Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... gene along the human genome started 1990 & the rough copy of HGP was obtained June 2000 Through this project the following information can be obtained: a) The function & site of each gene along specific chromosomes b) A genetic finger-print or a gene map for each individual can be done through w ...
... gene along the human genome started 1990 & the rough copy of HGP was obtained June 2000 Through this project the following information can be obtained: a) The function & site of each gene along specific chromosomes b) A genetic finger-print or a gene map for each individual can be done through w ...
Chapter 1-2: Genetics Progressed from Mendel to DNA in Less Than
... 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
... 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
Document
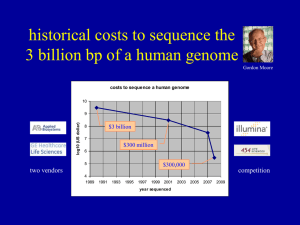
... How much data storage does 1 human genome require? About 1.5 GB (2 CDs) if your stored only one copy of each letter. For the raw format containing image files and base quality data 2-30 TB are required. 30-50x coverage requires more data storage capacity. ...
... How much data storage does 1 human genome require? About 1.5 GB (2 CDs) if your stored only one copy of each letter. For the raw format containing image files and base quality data 2-30 TB are required. 30-50x coverage requires more data storage capacity. ...
Genetic Disorders - Michigan Department of Education Technology
... B4.2A Show that when mutations occur in sex cells, they can be passed on to offspring (inherited mutations), but if they occur in other cells, they can be passed on to descendant cells only (noninherited mutations). B4.2D Predict the consequences that changes in the DNA composition of particular ge ...
... B4.2A Show that when mutations occur in sex cells, they can be passed on to offspring (inherited mutations), but if they occur in other cells, they can be passed on to descendant cells only (noninherited mutations). B4.2D Predict the consequences that changes in the DNA composition of particular ge ...
HEREDITY AND GENETICS vocabulary terms and
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
HEREDITY - Susquehanna University
... • All people who will be born have been formed • The homunculus unfolds to form the adult • Came from Egyptian alchemy ...
... • All people who will be born have been formed • The homunculus unfolds to form the adult • Came from Egyptian alchemy ...
RECOMBINANT DNA
... The scientists will use the transgenic pigs to study human disease. Because the pig's genetic material is green, it is easy to spot. So if, for instance, some of its stem cells are injected into another animal, scientists can track how they develop without the need for a biopsy or invasive test. The ...
... The scientists will use the transgenic pigs to study human disease. Because the pig's genetic material is green, it is easy to spot. So if, for instance, some of its stem cells are injected into another animal, scientists can track how they develop without the need for a biopsy or invasive test. The ...
Lecture 6 pdf - Institute for Behavioral Genetics
... RNA polymerase 2. RNA processing introns spliced out leaving exons alternative splicing (+1/2 of all genes) ...
... RNA polymerase 2. RNA processing introns spliced out leaving exons alternative splicing (+1/2 of all genes) ...
Generation and phenotyping of genetically engineered animals
... e-mail: [email protected] Genetically engineered animals play an increasingly important role in biomedical research, such as, functional genomics, “gene farming”, drug testing and animal models of human diseases. Contemporary genetic engineering techniques include (i.) overexpression of ...
... e-mail: [email protected] Genetically engineered animals play an increasingly important role in biomedical research, such as, functional genomics, “gene farming”, drug testing and animal models of human diseases. Contemporary genetic engineering techniques include (i.) overexpression of ...
Student Name: Teacher
... 30. The final alignment of chromosomes, important in determining the genetic composition of offspring, occurs in what stage of meiosis? A. ...
... 30. The final alignment of chromosomes, important in determining the genetic composition of offspring, occurs in what stage of meiosis? A. ...
Glossary 29Sept2012_Genetics
... complementary DNA (cDNA): DNA that is synthesized from a messenger RNA template; the single-stranded form is often used as a probe in physical mapping. co-dominance – a condition in which both alleles are expressed; neither allele is recessive and the phenotypes of both alleles are expressed. domina ...
... complementary DNA (cDNA): DNA that is synthesized from a messenger RNA template; the single-stranded form is often used as a probe in physical mapping. co-dominance – a condition in which both alleles are expressed; neither allele is recessive and the phenotypes of both alleles are expressed. domina ...
GMO and gene therapy - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... What are the benefits to genetically modified plants and animals? 1)To make pesticide __________ resistant plants. 2)GM plants can produce natural __________. pesticide ...
... What are the benefits to genetically modified plants and animals? 1)To make pesticide __________ resistant plants. 2)GM plants can produce natural __________. pesticide ...
m12-comparative_genomics
... Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)-based methods o Maximum Parsimony: Considering all possible tree topologies (computationally expensive!), pick the one that explains observed changes using the smallest number of point mutations o Maximum Likelihood: Analog of Maximum Parsimony that attempts to id ...
... Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)-based methods o Maximum Parsimony: Considering all possible tree topologies (computationally expensive!), pick the one that explains observed changes using the smallest number of point mutations o Maximum Likelihood: Analog of Maximum Parsimony that attempts to id ...
What are genomes and how are they studied
... More alternative transcripts: Increased RNA splice variants thereby expanding proteins by 5 fold 2) Proteome: proteome more complex than invertebrates Domain arrangements in human: largest total number of domains is 130 largest number of domain types per protein is 9 Mostly identical arrangeme ...
... More alternative transcripts: Increased RNA splice variants thereby expanding proteins by 5 fold 2) Proteome: proteome more complex than invertebrates Domain arrangements in human: largest total number of domains is 130 largest number of domain types per protein is 9 Mostly identical arrangeme ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _________________________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be _________________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene causes what disorder: _____________________________________ ...
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _________________________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be _________________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene causes what disorder: _____________________________________ ...
1/25
... localized to a sequenced region of the chromosome, then look for genes that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
... localized to a sequenced region of the chromosome, then look for genes that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
BIOL 433 Plant Genetics Term 1, 2005
... Place BAC clones into contigs (contiguous DNA segments) by sequencing a few (500) clones (seed BACs) completely and sequencing only the ends of many more clones (10,000). Use a computer to match the end sequences to the seed clones to group and align the BAC clones. ...
... Place BAC clones into contigs (contiguous DNA segments) by sequencing a few (500) clones (seed BACs) completely and sequencing only the ends of many more clones (10,000). Use a computer to match the end sequences to the seed clones to group and align the BAC clones. ...
BIOL 433 Plant Genetics Term 1, 2005
... Place BAC clones into contigs (contiguous DNA segments) by sequencing a few (500) clones (seed BACs) completely and sequencing only the ends of many more clones (10,000). Use a computer to match the end sequences to the seed clones to group and align the BAC clones. ...
... Place BAC clones into contigs (contiguous DNA segments) by sequencing a few (500) clones (seed BACs) completely and sequencing only the ends of many more clones (10,000). Use a computer to match the end sequences to the seed clones to group and align the BAC clones. ...
lecture28_Sequencing.. - University of Alberta
... There are 96 plant species with more than 20,000 expressed sequence tags (ESTs), but most are crop plants. If we count only medicinal plants, generously defined to include makers of secondary metabolites with purported health benefits, such as lycopene for tomatoes and resveratrol for grapes, there ...
... There are 96 plant species with more than 20,000 expressed sequence tags (ESTs), but most are crop plants. If we count only medicinal plants, generously defined to include makers of secondary metabolites with purported health benefits, such as lycopene for tomatoes and resveratrol for grapes, there ...