Unit 7 Lesson 2 The Republic and Roman Expansion
... Assemblies and Tribunes - Represented the common people, approved or rejected laws, declared war, elected magistrates ...
... Assemblies and Tribunes - Represented the common people, approved or rejected laws, declared war, elected magistrates ...
Topic
... Cinicinnatus and Civic Duty ------------What was the role of dictator and how were they chosen? During difficult or dangerous times, the ______________ appointed a dictator to rule. A dictator had absolute _________________. The dictator was to serve for a _________________ time period. Cincinnatus ...
... Cinicinnatus and Civic Duty ------------What was the role of dictator and how were they chosen? During difficult or dangerous times, the ______________ appointed a dictator to rule. A dictator had absolute _________________. The dictator was to serve for a _________________ time period. Cincinnatus ...
HIS 28 – Part 14
... ii) GNAEUS NAEVIUS (died 201 BC), again an epic poet and dramatist, ran foul of the powerful Cecilii Metelli and was forced into exile. He too adapted Greek ‘New Comedy’ to the Roman stage, but extended tragedy to deal with national Roman figures and incidents from Roman history. iii) TITUS MACCIUS ...
... ii) GNAEUS NAEVIUS (died 201 BC), again an epic poet and dramatist, ran foul of the powerful Cecilii Metelli and was forced into exile. He too adapted Greek ‘New Comedy’ to the Roman stage, but extended tragedy to deal with national Roman figures and incidents from Roman history. iii) TITUS MACCIUS ...
chapter 6
... patriancian: member of the landholding upper class in ancient Rome. consul: official from the patriacian class who supervised the government and commanded the army. dictator: a ruler appointed for six months in time of emergency. plebian: member of the lower class in Rome, including farmers, merchan ...
... patriancian: member of the landholding upper class in ancient Rome. consul: official from the patriacian class who supervised the government and commanded the army. dictator: a ruler appointed for six months in time of emergency. plebian: member of the lower class in Rome, including farmers, merchan ...
4 3 2 1 0 ROME: LEARNING GOAL #1 SCALE AND FOCUS
... Describe the two main classes of the early Roman republic (Patricians and Plebeians). What was the “Twelve Tables,” and why would it be considered important? How did the 3 branches of the Roman Republic work? What would happen to the Roman government during times of war during the early Republic? Wh ...
... Describe the two main classes of the early Roman republic (Patricians and Plebeians). What was the “Twelve Tables,” and why would it be considered important? How did the 3 branches of the Roman Republic work? What would happen to the Roman government during times of war during the early Republic? Wh ...
Roman Art 2
... sometimes were incompatible with a realistic treatment of space •Commemorated Trajan’s victories over the Dacians (ancient Romanians) •Free standing columns were used as monuments since Hellenic times •Continuous spiral band of relief documents the history of the war •Column was originally topped wi ...
... sometimes were incompatible with a realistic treatment of space •Commemorated Trajan’s victories over the Dacians (ancient Romanians) •Free standing columns were used as monuments since Hellenic times •Continuous spiral band of relief documents the history of the war •Column was originally topped wi ...
Decline of the Roman Empire
... Diocletian and Constantine, helped the Roman Empire cling to power. It was Diocletian who first suggested that Rome have two emperors, one in the East and one in the West, to share power and responsibilities. Constantine created the new capital city in the East which was known as Constantinople. Eve ...
... Diocletian and Constantine, helped the Roman Empire cling to power. It was Diocletian who first suggested that Rome have two emperors, one in the East and one in the West, to share power and responsibilities. Constantine created the new capital city in the East which was known as Constantinople. Eve ...
Class Struggle
... was a problem with the Roman republic. ► We call it class distinction, the feeling that some people are "upper class" while others are "lower class" and inferior. ...
... was a problem with the Roman republic. ► We call it class distinction, the feeling that some people are "upper class" while others are "lower class" and inferior. ...
From Republic to Empire
... Carthage in the Punic Wars between 246 B.C. and 146 B.C. In the end, Rome destroyed Carthage and gained control of its lands and peoples. In the eastern Mediterranean, Rome ...
... Carthage in the Punic Wars between 246 B.C. and 146 B.C. In the end, Rome destroyed Carthage and gained control of its lands and peoples. In the eastern Mediterranean, Rome ...
File
... branches are set forth in our Constitution, just like the Roman officials’ powers were. Our government also has a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch from becoming too strong. For ...
... branches are set forth in our Constitution, just like the Roman officials’ powers were. Our government also has a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch from becoming too strong. For ...
File
... City-State – independent community that includes a city and its surrounding territory Democracy – government in which the people can influence law and vote for representatives ...
... City-State – independent community that includes a city and its surrounding territory Democracy – government in which the people can influence law and vote for representatives ...
The Roman Empire, at its height, extended from modern Sudan in
... really understand what the Romans have ever done for us. Their architecture, art and culture pervade our lives, and we’re extremely lucky that we can go and see for ourselves how they lived and where this influence comes from. Their vast civic buildings tell us of their pride and engineering prowess ...
... really understand what the Romans have ever done for us. Their architecture, art and culture pervade our lives, and we’re extremely lucky that we can go and see for ourselves how they lived and where this influence comes from. Their vast civic buildings tell us of their pride and engineering prowess ...
Roman Art/Architecture
... • Some art serves a purpose. • Other art is created simply to enjoy. • On the lines to the right, write down your favorite song and movie. • In your groups, determine if your song or movie is purposeful or enjoyable. ...
... • Some art serves a purpose. • Other art is created simply to enjoy. • On the lines to the right, write down your favorite song and movie. • In your groups, determine if your song or movie is purposeful or enjoyable. ...
Rome Millionaire
... __________, was a great war general who led Carthage against Rome in the Second Punic War. ...
... __________, was a great war general who led Carthage against Rome in the Second Punic War. ...
Ancient Roman Society
... Twelve Tables, which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens of Rome had a right to the protection of the law ...
... Twelve Tables, which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens of Rome had a right to the protection of the law ...
Social Studies 9R – Mr. Berman Aim #8: Is the Pax Romana really
... entertainment. The entertainment on display was some of the most violent the world has ever seen. This combination of food and violent spectacle became known as “Bread and Circuses.” Countless men and women (many of them slaves) and hundreds of thousands of animals were killed providing entertainmen ...
... entertainment. The entertainment on display was some of the most violent the world has ever seen. This combination of food and violent spectacle became known as “Bread and Circuses.” Countless men and women (many of them slaves) and hundreds of thousands of animals were killed providing entertainmen ...
The Roman Republic - Mr. Schabo`s Class Website
... • Rome battled Carthage in a long series of wars known as the Punic Wars. (264-146 B.C) • Lead by Hannibal, the Carthaginian army attacked Rome from Spain through the alps. • With the help of its allies, Rome defeated the Carthaginian army, giving it complete control over the Western Mediterranean S ...
... • Rome battled Carthage in a long series of wars known as the Punic Wars. (264-146 B.C) • Lead by Hannibal, the Carthaginian army attacked Rome from Spain through the alps. • With the help of its allies, Rome defeated the Carthaginian army, giving it complete control over the Western Mediterranean S ...
Decline and Fall of Roman Empire
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire
... realizing Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The empire was divided But, the empire The East was far wealthier than ...
... realizing Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The empire was divided But, the empire The East was far wealthier than ...
World History Study Guide Ch 7 The Roman World File
... 2. How was the government of the Rome Republic set up? 3. What was the Conflict of the Orders, and how did it change the early Roman Republic? 4. How were the roles of citizens and noncitizens under Roman rule different? 5. How was Rome helped by its location? 6. How did the Romans organize the gove ...
... 2. How was the government of the Rome Republic set up? 3. What was the Conflict of the Orders, and how did it change the early Roman Republic? 4. How were the roles of citizens and noncitizens under Roman rule different? 5. How was Rome helped by its location? 6. How did the Romans organize the gove ...
Rome Power Point
... – Wealthy landowners increasingly used slaves which put small farmers and laborers out of work ...
... – Wealthy landowners increasingly used slaves which put small farmers and laborers out of work ...
Rome - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... – Nerva / Trajan / Hadrian / Antoninus Pius / Marcus Aurelius ...
... – Nerva / Trajan / Hadrian / Antoninus Pius / Marcus Aurelius ...
Document
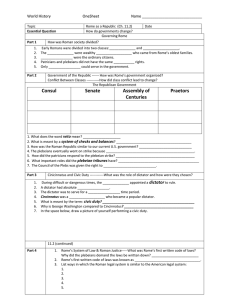
... – Assembly of Tribes (comprised of plebeians that represented the 35 tribes to which Roman citizens ...
... – Assembly of Tribes (comprised of plebeians that represented the 35 tribes to which Roman citizens ...
Military of ancient Rome
The Roman military was intertwined with the Roman state much more closely than in a modern European nation. Josephus describes the Roman people being as if they were ""born ready armed,"" and the Romans were for long periods prepared to engage in almost continuous warfare, absorbing massive losses. For a large part of Rome's history, the Roman state existed as an entity almost solely to support and finance the Roman military.The military's campaign history stretched over 1300 years and saw Roman armies campaigning as far East as Parthia (modern-day Iran), as far south as Africa (modern-day Tunisia) and Aegyptus (modern-day Egypt) and as far north as Britannia (modern-day England, south Scotland, and Wales). The makeup of the Roman military changed substantially over its history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much of its history, the vast majority of Rome's forces were maintained at or beyond the limits of its territory, in order to either expand Rome's domain, or protect its existing borders.