever tried to break through the walls of Rome. ...
... a wall around his village. When his brother leapt over the wall, Romulus was upset, and killed him. This legend further says that Romulus then stated that a similar fate would befall anyone who ever tried to break through the walls of Rome. ...
Roman Republic
... Twelve Tables which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens had a right to the protection of the law ...
... Twelve Tables which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens had a right to the protection of the law ...
Impact of Geography on Rome - Social Circle City Schools
... Twelve Tables which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens had a right to the protection of the law ...
... Twelve Tables which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens had a right to the protection of the law ...
Chapter 10, Section 3 Student Note Form
... A. As the ______________ grew, many people left their ___________ and decided to live in Rome. B. They left their farms in the hands of ___________ who were in charge of growing one or two ____________. C. Roman ___________ also expanded as the Republic grew because farmers couldn’t grow enough ____ ...
... A. As the ______________ grew, many people left their ___________ and decided to live in Rome. B. They left their farms in the hands of ___________ who were in charge of growing one or two ____________. C. Roman ___________ also expanded as the Republic grew because farmers couldn’t grow enough ____ ...
EuroCamp 2014 ITALY - assoraider
... Each legion had its own special banner, its own name, and its own number. Within the legion, centuries (groups of 100 men) also had a banner. In the early republic, the strength of a legion was about 3,000 men; there were 4,800 legionaries in the days of Julius Caesar; the twenty-five legions that d ...
... Each legion had its own special banner, its own name, and its own number. Within the legion, centuries (groups of 100 men) also had a banner. In the early republic, the strength of a legion was about 3,000 men; there were 4,800 legionaries in the days of Julius Caesar; the twenty-five legions that d ...
Ancient Greece
... 2. They were eager to learn new _________________ 3. 2 leaders reformed the government into a democracy, rule by 4. Solon (594 BC) reforms the economy and politics. a. Canceled all debts, freed indebted slaves, made farming profitable and required sons to get a trade. b. Allowed all males to discuss ...
... 2. They were eager to learn new _________________ 3. 2 leaders reformed the government into a democracy, rule by 4. Solon (594 BC) reforms the economy and politics. a. Canceled all debts, freed indebted slaves, made farming profitable and required sons to get a trade. b. Allowed all males to discuss ...
Works Cited
... numbers so two Roman capable political large that the emperors, one in foreigners structure, late Latin word Rome and one in coming from characterized for "soldier" Constantinople— all ends of the by an came to be continued to Empire had oppressive demand that the kept Rome on burden of barbarus ("b ...
... numbers so two Roman capable political large that the emperors, one in foreigners structure, late Latin word Rome and one in coming from characterized for "soldier" Constantinople— all ends of the by an came to be continued to Empire had oppressive demand that the kept Rome on burden of barbarus ("b ...
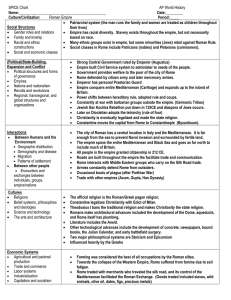
Rome SPICE Chart
... Rome defended by citizen army and later mercenary armies. Emperor has personal Praetorian Guard Empire conquers entire Mediterranean (Carthage) and expands up to the island of Britain. Power shifts between hereditary rule, adopted rule and coups. Constantly at war with barbarian groups outside the e ...
... Rome defended by citizen army and later mercenary armies. Emperor has personal Praetorian Guard Empire conquers entire Mediterranean (Carthage) and expands up to the island of Britain. Power shifts between hereditary rule, adopted rule and coups. Constantly at war with barbarian groups outside the e ...
Ancient Rome: The Roman Empire Ancient Roman civilization
... Roman emperors to a disappointing end. He was killed by his own ministers, which sparked another period of civil war. During the third century, Rome suffered from a cycle of near-constant conflict. Twenty-two emperors took the throne, many of them meeting violent ends at the hands of the same soldie ...
... Roman emperors to a disappointing end. He was killed by his own ministers, which sparked another period of civil war. During the third century, Rome suffered from a cycle of near-constant conflict. Twenty-two emperors took the throne, many of them meeting violent ends at the hands of the same soldie ...
Roman Republic - Ms. McLoughlin
... because of the constant threat of war. All male citizens were required to serve in the army, and no one could hold public office until he served 10 years as a soldier. ...
... because of the constant threat of war. All male citizens were required to serve in the army, and no one could hold public office until he served 10 years as a soldier. ...
Classical Rome
... Consul - Rulers of Rome There were Two, elected by the people. Senate - Representative body for patricians Senators chosen by Consuls Society and Laws protected the rights of the Patricians ...
... Consul - Rulers of Rome There were Two, elected by the people. Senate - Representative body for patricians Senators chosen by Consuls Society and Laws protected the rights of the Patricians ...
Ancient People of Rome
... Roman population. In 1st century BC, 30 to 40 percent of Italy’s population comprised of slaves. ...
... Roman population. In 1st century BC, 30 to 40 percent of Italy’s population comprised of slaves. ...
The Roman World
... Assemblies also existed in the Roman Republic Citizens in these assemblies voted on laws and elected officials Some assemblies voted to make war or peace while others served as courts They elected 10 officials called tribunes who had power over actions of the senate and other public official ...
... Assemblies also existed in the Roman Republic Citizens in these assemblies voted on laws and elected officials Some assemblies voted to make war or peace while others served as courts They elected 10 officials called tribunes who had power over actions of the senate and other public official ...
The Romans
... Plebeians resented their lack of power 494 B.C. plebeians refuse to join military Tribunes were selected to represent plebeians The Twelve Tables: basis of all Roman Law • All free citizens had a right to the law’s protection ...
... Plebeians resented their lack of power 494 B.C. plebeians refuse to join military Tribunes were selected to represent plebeians The Twelve Tables: basis of all Roman Law • All free citizens had a right to the law’s protection ...
Chapter 5 Ancient Rome and the Rise of Christianity
... • In 509 B.C. Rome established a Republic (A form of government in which citizens choose their leaders) • Citizenship was not granted to slaves or foreigners and women had no right to vote ...
... • In 509 B.C. Rome established a Republic (A form of government in which citizens choose their leaders) • Citizenship was not granted to slaves or foreigners and women had no right to vote ...
Step I: The Artist
... Augustus Caesar ushered in an era of extended peace and expansion in the Roman Empire that lasted for nearly 200 years, the Pax Romana. During this span of time, the Roman Empire reached the height of its power. As an expertly skilled Roman citizen, you have been tasked with reflecting back on impor ...
... Augustus Caesar ushered in an era of extended peace and expansion in the Roman Empire that lasted for nearly 200 years, the Pax Romana. During this span of time, the Roman Empire reached the height of its power. As an expertly skilled Roman citizen, you have been tasked with reflecting back on impor ...
Military of ancient Rome
The Roman military was intertwined with the Roman state much more closely than in a modern European nation. Josephus describes the Roman people being as if they were ""born ready armed,"" and the Romans were for long periods prepared to engage in almost continuous warfare, absorbing massive losses. For a large part of Rome's history, the Roman state existed as an entity almost solely to support and finance the Roman military.The military's campaign history stretched over 1300 years and saw Roman armies campaigning as far East as Parthia (modern-day Iran), as far south as Africa (modern-day Tunisia) and Aegyptus (modern-day Egypt) and as far north as Britannia (modern-day England, south Scotland, and Wales). The makeup of the Roman military changed substantially over its history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much of its history, the vast majority of Rome's forces were maintained at or beyond the limits of its territory, in order to either expand Rome's domain, or protect its existing borders.