Genome Control - University of California, Los Angeles
... – mRNA stability controlled by part of sequence near 3’ ...
... – mRNA stability controlled by part of sequence near 3’ ...
Introduction to Next-Generation Sequence analysis
... – A complete set of chromosomes from a cell that has been photographed during cell division and arranged by size and shape in a standard order ...
... – A complete set of chromosomes from a cell that has been photographed during cell division and arranged by size and shape in a standard order ...
Genetic Engineering
... These are enzymes that scientists use in genetic engineering The enzyme recognizes a site on the DNA which is made of 4 to 6 bases. The enzyme will cut DNA at these recognition sites. These recognition sites are palindromes. Cutting DNA at recognition sites is the first step in many types of DNA tec ...
... These are enzymes that scientists use in genetic engineering The enzyme recognizes a site on the DNA which is made of 4 to 6 bases. The enzyme will cut DNA at these recognition sites. These recognition sites are palindromes. Cutting DNA at recognition sites is the first step in many types of DNA tec ...
9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics KEY CONCEPT Entire genomes are sequenced, studied, and compared.
... – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
... – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
Parts of a Cell
... filled with chapters made of letters. cell is a ______. nucleus Inside a ___ chromosomes nucleus Inside the ______are ...
... filled with chapters made of letters. cell is a ______. nucleus Inside a ___ chromosomes nucleus Inside the ______are ...
Genetic Exchange - Pennsylvania State University
... • During phage replication and assembly, capsids may package chromosomal or plasmid DNA by mistake. • When transferred to a new host it may recombine. ...
... • During phage replication and assembly, capsids may package chromosomal or plasmid DNA by mistake. • When transferred to a new host it may recombine. ...
NAME CH11 In class assignment Due 2/18/14 Across 1. Initials of
... _____4_____ Bacterium inserts plasmid DNA into a plant cell’s DNA. ____1____ Restrictive enzymes cut complimentary sections on both the Bt gene and a plasmid 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is ...
... _____4_____ Bacterium inserts plasmid DNA into a plant cell’s DNA. ____1____ Restrictive enzymes cut complimentary sections on both the Bt gene and a plasmid 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
Table 3.
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
Slide 1 - tacademy.ca
... • Down Syndrome – caused by the presence of all or part of a 21st chromosome • Turner Syndrome – caused by one or many parts of the X chromosome remaining absent during cell formation. Specific only to females. • Cystic Fibrosis – Number one most common fatally genetic disease. Caused by a single ge ...
... • Down Syndrome – caused by the presence of all or part of a 21st chromosome • Turner Syndrome – caused by one or many parts of the X chromosome remaining absent during cell formation. Specific only to females. • Cystic Fibrosis – Number one most common fatally genetic disease. Caused by a single ge ...
Modes of Prokaryotic Genetic Exchange
... a. Specialized transduction- only introduces new genes adjacent to integration site of virus (gal and bio) b. Generalized transduction- can introduce any part of host genome ...
... a. Specialized transduction- only introduces new genes adjacent to integration site of virus (gal and bio) b. Generalized transduction- can introduce any part of host genome ...
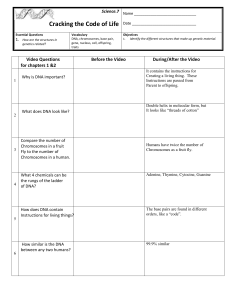
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Humans have twice the number of Chromosomes as a fruit fly. ...
... Humans have twice the number of Chromosomes as a fruit fly. ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology and Genomics
... 20.6 The public consortium followed a hierarchy of three stages: (1) genetic (linkage) mapping that established about 200 markers/chromosome; (2) physical mapping that clones and ordered smaller and smaller overlapping fragments (using YAC or BAC vectors for cloning the large fragments); and (3) DNA ...
... 20.6 The public consortium followed a hierarchy of three stages: (1) genetic (linkage) mapping that established about 200 markers/chromosome; (2) physical mapping that clones and ordered smaller and smaller overlapping fragments (using YAC or BAC vectors for cloning the large fragments); and (3) DNA ...
Slide 1 - Montville.net
... Take out the copied genes in plasmid from the bacteria. Take out the copied genes from the plasmids. Put the gene in another organism’s genomic DNA Reason #2 – Use to make a protein like a hormone. Gene in the plasmid can be turned on by the bacteria or yeast cell to make a protein. Extract the prot ...
... Take out the copied genes in plasmid from the bacteria. Take out the copied genes from the plasmids. Put the gene in another organism’s genomic DNA Reason #2 – Use to make a protein like a hormone. Gene in the plasmid can be turned on by the bacteria or yeast cell to make a protein. Extract the prot ...
Genetic Engineering
... cut these repeating sequences into fragments that vary in length. These pieces of different lengths are called RFLPrestriction fragment length polymorphisms This makes different numbers and different sized pieces for every individual human- a one-of-a-kind DNA fingerprint ...
... cut these repeating sequences into fragments that vary in length. These pieces of different lengths are called RFLPrestriction fragment length polymorphisms This makes different numbers and different sized pieces for every individual human- a one-of-a-kind DNA fingerprint ...
Gene Technology
... – Nucleotide sequences are complementary to the gene of interest • Southern blot – used to indicate certain fragments that hybridized with a probe. ...
... – Nucleotide sequences are complementary to the gene of interest • Southern blot – used to indicate certain fragments that hybridized with a probe. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.