Bio 309F
... 29. Why have geneticists been able to identify several genes linked to the X chromosome in humans? A. the X chromosome is much easier to identify than the other chromosomes. B. the X chromosome is one of the smaller chromosomes, therefore easier to study C. only dominant genes are localized on the X ...
... 29. Why have geneticists been able to identify several genes linked to the X chromosome in humans? A. the X chromosome is much easier to identify than the other chromosomes. B. the X chromosome is one of the smaller chromosomes, therefore easier to study C. only dominant genes are localized on the X ...
Molecular Characterization of NADH-Dependent
... We therefore screened a second cDNA library by plaque hybridization using the 1.7-kb insert. A 765-bp BamHl fragment from the 5’end of the longest resulting cDNA (2.7 kb) was then used as a hybridization probe to screen a third cDNA library that had been prepared using a reverse transcriptase lackin ...
... We therefore screened a second cDNA library by plaque hybridization using the 1.7-kb insert. A 765-bp BamHl fragment from the 5’end of the longest resulting cDNA (2.7 kb) was then used as a hybridization probe to screen a third cDNA library that had been prepared using a reverse transcriptase lackin ...
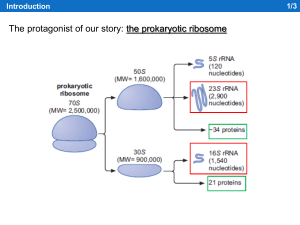
RiboT
... the Pro166 codon of SecM. Translation arrest ensues because specific interactions of the SecM nascent chain with the ribosomal exit tunnel impair the PTC (Peptydil-Trasferase Center) function, preventing the transfer of the 165-amino-acid long peptide to the ...
... the Pro166 codon of SecM. Translation arrest ensues because specific interactions of the SecM nascent chain with the ribosomal exit tunnel impair the PTC (Peptydil-Trasferase Center) function, preventing the transfer of the 165-amino-acid long peptide to the ...
Four types of controls were performed to support these
... mutator phenotype (mutS, mutL, mutH, uvrD, mutT and mutY) were amplified ...
... mutator phenotype (mutS, mutL, mutH, uvrD, mutT and mutY) were amplified ...
Protein and DNA sequence determinants of
... resulting artificially randomized proteome-temperature combinations. The distribution of the maximum correlation coefficient Rmax obtained in 1000 such reshufflings follows a Gaussian shape centered around=0.344, σ=0.060. Therefore, the probability to
find the observed correlation of R=0.93 a ...
... resulting artificially randomized proteome-temperature combinations. The distribution of the maximum correlation coefficient Rmax obtained in 1000 such reshufflings follows a Gaussian shape centered around
Origin and evolution of Y chromosomes: Drosophila tales
... mentioning a caveat. Ideally, the complete gene set of the Y chromosomes in the 12 species should be available before starting a comparative analysis, similar to the approach used (at least approximately) for analysing the euchromatic portion of the other chromosomes. However, given the notorious di ...
... mentioning a caveat. Ideally, the complete gene set of the Y chromosomes in the 12 species should be available before starting a comparative analysis, similar to the approach used (at least approximately) for analysing the euchromatic portion of the other chromosomes. However, given the notorious di ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiologyy
... the genera Agrobacterium, Pantoea, and Rhizobium and about half of the erwinias and pseudomonads tested synthesized detectable levels of AHLs. By contrast, only a few AHL producers could be identified among Xanthomonas sp. isolates. More recently, Elasri et al. (14) screened 137 soilborne and planta ...
... the genera Agrobacterium, Pantoea, and Rhizobium and about half of the erwinias and pseudomonads tested synthesized detectable levels of AHLs. By contrast, only a few AHL producers could be identified among Xanthomonas sp. isolates. More recently, Elasri et al. (14) screened 137 soilborne and planta ...
Protein sequence comparisons show that the
... be accounted for by their lack of Motif 3. Similar conclusions on relatedness were taken from exercises in constructing similarity trees (not shown). This set of sequence comparisons was completed by an unexpected finding: the absent herpesvirus Motif 3 is present in the N-terminal halves of the her ...
... be accounted for by their lack of Motif 3. Similar conclusions on relatedness were taken from exercises in constructing similarity trees (not shown). This set of sequence comparisons was completed by an unexpected finding: the absent herpesvirus Motif 3 is present in the N-terminal halves of the her ...
Protein A gene expression is regulated by DNA supercoiling which
... repressed by high salt concentrations (1 M NaCl) and as high osmolarity alters the degree of plasmid DNA supercoiling, we looked at the effect of changing the degree of DNA supercoiling on protein A gene expression. We first determined the concentration of novobiocin, a DNA gyrase inhibitor, which r ...
... repressed by high salt concentrations (1 M NaCl) and as high osmolarity alters the degree of plasmid DNA supercoiling, we looked at the effect of changing the degree of DNA supercoiling on protein A gene expression. We first determined the concentration of novobiocin, a DNA gyrase inhibitor, which r ...
Patterns of prokaryotic lateral gene transfers affecting
... A range of different methods have been used to detect LGTs, with varying degrees of agreement between methods [19]. Detailed phylogenetic analyses are probably the most rigorous approach [19], but can be time-consuming for large numbers of genes, requiring a trade-off between analytical sophisticati ...
... A range of different methods have been used to detect LGTs, with varying degrees of agreement between methods [19]. Detailed phylogenetic analyses are probably the most rigorous approach [19], but can be time-consuming for large numbers of genes, requiring a trade-off between analytical sophisticati ...
Chapter 8
... how genes are replicated • Chromosomes: structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information; the chromosomes contain genes • Genes: segments of DNA that encode functional products, usually proteins • Genome: all the genetic information in a cell ...
... how genes are replicated • Chromosomes: structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information; the chromosomes contain genes • Genes: segments of DNA that encode functional products, usually proteins • Genome: all the genetic information in a cell ...
Genetics of Down Syndrome
... Today, a necessary requirement in diagnostic investigations is a high differentiation of the euchromatin (usually 550 bands per genome). By that way, structural aberrations of chromosome 21 can be safely detected microscopically, starting with a minimal length of 5 Mb. In the 1980s, fluorescence-in- ...
... Today, a necessary requirement in diagnostic investigations is a high differentiation of the euchromatin (usually 550 bands per genome). By that way, structural aberrations of chromosome 21 can be safely detected microscopically, starting with a minimal length of 5 Mb. In the 1980s, fluorescence-in- ...
Identification of markers tightly linked to tomato yellow
... outbreak, but the majority of these defensive methods are not effective. Therefore, breeding for resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl disease (TYLCD) is the most advantageous approach to controlling the damage caused by this viral disease (Castro et al., 2007; Laterrot, 1992), but no resistance has ...
... outbreak, but the majority of these defensive methods are not effective. Therefore, breeding for resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl disease (TYLCD) is the most advantageous approach to controlling the damage caused by this viral disease (Castro et al., 2007; Laterrot, 1992), but no resistance has ...
Lecture 3 - Montefiore Institute ULg
... Surprises accompanying the sequence publication included: - the relatively small number of human genes, perhaps as few as ...
... Surprises accompanying the sequence publication included: - the relatively small number of human genes, perhaps as few as ...
Sleeping Beauty - Weber State University
... these putative functional domains was of key importance during the reactivation procedure. The first step of reactivating the transposase gene was to restore an open reading frame (SB1 through SB3 in Figure 1B) from bits and pieces of two inactive TcEs from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and a single ...
... these putative functional domains was of key importance during the reactivation procedure. The first step of reactivating the transposase gene was to restore an open reading frame (SB1 through SB3 in Figure 1B) from bits and pieces of two inactive TcEs from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and a single ...
rec-mediated recombinational hot spot activity in bacteriophage
... (1969) ;the extent of the b1319 and b1453 deletions is determined from the following evidence: b1319 and b1453 are missing 12% and 11% of the X DNA content, respectively, as judged from the intrinsic density of phage particles; both test as Spi-, Fec-, and int-; in addition, 1319 is apparently cZZZ- ...
... (1969) ;the extent of the b1319 and b1453 deletions is determined from the following evidence: b1319 and b1453 are missing 12% and 11% of the X DNA content, respectively, as judged from the intrinsic density of phage particles; both test as Spi-, Fec-, and int-; in addition, 1319 is apparently cZZZ- ...
Document
... Analyzing vertebrate genomes requires rapid mRNA/DNA and crossspecies protein alignments. BLAT (the BLAST-like alignment tool) was developed by Jim Kent from UCSC. It is more accurate and 500 times faster than popular existing tools such as BLAST for mRNA/DNA alignments and 50 times faster for prote ...
... Analyzing vertebrate genomes requires rapid mRNA/DNA and crossspecies protein alignments. BLAT (the BLAST-like alignment tool) was developed by Jim Kent from UCSC. It is more accurate and 500 times faster than popular existing tools such as BLAST for mRNA/DNA alignments and 50 times faster for prote ...
Engineering a tRNA and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase for the site
... Choice of tRNA-Aminoacyl Synthetase System. The original strategy that was used to generate an orthogonal tRNA for our in vitro mutagenesis methodology involved the use of the yeast phenylalanyl suppressor tRNA, which was known not to be a substrate for any E. coli aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (17). On ...
... Choice of tRNA-Aminoacyl Synthetase System. The original strategy that was used to generate an orthogonal tRNA for our in vitro mutagenesis methodology involved the use of the yeast phenylalanyl suppressor tRNA, which was known not to be a substrate for any E. coli aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (17). On ...
Structure of a Plasmodium yoelii gene
... at 45°C using radiolabeled M15. The blots were washed with 6x standard saline citrate (SSC: lxSSC is 0 . 1 5 M NaCl, 0.015M sodium citrate) for 4 x 30 min at 45 °C, dried, and exposed to Kodak X-Omat AR films at -70°C with intensifying screens. Films were developed in an automated Kodak processor. I ...
... at 45°C using radiolabeled M15. The blots were washed with 6x standard saline citrate (SSC: lxSSC is 0 . 1 5 M NaCl, 0.015M sodium citrate) for 4 x 30 min at 45 °C, dried, and exposed to Kodak X-Omat AR films at -70°C with intensifying screens. Films were developed in an automated Kodak processor. I ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.