Ancient Rome: Learning Outcomes
... government was a monarchy (king or queen). 10. The Romans rebelled against the Etruscans and formed a new government called a republic. 11. A republic is a form of government in which citizens elect leaders to make all government decisions. 12. The Romans had two social classes: Patricians and Plebe ...
... government was a monarchy (king or queen). 10. The Romans rebelled against the Etruscans and formed a new government called a republic. 11. A republic is a form of government in which citizens elect leaders to make all government decisions. 12. The Romans had two social classes: Patricians and Plebe ...
Ancient_Rome_Timeline_(cultural_events)
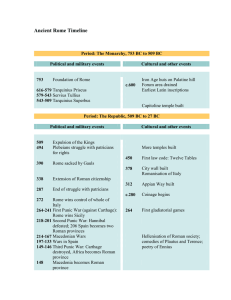
... Iron Age huts on Palatine hill Forum area drained Earliest Latin inscriptions ...
... Iron Age huts on Palatine hill Forum area drained Earliest Latin inscriptions ...
Name
... Empire expanded, these laws were combined with other laws and customs. The laws were written down as a code of justice that would apply to all people. According to Roman law, an accused person was considered innocent until he or she was proven guilty. The principles of Roman law became the basis for ...
... Empire expanded, these laws were combined with other laws and customs. The laws were written down as a code of justice that would apply to all people. According to Roman law, an accused person was considered innocent until he or she was proven guilty. The principles of Roman law became the basis for ...
Ancient Rome
... • Plebeians: craftspeople, merchants, small farmers, less wealthy landowners • Both groups could vote, only patricians could be officials/elected representative • Roman Senate – Select group of 300 patricians elected for life ...
... • Plebeians: craftspeople, merchants, small farmers, less wealthy landowners • Both groups could vote, only patricians could be officials/elected representative • Roman Senate – Select group of 300 patricians elected for life ...
The Founding of Rome
... contributed to the shaping of Roman society and the expansion of its political power in the Mediterranean region and beyond. (E, G, P) • 6.62 Explain the rise of the Roman Republic and the role of mythical and historical figures in Roman history, including Romulus and Remus, Hannibal and the Carthag ...
... contributed to the shaping of Roman society and the expansion of its political power in the Mediterranean region and beyond. (E, G, P) • 6.62 Explain the rise of the Roman Republic and the role of mythical and historical figures in Roman history, including Romulus and Remus, Hannibal and the Carthag ...
5104 EDU-092 Olympus Pre Visit Kit_Timeline_F.indd
... • 27 BC – Roman Empire begins when Octavios appoints himself emperor ...
... • 27 BC – Roman Empire begins when Octavios appoints himself emperor ...
Imperialism and Empire
... Gracchus, called for reforms like free land and free food for the poor • Senators felt threatened, called for street mobs to attack and kill the Gracchus brothers and supporters ...
... Gracchus, called for reforms like free land and free food for the poor • Senators felt threatened, called for street mobs to attack and kill the Gracchus brothers and supporters ...
Chapter 7: Roman Art Chapter Sheet Preview: The Roman Empire
... Chapter 7 List of Artworks (10 Cue Cards) 1. Chapter 7 Roman Context Card (dates, periods, Geography, key locations, key figures, religion, government, new ...
... Chapter 7 List of Artworks (10 Cue Cards) 1. Chapter 7 Roman Context Card (dates, periods, Geography, key locations, key figures, religion, government, new ...
5.2 Notes - Cloudfront.net
... became professional armies loyal to their commanders rather than the Senate. Rival armies marched on Rome. ...
... became professional armies loyal to their commanders rather than the Senate. Rival armies marched on Rome. ...
Roman Britain.
... Many buildings changed use but were not destroyed. There were growing barbarian attacks, but these were focused on rural settlements rather than towns. - Urban life had generally grown less intense by the fourth quarter of the fourth century, and coins minted between 378 and 388 are very rare, indic ...
... Many buildings changed use but were not destroyed. There were growing barbarian attacks, but these were focused on rural settlements rather than towns. - Urban life had generally grown less intense by the fourth quarter of the fourth century, and coins minted between 378 and 388 are very rare, indic ...
arts1303_11Antiquity5.pdf
... The Egyptians knew the round arch, but the Romans realized and developed its potential. As early as late Etruscan times, arches were combined with Greek Classical elements. When the barbarians sacked Rome off and on over the centuries, they left the Pantheon relatively undisturbed. Perhaps even they ...
... The Egyptians knew the round arch, but the Romans realized and developed its potential. As early as late Etruscan times, arches were combined with Greek Classical elements. When the barbarians sacked Rome off and on over the centuries, they left the Pantheon relatively undisturbed. Perhaps even they ...
The Rise of Rome: Notes
... The _________________________________ had the greatest influence on the Romans They were located North of Rome in Etruria, they expanded into _________________ and came into control Rome and most of Latium They turned the Latin villages into the city of __________________ Romans adopted thei ...
... The _________________________________ had the greatest influence on the Romans They were located North of Rome in Etruria, they expanded into _________________ and came into control Rome and most of Latium They turned the Latin villages into the city of __________________ Romans adopted thei ...
Ancient Rome - Portlaoise College
... army was the LEGION. • There were 30 legions in the Roman army • Each was made up of 5000 legionaires. ...
... army was the LEGION. • There were 30 legions in the Roman army • Each was made up of 5000 legionaires. ...
File ancient rome pp shell notes
... MAJOR Achievements of Ancient Rome: a) Temple Architecture: blended ___________________ and _________________ features with an emphasis on the ________________ of the building b) Learned how to construct the _________________ and ______________....evidence of this is found with the _________________ ...
... MAJOR Achievements of Ancient Rome: a) Temple Architecture: blended ___________________ and _________________ features with an emphasis on the ________________ of the building b) Learned how to construct the _________________ and ______________....evidence of this is found with the _________________ ...
The Roman Empire
... 60 B.C. Julius Caesar joined forces with Crauss and Pompey and for the next ten years they ruled Rome as a triumvirates (group of 3 rulers). He then after a year appointed himself Governor of Gaul and after a gruesome campaign conquered all and earned his men’s loyalty by fighting besides them. ...
... 60 B.C. Julius Caesar joined forces with Crauss and Pompey and for the next ten years they ruled Rome as a triumvirates (group of 3 rulers). He then after a year appointed himself Governor of Gaul and after a gruesome campaign conquered all and earned his men’s loyalty by fighting besides them. ...
The life of Julius caesar
... ■ The amphitheater were used for things like gladiator fights, chariot races, public executions, and other events. ...
... ■ The amphitheater were used for things like gladiator fights, chariot races, public executions, and other events. ...
The Roman Republic - White Plains Public Schools
... because it allowed only patricians to vote. The wealthy patrician class made up only 10 percent of the population of Rome. Yet, patricians ran the government. Most Romans were plebeians or “the common people.” As citizens, the plebeians paid taxes and served in the army. But they had little ...
... because it allowed only patricians to vote. The wealthy patrician class made up only 10 percent of the population of Rome. Yet, patricians ran the government. Most Romans were plebeians or “the common people.” As citizens, the plebeians paid taxes and served in the army. But they had little ...
A. Aqueducts
... skin parchment that more clearly resembled pages. Ancient historians note that Julius Caesar created an early version of a codex by stacking pages of papyrus to form a primitive notebook, but bound codices did not become popular in Rome until the first century or thereabouts. Early Christians became ...
... skin parchment that more clearly resembled pages. Ancient historians note that Julius Caesar created an early version of a codex by stacking pages of papyrus to form a primitive notebook, but bound codices did not become popular in Rome until the first century or thereabouts. Early Christians became ...
The Roman Republic
... because it allowed only patricians to vote. The wealthy patrician class made up only 10 percent of the population of Rome. Yet, patricians ran the government. Most Romans were plebeians or “the common people.” As citizens, the plebeians paid taxes and served in the army. But they had little ...
... because it allowed only patricians to vote. The wealthy patrician class made up only 10 percent of the population of Rome. Yet, patricians ran the government. Most Romans were plebeians or “the common people.” As citizens, the plebeians paid taxes and served in the army. But they had little ...
Chapter 11 Bentley
... (1) What do modern scholars believe about the origins of Rome? (2) What political and economic changes occurred in Italy during the middle centuries of the first millennium? Who brought about these changes? (3) Describe the kingdom of Rome during this period. (4) What political changes occurred in R ...
... (1) What do modern scholars believe about the origins of Rome? (2) What political and economic changes occurred in Italy during the middle centuries of the first millennium? Who brought about these changes? (3) Describe the kingdom of Rome during this period. (4) What political changes occurred in R ...
Ancient Rome and Early Christianity
... Rome is growing… From a collection of hilltop villages to… A city that covered nearly 500 square miles FORUM heart of Roman political life Last king of Rome Tarquin the Proud ...
... Rome is growing… From a collection of hilltop villages to… A city that covered nearly 500 square miles FORUM heart of Roman political life Last king of Rome Tarquin the Proud ...
Education in ancient Rome

Education in Ancient Rome progressed from an informal, familial system of education in the early Republic to a tuition-based system during the late Republic and the Empire. The Roman education system was based on the Greek system – and many of the private tutors in the Roman system were Greek slaves or freedmen. Due to the extent of Rome's power, the methodology and curriculum used in Rome was copied in its provinces, and thereby proved the basis for education systems throughout later Western civilization. Organized education remained relatively rare, and there are few primary sources or accounts of the Roman educational process until the 2nd century AD. Due to the extensive power wielded by the paterfamilias over Roman families, the level and quality of education provided to Roman children varied drastically from family to family; nevertheless, Roman popular morality came eventually to expect fathers to have their children educated to some extent, and a complete advanced education was expected of any Roman who wished to enter politics.