Molecular function - SGD-Wiki - Saccharomyces Genome Database
... Tabs, access to detailed info (sequence, gene ontology, phenotype, interaction, expression and regulation) • Data analysis: GO tools, YeastMine basics and use-cases ...
... Tabs, access to detailed info (sequence, gene ontology, phenotype, interaction, expression and regulation) • Data analysis: GO tools, YeastMine basics and use-cases ...
Centromere Locations and Associated Chromosome
... CEN5 is more complex. The formation of chromosome V of A. thaliana involved a reciprocal translocation (see above and Figure 1), and an understanding of this event is critical for interpreting the origin of CEN5. Previous comparative molecular cytogenetic analyses of A. thaliana and A. lyrata could ...
... CEN5 is more complex. The formation of chromosome V of A. thaliana involved a reciprocal translocation (see above and Figure 1), and an understanding of this event is critical for interpreting the origin of CEN5. Previous comparative molecular cytogenetic analyses of A. thaliana and A. lyrata could ...
Genetic recombination in plants
... events resolve in regions of the bzl locus that have high densities of heterologies [38”]. The impact of heterologies, however, on recombination in plants appears to be significantly less than is observed in Sacdzaromyces [45] and other fungi. For example, in Ascobohs, heterozygotes at the 62 locus ...
... events resolve in regions of the bzl locus that have high densities of heterologies [38”]. The impact of heterologies, however, on recombination in plants appears to be significantly less than is observed in Sacdzaromyces [45] and other fungi. For example, in Ascobohs, heterozygotes at the 62 locus ...
A High Density Integrated Genetic Linkage Map of Soybean and the
... be the most abundant source of DNA polymorphisms in soybean (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). Despite being the most common molecular marker in soybean, the SNP frequency is relatively low compared to other cultivated crop species (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). The relatively low sequ ...
... be the most abundant source of DNA polymorphisms in soybean (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). Despite being the most common molecular marker in soybean, the SNP frequency is relatively low compared to other cultivated crop species (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). The relatively low sequ ...
Locus in Salmonid Fishes Comparative Genome Analysis of the
... in Atlantic salmon using 3 and 15 AFLP and VNTR markers, respectively (Fig. 1). Sakamoto et al. (2000) previously reported two microsatellite markers (OmyFGT19TUF and OmyRGT28TUF) linked to SEX in rainbow trout. We identified two additional sex-linked microsatellite markers (Ots517NWFSC and Ssa1NVH) ...
... in Atlantic salmon using 3 and 15 AFLP and VNTR markers, respectively (Fig. 1). Sakamoto et al. (2000) previously reported two microsatellite markers (OmyFGT19TUF and OmyRGT28TUF) linked to SEX in rainbow trout. We identified two additional sex-linked microsatellite markers (Ots517NWFSC and Ssa1NVH) ...
pdf
... [Thompson et al., 1997]. Neighbor-joining trees were produced using distance matrix methods (PAUP 4.0, Sinauer Associates), and the reliability of the phylogenetic reconstructions (1000 replicates) was evaluated by bootstrapping. For descriptive purposes, nirS and nirK gene clusters were identified ...
... [Thompson et al., 1997]. Neighbor-joining trees were produced using distance matrix methods (PAUP 4.0, Sinauer Associates), and the reliability of the phylogenetic reconstructions (1000 replicates) was evaluated by bootstrapping. For descriptive purposes, nirS and nirK gene clusters were identified ...
Article Old but Not (So) Degenerated—Slow
... evolutionary processes, although the rate of sex chromosome differentiation has been atypically low. Lack of dosage compensation may be a factor hindering sex chromosome evolution in this lineage. Key words: Z chromosome, W chromosome, evolutionary strata, gametologs, nonrecombining chromosome, bias ...
... evolutionary processes, although the rate of sex chromosome differentiation has been atypically low. Lack of dosage compensation may be a factor hindering sex chromosome evolution in this lineage. Key words: Z chromosome, W chromosome, evolutionary strata, gametologs, nonrecombining chromosome, bias ...
Manipulating the Plasmodium Genome
... about two-thirds of the predicted genes without function, either having no detectable homolog or a Plasmodium/ Apicomplexa-specific homolog for which we have no functional information. Function was tentatively assigned to only a third of the predicted genes, but most of these significant matches rem ...
... about two-thirds of the predicted genes without function, either having no detectable homolog or a Plasmodium/ Apicomplexa-specific homolog for which we have no functional information. Function was tentatively assigned to only a third of the predicted genes, but most of these significant matches rem ...
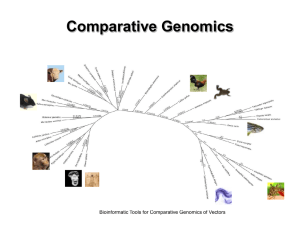
Comparative Genomics
... (6) For each aligned cluster, build a phylogenetic tree using PHYML. An unrooted tree is obtained at this stage. (7) Reconcile each gene tree with the species tree to call duplication event on internal nodes and root the tree (TreeBeSt). (8) From each gene tree, infer gene pairwise relations of orth ...
... (6) For each aligned cluster, build a phylogenetic tree using PHYML. An unrooted tree is obtained at this stage. (7) Reconcile each gene tree with the species tree to call duplication event on internal nodes and root the tree (TreeBeSt). (8) From each gene tree, infer gene pairwise relations of orth ...
Population Differences in Transcript
... used as a quantitative phenotypic trait to locate regions in the genome that have polymorphisms governing differential transcription within populations [1,2,3,4]. This type of inference termed expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analysis has been used in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) ...
... used as a quantitative phenotypic trait to locate regions in the genome that have polymorphisms governing differential transcription within populations [1,2,3,4]. This type of inference termed expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analysis has been used in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) ...
Amplification of 16S rRNA Genes from Frankia Strains in Root
... Phenolic compounds present in actinorhizal nodule homogenates normally turn bright red or orange because of spontaneous oxidation in air and can complicate the purification of proteins or DNA. Adding ascorbate to the TE buffer and washing the hyphal clusters thoroughly on the 25-mm-mesh nylon screen ...
... Phenolic compounds present in actinorhizal nodule homogenates normally turn bright red or orange because of spontaneous oxidation in air and can complicate the purification of proteins or DNA. Adding ascorbate to the TE buffer and washing the hyphal clusters thoroughly on the 25-mm-mesh nylon screen ...
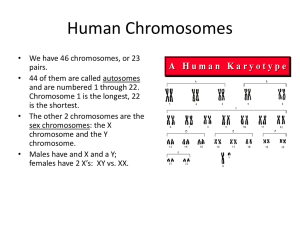
Chromosomes and Genetics
... 1. Sometimes inversions or translocations change phenotypic expression of genes by the position effect, for example, by moving a gene from euchromatin to heterochromatin (transcription generally occurs in euchromatin but not in heterochromatin). 2. This is an example of an epigenetic effect since th ...
... 1. Sometimes inversions or translocations change phenotypic expression of genes by the position effect, for example, by moving a gene from euchromatin to heterochromatin (transcription generally occurs in euchromatin but not in heterochromatin). 2. This is an example of an epigenetic effect since th ...
gene duplication in the evolution of sexual dimorphism
... the statistical approach and power of a given experimental design, which may partly explain differences among studies in the number of sex-biased genes identified. Furthermore, because evolutionarily recent gene duplicates are expected to be more similar in expression, minor differences in expressio ...
... the statistical approach and power of a given experimental design, which may partly explain differences among studies in the number of sex-biased genes identified. Furthermore, because evolutionarily recent gene duplicates are expected to be more similar in expression, minor differences in expressio ...
Characterization of sex chromosomes in rainbow trout and coho
... we need to demonstrate its chromosomal colocalization with OmyP9 probe. Studies of the distribution pattern of the 5S rDNA genes in the genome of salmonids indicates that these genes can occupy one or more loci (Pendás et al., 1994; Moran et al., 1996; Pardo et al., 2000). Our FISH analysis with the ...
... we need to demonstrate its chromosomal colocalization with OmyP9 probe. Studies of the distribution pattern of the 5S rDNA genes in the genome of salmonids indicates that these genes can occupy one or more loci (Pendás et al., 1994; Moran et al., 1996; Pardo et al., 2000). Our FISH analysis with the ...
Nonadaptive processes in primate and human evolution
... which have effective population sizes an order of magnitude larger than mammal species (1–2 million; see Eyre-Walker et al., 2002), they provide a useful contrast for studying the evolutionary effects of differences in population size. A reduction in Ne in the evolution of primates and more so in th ...
... which have effective population sizes an order of magnitude larger than mammal species (1–2 million; see Eyre-Walker et al., 2002), they provide a useful contrast for studying the evolutionary effects of differences in population size. A reduction in Ne in the evolution of primates and more so in th ...
The Evolution of Vertebrate Sex Chromosomes
... of stone from different periods in the past, and christened these groups “evolutionary ...
... of stone from different periods in the past, and christened these groups “evolutionary ...
Cleavage of a model DNA replication fork by a Type I restriction
... can cleave a stalled replication fork (10,11), but contribution of the fork cleavage to fork restart is yet to be elucidated (11). Archaeal Hef that cleaves several branched forms of DNA in vitro was proposed to be involved in cutting off the arm containing a newly synthesized leading strand from a s ...
... can cleave a stalled replication fork (10,11), but contribution of the fork cleavage to fork restart is yet to be elucidated (11). Archaeal Hef that cleaves several branched forms of DNA in vitro was proposed to be involved in cutting off the arm containing a newly synthesized leading strand from a s ...
Supplementary Data - Word file
... Growing evidence suggests that subtelomeric regions in fungi contain genes with roles in niche adaptation and virulence. It is thus noteworthy that sub-telomeric regions in both A. nidulans and A. fumigatus show enrichment for gene clusters with predicted roles in secondary metabolism. In A. fumigat ...
... Growing evidence suggests that subtelomeric regions in fungi contain genes with roles in niche adaptation and virulence. It is thus noteworthy that sub-telomeric regions in both A. nidulans and A. fumigatus show enrichment for gene clusters with predicted roles in secondary metabolism. In A. fumigat ...
Chpt2_Struc_Nucleic_Acids.doc
... DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids, which are the polymeric acids isolated from the nucleus of cells. DNA and RNA can be represented as simple strings of letters, where each letter corresponds to a particular nucleotide, the monomeric component of the nucleic acid polymers. Although this conveys alm ...
... DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids, which are the polymeric acids isolated from the nucleus of cells. DNA and RNA can be represented as simple strings of letters, where each letter corresponds to a particular nucleotide, the monomeric component of the nucleic acid polymers. Although this conveys alm ...
Isolation, Characterization, and Annotation: The Search for Novel
... to the host, penetrates the cell membrane and injects its DNA. The genetic information can then follow two potential paths. In the lysogenic cycle, the DNA is incorporated into the host genome as a prophage and remains a part of the host’s genome as long as conditions remain stable for the prophage. ...
... to the host, penetrates the cell membrane and injects its DNA. The genetic information can then follow two potential paths. In the lysogenic cycle, the DNA is incorporated into the host genome as a prophage and remains a part of the host’s genome as long as conditions remain stable for the prophage. ...
A Bayesian analysis of the chromosome architecture of
... disorders. Formally, both networks can be easily constructed from the DISEASOME. In the meanwhile there are various applications of the DISEASOME that studied in detail the modular structure of the disease network14, improved algorithmic methods for predicting diseasegenes and modules15 or integrate ...
... disorders. Formally, both networks can be easily constructed from the DISEASOME. In the meanwhile there are various applications of the DISEASOME that studied in detail the modular structure of the disease network14, improved algorithmic methods for predicting diseasegenes and modules15 or integrate ...
Co-dominant SCAR marker for detection of the begomovirus
... one of 3 nt, and one of 120 nt). The sequence for the T0302 marker from S. habrochaites LA0386 (909 bp, EU046611) was identical to the sequence from H24. The sequence for the T0302 marker (789 bp, EU046612) was also obtained for another accession, S. chilense LA2779, that has been used as a source ...
... one of 3 nt, and one of 120 nt). The sequence for the T0302 marker from S. habrochaites LA0386 (909 bp, EU046611) was identical to the sequence from H24. The sequence for the T0302 marker (789 bp, EU046612) was also obtained for another accession, S. chilense LA2779, that has been used as a source ...
SNP
... Polymorphisms (SNPs) the variant sequence type has a frequency of at least 1% in the population. high frequency of SNPs in human genome: estimated ~1 SNP/Kb. ...
... Polymorphisms (SNPs) the variant sequence type has a frequency of at least 1% in the population. high frequency of SNPs in human genome: estimated ~1 SNP/Kb. ...
Promega Notes: T4 RNA Ligase: A Molecular Tool for RNA and DNA
... amber suppressor tRNA lacking the terminal 3´-CA sequence to a CA dinucleotide that had been chemically modified with an unnatural amino acid. This improvement greatly simplified the original anticodon loop replacement procedure, and they demonstrated that, while lacking post-transcriptional base mo ...
... amber suppressor tRNA lacking the terminal 3´-CA sequence to a CA dinucleotide that had been chemically modified with an unnatural amino acid. This improvement greatly simplified the original anticodon loop replacement procedure, and they demonstrated that, while lacking post-transcriptional base mo ...
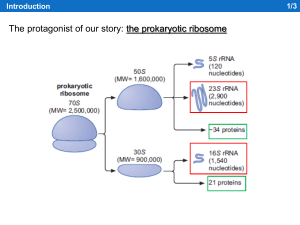
RiboT
... • Revision of one of the key concepts of molecular biology: reversible association and dissociation of ribosomal subunits is not essential in order to succesfully express the entire genome • Ribosome with inseparable subunits (RiboT) are able to substain the expression of entire bacterial genome • R ...
... • Revision of one of the key concepts of molecular biology: reversible association and dissociation of ribosomal subunits is not essential in order to succesfully express the entire genome • Ribosome with inseparable subunits (RiboT) are able to substain the expression of entire bacterial genome • R ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.