AncientRome
... Gods and goddesses resembled those of Greeks. Religious festivals inspired sense of community. Romans built many temples for worship. ...
... Gods and goddesses resembled those of Greeks. Religious festivals inspired sense of community. Romans built many temples for worship. ...
Roman History The Roman Republic The Greeks produced artistic
... turn forced them to direct all their energies to political dealings. The nobles in Rome could never develop their own forms of life, as they are expressed in, e.g., the Olympic Games of the Greeks. They were forced into actions on behalf of the res publica, the state, into a life as a politician or ...
... turn forced them to direct all their energies to political dealings. The nobles in Rome could never develop their own forms of life, as they are expressed in, e.g., the Olympic Games of the Greeks. They were forced into actions on behalf of the res publica, the state, into a life as a politician or ...
Rome republic and government
... Conquering Italy By the mid 200s Rome had conquered all of Italy. Expanded Roman citizenship to all “Italians” (big advantage over the Greeks) One of the Rome’s best traits was their willingness to learn from other people. Took best ideas/skills of conquered peoples and made them part of Roman soc ...
... Conquering Italy By the mid 200s Rome had conquered all of Italy. Expanded Roman citizenship to all “Italians” (big advantage over the Greeks) One of the Rome’s best traits was their willingness to learn from other people. Took best ideas/skills of conquered peoples and made them part of Roman soc ...
Founding the Roman Republic
... Rome was at the center of trade routes that spread out across the land in all directions Roman Republic Republic- A form of government in which voters elect officials to run the state. Only adult male citizens were entitled to vote and take part in government Senate Most influential and ...
... Rome was at the center of trade routes that spread out across the land in all directions Roman Republic Republic- A form of government in which voters elect officials to run the state. Only adult male citizens were entitled to vote and take part in government Senate Most influential and ...
The Fall of the Roman Empire
... in the field of law. The Roman government set standards of law that still influence people today. Some of the most important principles of Roman law were: ...
... in the field of law. The Roman government set standards of law that still influence people today. Some of the most important principles of Roman law were: ...
Thematic: Empires
... How is this similar to a football team? BEST EQUPMENT: The best equipped soldier in the army was the legionaries. The legionaries were armed with a javelin, sword, dagger and shield and protected by body armour. TOTAL COMMITMENT: All soldiers were volunteers staying in the army for 25 years. The ar ...
... How is this similar to a football team? BEST EQUPMENT: The best equipped soldier in the army was the legionaries. The legionaries were armed with a javelin, sword, dagger and shield and protected by body armour. TOTAL COMMITMENT: All soldiers were volunteers staying in the army for 25 years. The ar ...
- Katella HS
... • The Pax Romana will last for approximately 200 years. • This is the period of the reign of Augustus to the death of Marcus Aurelius. • The empire is held together by factors such as: – Law, • military organization, and • widespread trade and transportation* *nearly 180,000 miles of paved highways ...
... • The Pax Romana will last for approximately 200 years. • This is the period of the reign of Augustus to the death of Marcus Aurelius. • The empire is held together by factors such as: – Law, • military organization, and • widespread trade and transportation* *nearly 180,000 miles of paved highways ...
The Roman Republic - Mrs. Brewington World History
... Conflict with Carthage (Northern Africa) 1st Punic war, Rome dominated by Carthage navy, Rome builds a navy and wins 2nd Punic War, Hannibal raids Italy with superior forces. (War Elephants) Rome attacks Carthage and wins,(Scipio Africanus) 3rd Punic War, Carthage is sacked and burned. Rom ...
... Conflict with Carthage (Northern Africa) 1st Punic war, Rome dominated by Carthage navy, Rome builds a navy and wins 2nd Punic War, Hannibal raids Italy with superior forces. (War Elephants) Rome attacks Carthage and wins,(Scipio Africanus) 3rd Punic War, Carthage is sacked and burned. Rom ...
The Roman Republic Assesment.key
... they commanded the army and directed the government. However, their power was limited. A consul’s term was only one year long. The same person could not be elected consul again for ten years. Also, one consul could always overrule, or veto, the other’s decisions. ...
... they commanded the army and directed the government. However, their power was limited. A consul’s term was only one year long. The same person could not be elected consul again for ten years. Also, one consul could always overrule, or veto, the other’s decisions. ...
MENU The Coliseum Roman Temples The Material Roman Baths
... exercise in one of the exercise yards. From here they would move to the tepidarium or warm room where they would lie around chatting with their friends. ...
... exercise in one of the exercise yards. From here they would move to the tepidarium or warm room where they would lie around chatting with their friends. ...
Republic
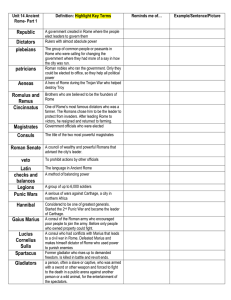
... To prohibit actions by other officials The language in Ancient Rome A method of balancing power A group of up to 6,000 soldiers A serious of wars against Carthage, a city in northern Africa Considered to be one of greatest generals. Started the 2nd Punic War and became the leader of Carthage. A cons ...
... To prohibit actions by other officials The language in Ancient Rome A method of balancing power A group of up to 6,000 soldiers A serious of wars against Carthage, a city in northern Africa Considered to be one of greatest generals. Started the 2nd Punic War and became the leader of Carthage. A cons ...
File
... Etruscans ruled northern Italy from the planes of Etruria 900BC to 500BC Beginning of the 8th century and continuing over the next three centuries, Etruria, Latium and Campania witnessed a series of political, social and cultural innovations that would lead to the formation of the first central ...
... Etruscans ruled northern Italy from the planes of Etruria 900BC to 500BC Beginning of the 8th century and continuing over the next three centuries, Etruria, Latium and Campania witnessed a series of political, social and cultural innovations that would lead to the formation of the first central ...
Theories on Why Rome Declined and Fell
... Rome had conquered a huge empire. This meant that they also had huge borders to defend. Right when the Roman economy could have used investments in infrastructure, such as new roads or public housing, or new businesses, the Roman Empire had to spend most of its money on the huge armies needed to def ...
... Rome had conquered a huge empire. This meant that they also had huge borders to defend. Right when the Roman economy could have used investments in infrastructure, such as new roads or public housing, or new businesses, the Roman Empire had to spend most of its money on the huge armies needed to def ...
World History II Midterm Review Sheet Fall Semester 2015 Term
... In what ways would the transition from hunting and gathering to a settled, agricultural society have improved people's lives, and in what ways would the transition have decreased the quality of life? Discuss the differences between Sparta and Athens. Compare and contrast their political life, milita ...
... In what ways would the transition from hunting and gathering to a settled, agricultural society have improved people's lives, and in what ways would the transition have decreased the quality of life? Discuss the differences between Sparta and Athens. Compare and contrast their political life, milita ...
Chapter 8, Section 1
... In 509 B.C., Romans revolted because they did not like being ruled by an allpowerful King. Not much is known about the Etruscans. ...
... In 509 B.C., Romans revolted because they did not like being ruled by an allpowerful King. Not much is known about the Etruscans. ...
The Roman civilization From Republic to Empire
... notable for its peaceful method of succession. Each emperor chose his successor by adopting an heir. This prevented the civil wars that occurred when other emperors did not chose a successor in advance. This time period came to be known as… ...
... notable for its peaceful method of succession. Each emperor chose his successor by adopting an heir. This prevented the civil wars that occurred when other emperors did not chose a successor in advance. This time period came to be known as… ...
Chapter 7: Roman Art Chapter Sheet Preview: The Roman Empire
... Preview: The Roman Empire was the most expansive and powerful of the ancient world, and its cultural productions, architectural forms, social and legal structures, and language has indelibly marked the Western world as we know it today. The empire dates from 753, with the establishment of the city o ...
... Preview: The Roman Empire was the most expansive and powerful of the ancient world, and its cultural productions, architectural forms, social and legal structures, and language has indelibly marked the Western world as we know it today. The empire dates from 753, with the establishment of the city o ...
The Roman civilization From Republic to Empire
... notable for its peaceful method of succession. Each emperor chose his successor by adopting an heir. This prevented the civil wars that occurred when other emperors did not chose a successor in advance. This time period came to be known as… ...
... notable for its peaceful method of succession. Each emperor chose his successor by adopting an heir. This prevented the civil wars that occurred when other emperors did not chose a successor in advance. This time period came to be known as… ...
Roman Patrician with Busts of his Ancestors
... The current building dates from about 125 AD, during the reign of the Emperor Hadrian, as date-stamps on the bricks reveal. It was totally reconstructed with the text of the original inscription "M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT" meaning, "Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, three times consul made it" w ...
... The current building dates from about 125 AD, during the reign of the Emperor Hadrian, as date-stamps on the bricks reveal. It was totally reconstructed with the text of the original inscription "M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT" meaning, "Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, three times consul made it" w ...
THE FALL of ROME
... The government and economy fell to pieces. (inflation) The senate lost its power. Emperors were not safe. In 104 years, there were 29 emperors. . . . most were murdered (assassinated). ...
... The government and economy fell to pieces. (inflation) The senate lost its power. Emperors were not safe. In 104 years, there were 29 emperors. . . . most were murdered (assassinated). ...
Military of ancient Rome
The Roman military was intertwined with the Roman state much more closely than in a modern European nation. Josephus describes the Roman people being as if they were ""born ready armed,"" and the Romans were for long periods prepared to engage in almost continuous warfare, absorbing massive losses. For a large part of Rome's history, the Roman state existed as an entity almost solely to support and finance the Roman military.The military's campaign history stretched over 1300 years and saw Roman armies campaigning as far East as Parthia (modern-day Iran), as far south as Africa (modern-day Tunisia) and Aegyptus (modern-day Egypt) and as far north as Britannia (modern-day England, south Scotland, and Wales). The makeup of the Roman military changed substantially over its history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much of its history, the vast majority of Rome's forces were maintained at or beyond the limits of its territory, in order to either expand Rome's domain, or protect its existing borders.