11.2 From Edward N. Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
Gr. 7 CS: 17. Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were
... Gr. 7 CS: 17.Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were radical departures from monarchy and theocracy, influencing the structure and function of modern democratic governments. ...
... Gr. 7 CS: 17.Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were radical departures from monarchy and theocracy, influencing the structure and function of modern democratic governments. ...
Sources on M. Valerius Laevinus in the East Polybius 8.1: The
... the dead of the night, without the slightest noise or confusion, he got within the enemy's camp, which was so unguarded and open that it is credibly stated that more than a thousand men were inside the lines before they were detected, and if they had only refrained from using their swords they cou ...
... the dead of the night, without the slightest noise or confusion, he got within the enemy's camp, which was so unguarded and open that it is credibly stated that more than a thousand men were inside the lines before they were detected, and if they had only refrained from using their swords they cou ...
The Etruscans
... The Roman Military was no match for Etruscans. Etruscans A) Enforced compulsory military service training. B) Troops organized and experienced. Romans A) Summoned men only when necessary. B) Men had to supply own weapons. C) Only wealthy aristocrats. ...
... The Roman Military was no match for Etruscans. Etruscans A) Enforced compulsory military service training. B) Troops organized and experienced. Romans A) Summoned men only when necessary. B) Men had to supply own weapons. C) Only wealthy aristocrats. ...
Notes (Fill-in) - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Many prominent Romans were put to death following the ___________________________ (public identification and official condemnation of enemies of the state) of the Second Triumvirate as the three men tightened their ...
... Many prominent Romans were put to death following the ___________________________ (public identification and official condemnation of enemies of the state) of the Second Triumvirate as the three men tightened their ...
Understand geographic features that helped build roman civilizations
... 3 of the gospels said that Jesus’ followers hailed to him as a king when he journeyed to Jerusalem to celebrate the Jewish holy day of Passover. In that city a temple was bring run and Jesus publically criticized how it was being run. For Jesus’ criticism he was arrested and the Romans were to ...
... 3 of the gospels said that Jesus’ followers hailed to him as a king when he journeyed to Jerusalem to celebrate the Jewish holy day of Passover. In that city a temple was bring run and Jesus publically criticized how it was being run. For Jesus’ criticism he was arrested and the Romans were to ...
The Roman Republic
... monarchy. To avoid giving too much power to a single person, they came up with the idea of the republic. In this new form of government, all citizens who had the right to vote could participate in the selection of their leaders. Once a year, they elected two consuls. The individuals who won the ...
... monarchy. To avoid giving too much power to a single person, they came up with the idea of the republic. In this new form of government, all citizens who had the right to vote could participate in the selection of their leaders. Once a year, they elected two consuls. The individuals who won the ...
Pro Murena
... The View from the Top: the ‘Poor’ in Cicero’s Pro Murena Rome of Cicero’s day would have been crowded and poor (Harris 2011; Holleran 2011), but it was not bifurcated between an economic and political elite and the impoverished masses (Jongman 2007; Scheidel 2006). Cicero, however, thought it was. I ...
... The View from the Top: the ‘Poor’ in Cicero’s Pro Murena Rome of Cicero’s day would have been crowded and poor (Harris 2011; Holleran 2011), but it was not bifurcated between an economic and political elite and the impoverished masses (Jongman 2007; Scheidel 2006). Cicero, however, thought it was. I ...
Hist/Cult
... Po (= the Latin 'Padus') - considered more Roman and sophisticated; Gallia comata ('longhaired') = the rest of Gaul, considered less cultivated and thus known by the traditional Gallic long hair *months -originally 10 months, March - December, with gap between years -January and February: added by N ...
... Po (= the Latin 'Padus') - considered more Roman and sophisticated; Gallia comata ('longhaired') = the rest of Gaul, considered less cultivated and thus known by the traditional Gallic long hair *months -originally 10 months, March - December, with gap between years -January and February: added by N ...
History - Early Britain (Invasions)
... Many types of animals and plants were brought to Britain in Roman times. e.g. chestnut trees and chickens. Miles, feet, and inches. All these are Roman measurements. The Romans introduced Christianity to Britain. Many churches are still built using designs like a Roman Basilica. Reading and writing ...
... Many types of animals and plants were brought to Britain in Roman times. e.g. chestnut trees and chickens. Miles, feet, and inches. All these are Roman measurements. The Romans introduced Christianity to Britain. Many churches are still built using designs like a Roman Basilica. Reading and writing ...
camillus - latinata
... help the Veientians. It was also said that as soon as the twelve armies had driven the Romans away from the walls of Veii, they would march to Rome and destroy the city. The Romans were much alarmed by these reports, and they resolved that there should be a dictator. So the Senate appointed a dictat ...
... help the Veientians. It was also said that as soon as the twelve armies had driven the Romans away from the walls of Veii, they would march to Rome and destroy the city. The Romans were much alarmed by these reports, and they resolved that there should be a dictator. So the Senate appointed a dictat ...
The Age of Augustus I - CLIO History Journal
... o Gained support from the senatorial class, equestrians and the plebians o Worked with republican forms and did not advertise his supremacy ...
... o Gained support from the senatorial class, equestrians and the plebians o Worked with republican forms and did not advertise his supremacy ...
Roman Research Topics
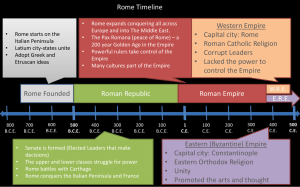
... Rome expands conquering all across Europe and into The Middle East. The Pax Romana (peace of Rome) – a 200 year Golden Age in the Empire Powerful rulers take control of the Empire Many cultures part of the Empire ...
... Rome expands conquering all across Europe and into The Middle East. The Pax Romana (peace of Rome) – a 200 year Golden Age in the Empire Powerful rulers take control of the Empire Many cultures part of the Empire ...
Punic Wars
... Roman army was pinned between the lake and a mountain range. The mist rising from the water prevented the Romans from realizing that they were heading ...
... Roman army was pinned between the lake and a mountain range. The mist rising from the water prevented the Romans from realizing that they were heading ...
The Roman Baths Next stop, the Baths! The ancient Romans might
... The baths were packed. The people loved them. At one time, there were as many as 900 public baths in ancient Rome. Small ones held about 300 people, and the big ones held 1500 people or more! Some Roman hospitals even had their own bathhouses. A trip to the bath was a very important part of ancient ...
... The baths were packed. The people loved them. At one time, there were as many as 900 public baths in ancient Rome. Small ones held about 300 people, and the big ones held 1500 people or more! Some Roman hospitals even had their own bathhouses. A trip to the bath was a very important part of ancient ...
James B. Tschen
... of the city by romulus. rome, however, was one tiny village among many italic settlements and in its earliest days was overshadowed by more powerful neighbors, such as the etruscans. from these obscure origins, rome came to rule not only italy but also the mediterranean, europe, parts of southwest A ...
... of the city by romulus. rome, however, was one tiny village among many italic settlements and in its earliest days was overshadowed by more powerful neighbors, such as the etruscans. from these obscure origins, rome came to rule not only italy but also the mediterranean, europe, parts of southwest A ...
First Punic War
... they boarded from all directions but if they charged with the prow, they attacked by passing over the gangway of the raven itself two abreast. [At the battle of Mylae in 260,] when the ships that came into collision were in every case held fast by the machines, and the Roman crews boarded by means o ...
... they boarded from all directions but if they charged with the prow, they attacked by passing over the gangway of the raven itself two abreast. [At the battle of Mylae in 260,] when the ships that came into collision were in every case held fast by the machines, and the Roman crews boarded by means o ...
word document - Timetrail
... organisations and individuals, including the Royal Airforce, The Potato Board, Warwickshire Museum. The collection is held at the Warwickshire Sites and Monuments Record. West Midlands Archaeological News Sheet, a publication that was produced each year, this later became West Midlands Archaeology. ...
... organisations and individuals, including the Royal Airforce, The Potato Board, Warwickshire Museum. The collection is held at the Warwickshire Sites and Monuments Record. West Midlands Archaeological News Sheet, a publication that was produced each year, this later became West Midlands Archaeology. ...
February 1, 2012
... ~ Every five years, each male Roman citizen had to register in Rome for the census. In this he had to declare his family, wife, children, slaves and riches. Should he fail to do this, his possessions would be confiscated and he would be sold into slavery. ~ What did most mother and wives do? How do ...
... ~ Every five years, each male Roman citizen had to register in Rome for the census. In this he had to declare his family, wife, children, slaves and riches. Should he fail to do this, his possessions would be confiscated and he would be sold into slavery. ~ What did most mother and wives do? How do ...
Chapter 33 – The Rise of the Roman Republic What were the
... Rome was now a republic, but the patricians held all the power. They made sure that only they could be part of the government. Only they could become senators or consuls. Plebeians had to obey their decisions. Because laws were not written down, patricians often changed or interpreted the laws to be ...
... Rome was now a republic, but the patricians held all the power. They made sure that only they could be part of the government. Only they could become senators or consuls. Plebeians had to obey their decisions. Because laws were not written down, patricians often changed or interpreted the laws to be ...