Introduction to Genetics Klug 8th Edition
... 1866 Mendel’s work is published 1886 Advances in microscopes=chromosomes 1880’s 1890’s Mitosis/meiosis 1900 Correns confirms Mendel’s work early1900’s Sutton and Boveri-Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Early 1900’s Mutations discoveries led to gene ...
... 1866 Mendel’s work is published 1886 Advances in microscopes=chromosomes 1880’s 1890’s Mitosis/meiosis 1900 Correns confirms Mendel’s work early1900’s Sutton and Boveri-Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Early 1900’s Mutations discoveries led to gene ...
Document
... would explain the variation and why it was developed. 23,000 genes in humans (The human genome project) Many of our key genes are identical to many other animals What else contributes to evolution? The embryo is the platform for diversity based on the genes. All living creatures are made from the sa ...
... would explain the variation and why it was developed. 23,000 genes in humans (The human genome project) Many of our key genes are identical to many other animals What else contributes to evolution? The embryo is the platform for diversity based on the genes. All living creatures are made from the sa ...
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk
... 2. How does the length of exons compare to the length of introns in different organisms ranging from prokaryotes to vertebrates? 3. Discuss the evidence that supports both the “introns early” and the “introns late” models to explain the origin of interrupted genes. 4. Compare the human nuclear genom ...
... 2. How does the length of exons compare to the length of introns in different organisms ranging from prokaryotes to vertebrates? 3. Discuss the evidence that supports both the “introns early” and the “introns late” models to explain the origin of interrupted genes. 4. Compare the human nuclear genom ...
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
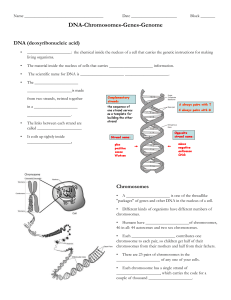
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Bononformatics
... computational statistics, and biochemistry. The term computational biology is often used interchangeably with bioinformatics. Computational biology, however, deals more with the solution to specific experimental research completed with a definite goal in mind. Bioinformatics is more practically appl ...
... computational statistics, and biochemistry. The term computational biology is often used interchangeably with bioinformatics. Computational biology, however, deals more with the solution to specific experimental research completed with a definite goal in mind. Bioinformatics is more practically appl ...
E. coli
... • About 3000 Mb of DNA on 23 chromosomes • About 35000 genes (only about twice as many as flies and worms) • Most human genes have homologues in other organisms (vertebrates, insects, yeast etc) ...
... • About 3000 Mb of DNA on 23 chromosomes • About 35000 genes (only about twice as many as flies and worms) • Most human genes have homologues in other organisms (vertebrates, insects, yeast etc) ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
Genomes and their evolution
... and its number of genes. The 1mm nematode C. elegans and humans both have between 20,000 and 21,000 genes. •The human genome is able to function with relatively few genes by utilizing alternative splicing of RNA transcripts. • *Recall: This process results in more than one functional protein from a ...
... and its number of genes. The 1mm nematode C. elegans and humans both have between 20,000 and 21,000 genes. •The human genome is able to function with relatively few genes by utilizing alternative splicing of RNA transcripts. • *Recall: This process results in more than one functional protein from a ...
Red line Introduction
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
Insects and genetics
... 16. Which of the following is an insect transposon? a. hermes b. Herves c. woot d. all of the above Which of the following transposons was isolated from a Drosophila speces? a. mariner b. Minos d. hobo d. all of the above 17. What's a transcription factor? 18.What species was genetically engineered ...
... 16. Which of the following is an insect transposon? a. hermes b. Herves c. woot d. all of the above Which of the following transposons was isolated from a Drosophila speces? a. mariner b. Minos d. hobo d. all of the above 17. What's a transcription factor? 18.What species was genetically engineered ...
Gene Technology
... out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female tiger, and the result is an enormous offspring that has the best physical and mental characteristics of the parents. It is important to note that there are no documented cases of ligers appearing naturally in the wild. Lions and t ...
... out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female tiger, and the result is an enormous offspring that has the best physical and mental characteristics of the parents. It is important to note that there are no documented cases of ligers appearing naturally in the wild. Lions and t ...
word doc - CSUN.edu
... The other 22 pairs (44 chromosomes) are called autosomes. All egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23X). However, half of all the sperm carry an X chromosome (23X) and half carry a Y… ½ girls and ½ boys. ...
... The other 22 pairs (44 chromosomes) are called autosomes. All egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23X). However, half of all the sperm carry an X chromosome (23X) and half carry a Y… ½ girls and ½ boys. ...
EXAM 2
... True/False (1 point each) 20. ___T___ Satellite DNA is highly repetitive 21. ___T___ The more repetitive DNA included in a genome, the more quickly it will reanneal after being denatured. 22. ___T___ For most diploid eukaryotic organisms, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new me ...
... True/False (1 point each) 20. ___T___ Satellite DNA is highly repetitive 21. ___T___ The more repetitive DNA included in a genome, the more quickly it will reanneal after being denatured. 22. ___T___ For most diploid eukaryotic organisms, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new me ...
No Slide Title
... • Many developmental studies done with worm • Simple genome – small genome (97mbmegabase pairs, or 97,000,000 base pairs) • Little highly repetitive DNA sequences • About 19,000 genes ...
... • Many developmental studies done with worm • Simple genome – small genome (97mbmegabase pairs, or 97,000,000 base pairs) • Little highly repetitive DNA sequences • About 19,000 genes ...
1 - contentextra
... 10 Special combinations of letters are used to show the above cases: IA, IB and i for the alleles of ABO blood types, XB, Xb or Y for colour blindness alleles, or HbS or HbA for sickle cell anaemia. 11 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used on small quantities of DNA (from a crime scene ...
... 10 Special combinations of letters are used to show the above cases: IA, IB and i for the alleles of ABO blood types, XB, Xb or Y for colour blindness alleles, or HbS or HbA for sickle cell anaemia. 11 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used on small quantities of DNA (from a crime scene ...
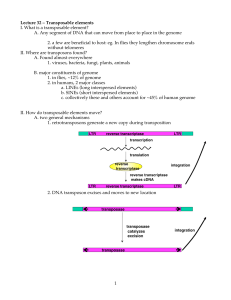
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
What are multiple alleles
... These are the sex chromosomes. Among other things they code for the production of hormones that make males - males and females – females. In humans the sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair. ...
... These are the sex chromosomes. Among other things they code for the production of hormones that make males - males and females – females. In humans the sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair. ...
Epigenetics - Hospital Melaka Department of Medicine Haematology
... Different genes are turned on and different genes are turned off in the development of different tissues/cells ...
... Different genes are turned on and different genes are turned off in the development of different tissues/cells ...
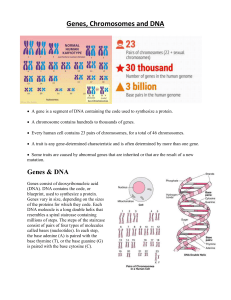
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
Advances in genetics
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
genome433
... microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are made in replicating such sequences the “n” often varies from one individual to another (i.e., it is polymorphic.) ...
... microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are made in replicating such sequences the “n” often varies from one individual to another (i.e., it is polymorphic.) ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.