The Hellenistic Age, 336-31 BCE
... • Ca. 500 B.C.E. Roman monarchy abolished and republic is founded • Political participation by all free, male citizens who could afford their own weapon • Political power controlled by an oligarchy of patrician families • Social conflict between patrician and plebian classes shaped political institu ...
... • Ca. 500 B.C.E. Roman monarchy abolished and republic is founded • Political participation by all free, male citizens who could afford their own weapon • Political power controlled by an oligarchy of patrician families • Social conflict between patrician and plebian classes shaped political institu ...
Latin Term - WordPress.com
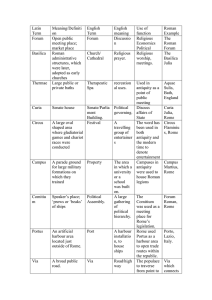
... antiquity as a point of public meeting Political Discuss governing. affairs of State A The word has travelling been used in group of both entertainer antiquity and s the modern time to denote entertainment The area Campuses in in which a antiquity university were used to or a house Roman school legi ...
... antiquity as a point of public meeting Political Discuss governing. affairs of State A The word has travelling been used in group of both entertainer antiquity and s the modern time to denote entertainment The area Campuses in in which a antiquity university were used to or a house Roman school legi ...
The Classical Empires - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 7). Describe the Structure of the Roman Republic. 8). Why is Augustus Caesar considered the 1st Emperor of Rome? 9). What is the difference between Plebeians and Patricians? 10). Thoroughly explain 1 reason why the Roman Empire fell in 476c.e. ...
... 7). Describe the Structure of the Roman Republic. 8). Why is Augustus Caesar considered the 1st Emperor of Rome? 9). What is the difference between Plebeians and Patricians? 10). Thoroughly explain 1 reason why the Roman Empire fell in 476c.e. ...
World History Chapter 6
... What scientific theory did Ptolemy propose? a) that the sun is the center of the universe b) that the Earth is the center of the universe c) that the Earth is flat d) that the planets revolved around the moon Roman principles of law a) led to civil war within the empire. b) were primitive and harsh. ...
... What scientific theory did Ptolemy propose? a) that the sun is the center of the universe b) that the Earth is the center of the universe c) that the Earth is flat d) that the planets revolved around the moon Roman principles of law a) led to civil war within the empire. b) were primitive and harsh. ...
Reasons for the Decline of the Western Roman Empire
... almost entirely to infrastructure engineering and the organization of public services. They built marvelous roads, bridges, and aqueducts. They established the first system of medicine for the benefit of the poor. But since the Romans relied so much on human and animal labor, they failed to find new ...
... almost entirely to infrastructure engineering and the organization of public services. They built marvelous roads, bridges, and aqueducts. They established the first system of medicine for the benefit of the poor. But since the Romans relied so much on human and animal labor, they failed to find new ...
Roman Art 1
... developed literature on the theory, history or criticism of art like the Greeks •we hear very little of specific artists who enjoyed individual fame •Probably looked upon their own time as a decline in art compared to Greece •Earlier seen by historians as just an extension of Greek art but now seen ...
... developed literature on the theory, history or criticism of art like the Greeks •we hear very little of specific artists who enjoyed individual fame •Probably looked upon their own time as a decline in art compared to Greece •Earlier seen by historians as just an extension of Greek art but now seen ...
CP World History (Unit 2, #4)
... A. In addition to Greece, a significant ________________________________________________________________ was ancient Rome B. The Geography of Rome 1. Rome was located on the ___________________ peninsula along the _____________________________________________ Sea 2. The Romans were influenced by the ...
... A. In addition to Greece, a significant ________________________________________________________________ was ancient Rome B. The Geography of Rome 1. Rome was located on the ___________________ peninsula along the _____________________________________________ Sea 2. The Romans were influenced by the ...
The city of Rome was founded on a group of hills about fourteen
... Rome was quickly rebuilt and a new army was raised. The Gaul’s had weakened the Etruscans, presenting the Romans with an opportunity conquer central and northern Italy. In addition, Rome defeated Greek colonies established in the south giving them control of all Italy. Carthage (located on the other ...
... Rome was quickly rebuilt and a new army was raised. The Gaul’s had weakened the Etruscans, presenting the Romans with an opportunity conquer central and northern Italy. In addition, Rome defeated Greek colonies established in the south giving them control of all Italy. Carthage (located on the other ...
gain ally - Gimnazjum 25
... who held most of the power. The other important group was the plebeians, the common farmers, artisans, and merchants who made up the majority of the population. The patricians inherited their power and social status. They claimed that their ancestry gave them the authority to make laws for Rome and ...
... who held most of the power. The other important group was the plebeians, the common farmers, artisans, and merchants who made up the majority of the population. The patricians inherited their power and social status. They claimed that their ancestry gave them the authority to make laws for Rome and ...
Chapter_6_Vocab_and_Questions
... 5) Who were the Etruscans and in what ways did the Etruscan rule benefit Rome? 6) How did rich patrician families maintain their power, and what was life like for plebeians? 7) What was Rome’s first written law code called and why did plebeians want the laws written down? 8) Why did the Romans estab ...
... 5) Who were the Etruscans and in what ways did the Etruscan rule benefit Rome? 6) How did rich patrician families maintain their power, and what was life like for plebeians? 7) What was Rome’s first written law code called and why did plebeians want the laws written down? 8) Why did the Romans estab ...
Ancient Rome - Regents Review
... • End of Western Roman Empire traditionally dated to 476 CE, when last emperor, Romulus Augustus, deposed • Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire continued until conquered by the Turks in 1453 ...
... • End of Western Roman Empire traditionally dated to 476 CE, when last emperor, Romulus Augustus, deposed • Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire continued until conquered by the Turks in 1453 ...
Roman Empire - Chaparral Middle School
... began to invade and overrun the western half of the empire. They destroyed homes and villages, and chaos and fear followed in their wake. How was this allowed to happen? Rome had kept invaders out for hundreds of years in the past. So what changed? ...
... began to invade and overrun the western half of the empire. They destroyed homes and villages, and chaos and fear followed in their wake. How was this allowed to happen? Rome had kept invaders out for hundreds of years in the past. So what changed? ...
Slide 1
... Rome gradually took over the Italian Peninsula in 200 years of fighting. Rome continued to fight for new territory and to protect the territory they captured. ...
... Rome gradually took over the Italian Peninsula in 200 years of fighting. Rome continued to fight for new territory and to protect the territory they captured. ...
Chapter 5 Outline -- The World of Rome - tms-ancient
... 1. Political disturbances in the last centuries of the Republic stemmed from the acquisition of empire. 2. Many people responded to the events of the second century B.C.E. by reasserting traditional Roman values. 3. The paterfamilias was the most powerful force in the Roman family in the traditional ...
... 1. Political disturbances in the last centuries of the Republic stemmed from the acquisition of empire. 2. Many people responded to the events of the second century B.C.E. by reasserting traditional Roman values. 3. The paterfamilias was the most powerful force in the Roman family in the traditional ...
Fusion Roman Republic - White Plains Public Schools
... “Italy is a long, narrow, boot-shaped peninsula extending into the Mediterranean Sea. Rome was a city-state located on a fertile plain in the middle of Italy near the west coast. To the north, the Alps Mountains protected Rome and the rest of Italy from most invaders. The sea provided further protec ...
... “Italy is a long, narrow, boot-shaped peninsula extending into the Mediterranean Sea. Rome was a city-state located on a fertile plain in the middle of Italy near the west coast. To the north, the Alps Mountains protected Rome and the rest of Italy from most invaders. The sea provided further protec ...
From Roman Republic to Empire
... ● Wealthy landowners who held most of the power ● Inherited power and social status ● Claimed ancestry gave them the power to make laws ...
... ● Wealthy landowners who held most of the power ● Inherited power and social status ● Claimed ancestry gave them the power to make laws ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... The archaeological site is located at the north-west of Rome, not far from Fiumicino ...
... The archaeological site is located at the north-west of Rome, not far from Fiumicino ...
homework_10-17 - WordPress.com
... Tables, as they came to be known, were the first Roman laws put in writing. Although the laws were rather harsh by today's standards, they did guarantee every citizen equal treatment under the law. ...
... Tables, as they came to be known, were the first Roman laws put in writing. Although the laws were rather harsh by today's standards, they did guarantee every citizen equal treatment under the law. ...
From Republic to Empire
... • Why did the Roman Republic fail to survive challenges by Julius Caesar? • How did military conquests alter economic and social life in Rome? • How did an imperial monarchy come to rule Rome? ...
... • Why did the Roman Republic fail to survive challenges by Julius Caesar? • How did military conquests alter economic and social life in Rome? • How did an imperial monarchy come to rule Rome? ...
Ancient Greece - Calaveras Unified School District
... 3. Pottery was another source of art - telling myths and legends. C. Sparta defeated Athens in Peloponnesian War of 27 years starting in 431 BC. 1. After having its navy destroyed and the city depleted by plagues, it surrenders. 2. Athens is shaken by defeat. a. Democracy begins to fail. b. Art begi ...
... 3. Pottery was another source of art - telling myths and legends. C. Sparta defeated Athens in Peloponnesian War of 27 years starting in 431 BC. 1. After having its navy destroyed and the city depleted by plagues, it surrenders. 2. Athens is shaken by defeat. a. Democracy begins to fail. b. Art begi ...
Rome`s Decline - 6th Grade Social Studies
... of the army fought each other to put new emperors on the throne. Rome had 22 emperors in a period of 50 years. This period of civil war caused great suffering, including: ...
... of the army fought each other to put new emperors on the throne. Rome had 22 emperors in a period of 50 years. This period of civil war caused great suffering, including: ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... -carved in bronze -kept at the forum -Established “rule of law” 1. Equality under the law 2. Innocent until proven guilty Rome’s rival –Carthage Punic Wars Rome vs. Carthage -control the Mediterranean Sea to control trade on it -control the islands in it and its shores Hannibal-Carthage leader (atta ...
... -carved in bronze -kept at the forum -Established “rule of law” 1. Equality under the law 2. Innocent until proven guilty Rome’s rival –Carthage Punic Wars Rome vs. Carthage -control the Mediterranean Sea to control trade on it -control the islands in it and its shores Hannibal-Carthage leader (atta ...
The Roman Republic - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Hannibal takes control of many Italian cities, free to roam Italy, but not powerful enough to take major cities 206 BC: Rome takes back Italian cities, and pushes Carthage out or Spain 202 BC: Battle of Zama, Rome takes fight to Carthage, Hannibal recalled from Italy, crushed by Romans Rome do ...
... Hannibal takes control of many Italian cities, free to roam Italy, but not powerful enough to take major cities 206 BC: Rome takes back Italian cities, and pushes Carthage out or Spain 202 BC: Battle of Zama, Rome takes fight to Carthage, Hannibal recalled from Italy, crushed by Romans Rome do ...
document
... sometimes were incompatible with a realistic treatment of space •Commemorated Trajan’s victories over the Dacians (ancient Romanians) •Free standing columns were used as monuments since Hellenic times •Continuous spiral band of relief documents the history of the war •Column was originally topped wi ...
... sometimes were incompatible with a realistic treatment of space •Commemorated Trajan’s victories over the Dacians (ancient Romanians) •Free standing columns were used as monuments since Hellenic times •Continuous spiral band of relief documents the history of the war •Column was originally topped wi ...
Military of ancient Rome
The Roman military was intertwined with the Roman state much more closely than in a modern European nation. Josephus describes the Roman people being as if they were ""born ready armed,"" and the Romans were for long periods prepared to engage in almost continuous warfare, absorbing massive losses. For a large part of Rome's history, the Roman state existed as an entity almost solely to support and finance the Roman military.The military's campaign history stretched over 1300 years and saw Roman armies campaigning as far East as Parthia (modern-day Iran), as far south as Africa (modern-day Tunisia) and Aegyptus (modern-day Egypt) and as far north as Britannia (modern-day England, south Scotland, and Wales). The makeup of the Roman military changed substantially over its history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much of its history, the vast majority of Rome's forces were maintained at or beyond the limits of its territory, in order to either expand Rome's domain, or protect its existing borders.