(Accredited) - GCSE Ancient History - J198
... This component has two elements: a period study and a source-based depth study. Learners must study the compulsory period study plus one of the three source-based depth studies. Each of the depth studies has a link to the period study, and will ensure that learners do not have a narrow approach to t ...
... This component has two elements: a period study and a source-based depth study. Learners must study the compulsory period study plus one of the three source-based depth studies. Each of the depth studies has a link to the period study, and will ensure that learners do not have a narrow approach to t ...
The Senatus Consultum Ultimum and its Relation to
... reigning consuls) to resolve a social or political crisis through military means, often for the sake of expediency as well as suppression of sedition. The function of the SCU, to this end, was to resolve crises without damage to the authority of the Senate. Most importantly, the decree allowed for r ...
... reigning consuls) to resolve a social or political crisis through military means, often for the sake of expediency as well as suppression of sedition. The function of the SCU, to this end, was to resolve crises without damage to the authority of the Senate. Most importantly, the decree allowed for r ...
ROME, 63 - Rackcdn.com
... Sallust continued, “... and it was just down that same street that, exactly 350 years later, the consul Opimius caved in the skull of the tribune Gaius Gracchus. History moves in cycles, as they say. As I was finishing my Massic wine (a foul vintage; not like the sweet Rhaetic that you are serving t ...
... Sallust continued, “... and it was just down that same street that, exactly 350 years later, the consul Opimius caved in the skull of the tribune Gaius Gracchus. History moves in cycles, as they say. As I was finishing my Massic wine (a foul vintage; not like the sweet Rhaetic that you are serving t ...
Dissertation - Emory University
... but literary and archaeological sources confirm that they were erected on the exterior walls of tombs. Group reliefs decline in popularity by the Tiberian period, when smaller funerary altars or cinerary urns with figural decoration become fashionable. These monuments closely follow contemporary typ ...
... but literary and archaeological sources confirm that they were erected on the exterior walls of tombs. Group reliefs decline in popularity by the Tiberian period, when smaller funerary altars or cinerary urns with figural decoration become fashionable. These monuments closely follow contemporary typ ...
Document
... On the other side, the matter is complicated by the fact that there are great differences between ‘great’, ‘middle’ and ‘small’ poleis, which affect their level of statehood, and even the question whether they may be called states at all. There can be no doubt whether a certain Greek community is a ...
... On the other side, the matter is complicated by the fact that there are great differences between ‘great’, ‘middle’ and ‘small’ poleis, which affect their level of statehood, and even the question whether they may be called states at all. There can be no doubt whether a certain Greek community is a ...
Polis - Sociostudies.org
... On the other side, the matter is complicated by the fact that there are great differences between ‘great’, ‘middle’ and ‘small’ poleis, which affect their level of statehood, and even the question whether they may be called states at all. There can be no doubt whether a certain Greek community is a ...
... On the other side, the matter is complicated by the fact that there are great differences between ‘great’, ‘middle’ and ‘small’ poleis, which affect their level of statehood, and even the question whether they may be called states at all. There can be no doubt whether a certain Greek community is a ...
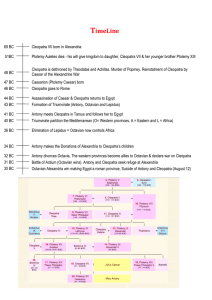
Cleopatra
... Married sister, Arsinoe II and associated her with the kingship and also became a god - Initiated custom of Brother-Sister marriage Ptolemy XII Auletes – Cleopatra’s Father Heavily disliked by Alexandrians and Egyptians due to heavy tax collection and sending huge sums of money to Rome for their ...
... Married sister, Arsinoe II and associated her with the kingship and also became a god - Initiated custom of Brother-Sister marriage Ptolemy XII Auletes – Cleopatra’s Father Heavily disliked by Alexandrians and Egyptians due to heavy tax collection and sending huge sums of money to Rome for their ...
Jupiter`s Legacy: The Symbol of the Eagle and Thunderbolt in
... The thunderbolt and the eagle, the armament and armour-bearer of Jupiter – these symbols had profound cultural significance to the ancients. At first one may think that what was sacred for the Romans has no bearing on modern society, but in truth these icons retain much of their meaning and importan ...
... The thunderbolt and the eagle, the armament and armour-bearer of Jupiter – these symbols had profound cultural significance to the ancients. At first one may think that what was sacred for the Romans has no bearing on modern society, but in truth these icons retain much of their meaning and importan ...
Rome`s vestal virgins: public spectacle and society
... discussion of the origin of the goddess Vesta and her priesthood and how they were crystallized in Roman religion provides an historical context for the Vestals and further emphasizes their importance to Roman society. The second chapter, entitled “Induction and Appearance: The Vestal as a Visual Ot ...
... discussion of the origin of the goddess Vesta and her priesthood and how they were crystallized in Roman religion provides an historical context for the Vestals and further emphasizes their importance to Roman society. The second chapter, entitled “Induction and Appearance: The Vestal as a Visual Ot ...
Slide 1
... The Senate elected, then re-elected Caesar consul, breaking the Roman tradition that a consul serve only one year. While in power, Caesar settled 80,000 of his soldiers in colonies, built buildings and monuments throughout the city, and reformed the calendar. When Caesar came to power, the calendar ...
... The Senate elected, then re-elected Caesar consul, breaking the Roman tradition that a consul serve only one year. While in power, Caesar settled 80,000 of his soldiers in colonies, built buildings and monuments throughout the city, and reformed the calendar. When Caesar came to power, the calendar ...
The Fall of the Roman Republic
... presided over meetings of the concilium plebis. The decisions of this body (plebiscita) bound the plebs and from early times could, if the consuls agreed, be passed through the state’s decisionmaking machinery to become law. The tribunes were to become extremely significant in the factional in-fight ...
... presided over meetings of the concilium plebis. The decisions of this body (plebiscita) bound the plebs and from early times could, if the consuls agreed, be passed through the state’s decisionmaking machinery to become law. The tribunes were to become extremely significant in the factional in-fight ...
Julius Caesar - Stamford High School
... It is impossible to tell if Caesar wished to destroy the last remnants of the old Republic and replace it with a formal autocracy or whether he merely intended to become the leading citizen—although one without rivals—in the Roman world. In the end, the result was the same, for Caesar for a brief ti ...
... It is impossible to tell if Caesar wished to destroy the last remnants of the old Republic and replace it with a formal autocracy or whether he merely intended to become the leading citizen—although one without rivals—in the Roman world. In the end, the result was the same, for Caesar for a brief ti ...
View - OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center
... here may be understood as a politically and culturally normative sign. Metonymy therefore proposes a greater level of abstraction and often a hierarchy between its terms. Synecdoche is the part used for the whole or the whole for the part. ...
... here may be understood as a politically and culturally normative sign. Metonymy therefore proposes a greater level of abstraction and often a hierarchy between its terms. Synecdoche is the part used for the whole or the whole for the part. ...
Jupiter`s Legacy: The Symbol of the Eagle and Thunderbolt in
... The thunderbolt and the eagle, the armament and armour-bearer of Jupiter – these symbols had profound cultural significance to the ancients. At first one may think that what was sacred for the Romans has no bearing on modern society, but in truth these icons retain much of their meaning and importan ...
... The thunderbolt and the eagle, the armament and armour-bearer of Jupiter – these symbols had profound cultural significance to the ancients. At first one may think that what was sacred for the Romans has no bearing on modern society, but in truth these icons retain much of their meaning and importan ...
Specimen - A2-Type
... known in English as Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, the Sun, Venus, Mercury and the Moon, each had an hour of the day assigned to them, and the planet which was regent during the first hour of any day of the week gave its name to that day. During the 1st and 2nd century, the week of seven days was introduced ...
... known in English as Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, the Sun, Venus, Mercury and the Moon, each had an hour of the day assigned to them, and the planet which was regent during the first hour of any day of the week gave its name to that day. During the 1st and 2nd century, the week of seven days was introduced ...
Why did they do that? Takes on the PUNIC WARS by David E Woody
... The Romans, meanwhile, had some problems of their own. One of these I call the Leadership Factor. Whereas Hannibal will be the leader of Carthaginian forces for the entirety of this conflict, the Romans would have many different leaders, of varying ability levels. Another Roman problem, was the Spec ...
... The Romans, meanwhile, had some problems of their own. One of these I call the Leadership Factor. Whereas Hannibal will be the leader of Carthaginian forces for the entirety of this conflict, the Romans would have many different leaders, of varying ability levels. Another Roman problem, was the Spec ...
sample
... retired from the camp of Cinna to the ancestral lands in Picenum after threats were made against his life. He did this so discreetly that it was soon widely rumoured that Cinna had had him murdered. According to Plutarch (Pomp. 5.1), it was this suspicion that gave rise to the mutiny that ended in C ...
... retired from the camp of Cinna to the ancestral lands in Picenum after threats were made against his life. He did this so discreetly that it was soon widely rumoured that Cinna had had him murdered. According to Plutarch (Pomp. 5.1), it was this suspicion that gave rise to the mutiny that ended in C ...
Caesar`s Rule and Caesar`s Death : Who Lost? Who Gained?
... political and social turbulence. Within less than two decades of Julius Caesar’s murder these effects would combine to emasculate all surviving forms of Republican government, which became subservient to one man who really held the power; Caesar’s great nephew and designated heir, Octavian. Rome had ...
... political and social turbulence. Within less than two decades of Julius Caesar’s murder these effects would combine to emasculate all surviving forms of Republican government, which became subservient to one man who really held the power; Caesar’s great nephew and designated heir, Octavian. Rome had ...
Marcus Tullius Cicero
... have the Gauls join in their rebellion, but the Gauls wanted little do with it and word reached Cicero of the conspirator's proposition. P. Cornelius Lentulus Sura was forced to admit to his own participation in the plot and a great debate over the punishment ensued. Gaius Julius Caesar, the praetor ...
... have the Gauls join in their rebellion, but the Gauls wanted little do with it and word reached Cicero of the conspirator's proposition. P. Cornelius Lentulus Sura was forced to admit to his own participation in the plot and a great debate over the punishment ensued. Gaius Julius Caesar, the praetor ...
sample
... why the Gauls repeatedly rebelled against his rule, even being willing to invite aid from the far side of the Rhine, and why his Aedui and Remi allies continued to intercede with him on the behalf of defeated rebels. Worse, he masks the war’s horrendous cost in human life and suffering. This is not ...
... why the Gauls repeatedly rebelled against his rule, even being willing to invite aid from the far side of the Rhine, and why his Aedui and Remi allies continued to intercede with him on the behalf of defeated rebels. Worse, he masks the war’s horrendous cost in human life and suffering. This is not ...