World History: Patterns of Interaction
... Different groups struggle for power in early Roman Republic Patricians—wealthy landowning class that holds most of the power Plebeians—artisans, merchants, and farmers; can vote, can’t rule Tribunes—elected representatives protect plebeians’ political rights ...
... Different groups struggle for power in early Roman Republic Patricians—wealthy landowning class that holds most of the power Plebeians—artisans, merchants, and farmers; can vote, can’t rule Tribunes—elected representatives protect plebeians’ political rights ...
analysis packet - cloudfront.net
... Military- reduced the size of the army but created a permanent, professional army of the best soldiers and a permanent navy =>Territorial expansion /Purpose of expansion was really to consolidate boundaries and ensure the peace Pax Romana ensued because Rome stopped seeking territories but was s ...
... Military- reduced the size of the army but created a permanent, professional army of the best soldiers and a permanent navy =>Territorial expansion /Purpose of expansion was really to consolidate boundaries and ensure the peace Pax Romana ensued because Rome stopped seeking territories but was s ...
Answer in complete sentences
... Much of the g______________ of R______ was created with *s________ labor; in 73BC, one Roman slave r______________ and built an army that caused as great deal of *d__st__u__t__on. Spartacus was forced to participate in gladiatorial games, but he escaped and built an army of soldiers from the slaves ...
... Much of the g______________ of R______ was created with *s________ labor; in 73BC, one Roman slave r______________ and built an army that caused as great deal of *d__st__u__t__on. Spartacus was forced to participate in gladiatorial games, but he escaped and built an army of soldiers from the slaves ...
How revolutionary were the military reforms of Gaius Marius?
... left for Africa with only “a considerably greater contingent than had been authorised.”7 – the proletarii did not become fully integrated into the army until well after the shocking defeat at Arausio (105 BC). Much debate has centred on Marius’s personal motives for extending the levy. Sallust holds ...
... left for Africa with only “a considerably greater contingent than had been authorised.”7 – the proletarii did not become fully integrated into the army until well after the shocking defeat at Arausio (105 BC). Much debate has centred on Marius’s personal motives for extending the levy. Sallust holds ...
File
... with his life. • While in Egypt his relationship with Cleopatra went far beyond a professional or political one. In the years he spent in Egypt they had several children. • Antony’s absence from Rome left him unable to adeptly battle the propaganda spread by Octavian that Antony was being unmanly, u ...
... with his life. • While in Egypt his relationship with Cleopatra went far beyond a professional or political one. In the years he spent in Egypt they had several children. • Antony’s absence from Rome left him unable to adeptly battle the propaganda spread by Octavian that Antony was being unmanly, u ...
Year 4: The Roman Empire – Roman Coins
... the invasion of the Romans, Britain was ruled by Celts. There were no roads or towns and most people were farmers, living in thatched houses made from wood. Between around 300 BC and AD 200, the people of Rome built a huge empire. It included all of the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and wa ...
... the invasion of the Romans, Britain was ruled by Celts. There were no roads or towns and most people were farmers, living in thatched houses made from wood. Between around 300 BC and AD 200, the people of Rome built a huge empire. It included all of the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and wa ...
The Calculus of Conquests: The Decline and Fall of the Returns to
... tax collections from the foreign provinces, and both the tax collectors and Roman officials engaged in wholesale extortion (Levy 1967, 60–65). Roman institutions determined the disposition of spoils and rewarded the abilities that enabled Rome to excel in warfare. Conquering generals had sole discre ...
... tax collections from the foreign provinces, and both the tax collectors and Roman officials engaged in wholesale extortion (Levy 1967, 60–65). Roman institutions determined the disposition of spoils and rewarded the abilities that enabled Rome to excel in warfare. Conquering generals had sole discre ...
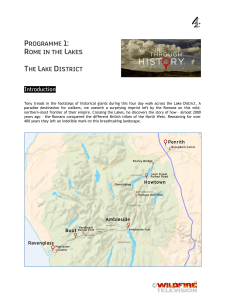
Rome in the Lakes walking guide
... again and follow this road round to the spectacular Mayburgh Henge, cared for by English Heritage. ...
... again and follow this road round to the spectacular Mayburgh Henge, cared for by English Heritage. ...
Background for Shakespeare`s Julius Caesar
... “In theory”, the tribunes could check the power of senators and protect the rights of ordinary citizens. They had “the power” to veto any Senate decree and keep it from becoming law. Tribunes were also immune from arrest. This prevented the patricians from silencing a tribune by throwing him in jail ...
... “In theory”, the tribunes could check the power of senators and protect the rights of ordinary citizens. They had “the power” to veto any Senate decree and keep it from becoming law. Tribunes were also immune from arrest. This prevented the patricians from silencing a tribune by throwing him in jail ...
The development of Roman mailed cavalry
... supply of Roman cavalry horses is contained in Germanicus' complaint that Gaul had been exhausted by supplying horses (Tacitus, Ann. 2, 5). From this we may infer that in A.D. 16 Gaul was a principal western source of cavalry horses, but it is not at all certain that these Gallic horses were suffici ...
... supply of Roman cavalry horses is contained in Germanicus' complaint that Gaul had been exhausted by supplying horses (Tacitus, Ann. 2, 5). From this we may infer that in A.D. 16 Gaul was a principal western source of cavalry horses, but it is not at all certain that these Gallic horses were suffici ...
Julius Caesar
... An introduction to Julius Caesar • Deals with Roman generals and the life and times of ancient Rome • It is a political play about a general who would be king, but who, because of his own PRIDE and AMBITION, meets an untimely death ...
... An introduction to Julius Caesar • Deals with Roman generals and the life and times of ancient Rome • It is a political play about a general who would be king, but who, because of his own PRIDE and AMBITION, meets an untimely death ...
Christians against Christians: The Anti
... From the same period we also have the so-called First Epistle of Peter to the brethren living in Pontus, Galatia, Cappadocia, Asia and Bithynia. This letter, written in the name of the apostle, is almost certainly pseudonymous, but the suggestion that it was sent from Babylon (i.e. Rome) to five dis ...
... From the same period we also have the so-called First Epistle of Peter to the brethren living in Pontus, Galatia, Cappadocia, Asia and Bithynia. This letter, written in the name of the apostle, is almost certainly pseudonymous, but the suggestion that it was sent from Babylon (i.e. Rome) to five dis ...
Roman Coins as Historical Evidence
... Alfoldi is anxious to show that Roman belief in their Trojan ancestry is not simply a Greek invention, prompted by the normal Greek speculation on the origins of non-Greeks, or a late literary invention designed to denegrate the Romans as barbarians or flatter them as descendants of Homeric heroes. ...
... Alfoldi is anxious to show that Roman belief in their Trojan ancestry is not simply a Greek invention, prompted by the normal Greek speculation on the origins of non-Greeks, or a late literary invention designed to denegrate the Romans as barbarians or flatter them as descendants of Homeric heroes. ...
BENJAMIN PROUST
... carving. The bust dates to the early Roman Imperial period, as the skilful carving still retains a softness more characteristic of earlier Hellenistic sculptures, rather than the stiffer looking carving o ...
... carving. The bust dates to the early Roman Imperial period, as the skilful carving still retains a softness more characteristic of earlier Hellenistic sculptures, rather than the stiffer looking carving o ...
Democracy and Civic Participation in Greek Cities under Roman
... (…) About magistracies and about sanctuaries and revenues, that they [scil. the Thisbeans who remained in Rome’s friendship] might have control of them; concerning this matter, it was resolved thus: that those who entered our friendship before Gaius Lucretius brought up his army to the city of Thisb ...
... (…) About magistracies and about sanctuaries and revenues, that they [scil. the Thisbeans who remained in Rome’s friendship] might have control of them; concerning this matter, it was resolved thus: that those who entered our friendship before Gaius Lucretius brought up his army to the city of Thisb ...
Julius Caesar
... the Rubicon River and seized control of Italy. Pompey, who had been a friend of Caesar, was forced to flee to Greece with his army. Caesar kept chasing him so Pompey went to Egypt. It was there that he was killed and his decapitated head was given to Caesar by the ten year old king of Egypt, Ptolemy ...
... the Rubicon River and seized control of Italy. Pompey, who had been a friend of Caesar, was forced to flee to Greece with his army. Caesar kept chasing him so Pompey went to Egypt. It was there that he was killed and his decapitated head was given to Caesar by the ten year old king of Egypt, Ptolemy ...
Rome`s Internal Crisis
... On January 13, 27 B.C., Octavian appeared before the Roman Senate and laid down his supreme powers. It was at this time that Octavian took the name of Augustus Caesar. The ...
... On January 13, 27 B.C., Octavian appeared before the Roman Senate and laid down his supreme powers. It was at this time that Octavian took the name of Augustus Caesar. The ...
Ancient Rome`s `JFK Moment`
... homicide the tests of means, motive and opportunity. So was it assassination? Powell casts doubt on the traditionally accepted view. “The evidence does not support the conclusion it was murder,” says Powell. “It may have been an accidental death, caused by a natural disease, or perhaps made fatal by ...
... homicide the tests of means, motive and opportunity. So was it assassination? Powell casts doubt on the traditionally accepted view. “The evidence does not support the conclusion it was murder,” says Powell. “It may have been an accidental death, caused by a natural disease, or perhaps made fatal by ...
Second Punic War Background Guide
... being structured in the manipular, or Polybian, form. During the Regal Era, and even well into the Republican Era, the Roman Army was not very strictly structured. Troops were levied only when needed to fight in wars, and were very loosely organized into roughly 100-man groups called centuriae . ...
... being structured in the manipular, or Polybian, form. During the Regal Era, and even well into the Republican Era, the Roman Army was not very strictly structured. Troops were levied only when needed to fight in wars, and were very loosely organized into roughly 100-man groups called centuriae . ...