BTEC Bowl Questions
... Q: A DNA microarray contains: A: A. double-stranded DNA molecules B. single-stranded DNA molecules C. pharmacogenomics D. all of the above (pg 15 and glossary pg G-6) Suzanne Visser: Q: How are recombinant proteins produced? A: By a gene cloning technique involved in transferring a gene of interest ...
... Q: A DNA microarray contains: A: A. double-stranded DNA molecules B. single-stranded DNA molecules C. pharmacogenomics D. all of the above (pg 15 and glossary pg G-6) Suzanne Visser: Q: How are recombinant proteins produced? A: By a gene cloning technique involved in transferring a gene of interest ...
Biochem 4 protein notes - The Bronx High School of Science
... Cause of some disorders EX: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and prion diseases (e.g., "mad-cow" disease) ??? possible a failure of chaperones is involved??? If so, perhaps treatment possible by increasing the efficiency of chaperones ????? Other Kinds of Proteins- Simple proteins contain ...
... Cause of some disorders EX: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and prion diseases (e.g., "mad-cow" disease) ??? possible a failure of chaperones is involved??? If so, perhaps treatment possible by increasing the efficiency of chaperones ????? Other Kinds of Proteins- Simple proteins contain ...
proteins aminacids notesKelly
... Cause of some disorders EX: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and prion diseases (e.g., "mad-cow" disease) ??? possible a failure of chaperones is involved??? If so, perhaps treatment possible by increasing the efficiency of chaperones ????? Other Kinds of Proteins- Simple proteins contain ...
... Cause of some disorders EX: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and prion diseases (e.g., "mad-cow" disease) ??? possible a failure of chaperones is involved??? If so, perhaps treatment possible by increasing the efficiency of chaperones ????? Other Kinds of Proteins- Simple proteins contain ...
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW SHEET
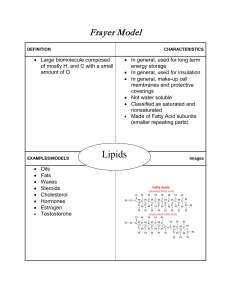
... w. If you combine the above molecules the process is called ___________________ x. If fat is digested, this process would be called _________________ and what molecule would be released? 7. PROTEINS Text section 5.4 a. Name 3 protein foods_______________________________ b. What elements would be fou ...
... w. If you combine the above molecules the process is called ___________________ x. If fat is digested, this process would be called _________________ and what molecule would be released? 7. PROTEINS Text section 5.4 a. Name 3 protein foods_______________________________ b. What elements would be fou ...
(Biological) networks
... PPIs can be identified by 1) affinity capture, in which a target protein (bait) is immunoprecipitated in complex with its binding partners (prey); or 2) two-hybrid approaches, where modified proteins produce measurable readouts (e.g. change in gene expression) upon interaction. TF-TG relationships a ...
... PPIs can be identified by 1) affinity capture, in which a target protein (bait) is immunoprecipitated in complex with its binding partners (prey); or 2) two-hybrid approaches, where modified proteins produce measurable readouts (e.g. change in gene expression) upon interaction. TF-TG relationships a ...
Protein Structure Prediction The Protein Folding Problem
... • but some exceptions – all proteins can be denatured – some molecules have multiple conformations – some proteins get folding help from chaperones – prions can change the conformation of other proteins ...
... • but some exceptions – all proteins can be denatured – some molecules have multiple conformations – some proteins get folding help from chaperones – prions can change the conformation of other proteins ...
Amino acids and prot..
... form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimer) twisted around each other forming triplet-helix molecule. • ⅓ of st ...
... form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimer) twisted around each other forming triplet-helix molecule. • ⅓ of st ...
DNA—From Genes to Proteins
... pigment A material that gives color to plants and animals. plasmid A small fragment of DNA from a prokaryotic cell that can be used to carry genes from one cell to another. prokaryotic Lacking a nuclear membrane. A bacterial cell is an example of a prokaryotic cell. glossary ...
... pigment A material that gives color to plants and animals. plasmid A small fragment of DNA from a prokaryotic cell that can be used to carry genes from one cell to another. prokaryotic Lacking a nuclear membrane. A bacterial cell is an example of a prokaryotic cell. glossary ...
CHEM501- Introduction to Biochemistry – Exam 1 w
... 17. The first step in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis generates a series of protein bands by isoelectric focusing. In a second step, a strip of this gel is turned 90 degrees, placed on another gel containing SDS, and electric current is again applied. In this second step: A) proteins with simila ...
... 17. The first step in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis generates a series of protein bands by isoelectric focusing. In a second step, a strip of this gel is turned 90 degrees, placed on another gel containing SDS, and electric current is again applied. In this second step: A) proteins with simila ...
Lectrure 9 - Columbus Labs
... Frederick Sanger was the first - in 1953, he sequenced the two chains of insulin. • Sanger's results established that all of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence. • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - amino acid sequencing - sequencing the corresponding DNA in the gene ...
... Frederick Sanger was the first - in 1953, he sequenced the two chains of insulin. • Sanger's results established that all of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence. • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - amino acid sequencing - sequencing the corresponding DNA in the gene ...
Systemic Response to Injury and Metabolic Support
... B. 50% reduction of carbs C. 50% of proteins are in the form of branched chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) D. Increased arginine, omega 3 fatty acids, and B carotene ...
... B. 50% reduction of carbs C. 50% of proteins are in the form of branched chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) D. Increased arginine, omega 3 fatty acids, and B carotene ...
Proteins
... Polypeptides are formed by condensation polymerisation of monomers called amino acids. Amino acids are essential biomolecules, not only because they are the building blocks of all proteins. All proteins in life forms on Earth are formed from a set of 20 amino acids. Most micro-organisms can synthesi ...
... Polypeptides are formed by condensation polymerisation of monomers called amino acids. Amino acids are essential biomolecules, not only because they are the building blocks of all proteins. All proteins in life forms on Earth are formed from a set of 20 amino acids. Most micro-organisms can synthesi ...
Introduction - Northern Illinois University
... is that eukaryotes have their DNA stored in a membranebound nucleus, while prokaryotes have their DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes are single celled organisms that are simpler than eukaryotes. They are also far more diverse in the conditions they grow in and their biochemistry. • ...
... is that eukaryotes have their DNA stored in a membranebound nucleus, while prokaryotes have their DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes are single celled organisms that are simpler than eukaryotes. They are also far more diverse in the conditions they grow in and their biochemistry. • ...
Food Industry
... A lowering of the pH results in the protein in milk clotting and a release of flavours and aromas. A lower pH also reduces the likelihood of contamination. The specific bacteria used will determine specific properties, textures and aromas in the final product. Sometimes a second inoculum of bac ...
... A lowering of the pH results in the protein in milk clotting and a release of flavours and aromas. A lower pH also reduces the likelihood of contamination. The specific bacteria used will determine specific properties, textures and aromas in the final product. Sometimes a second inoculum of bac ...
protein lesson
... I know the structure of protein. I can understand the different functions of protein in the diet. I know the difference between high biological value proteins and low biological value proteins and can list food examples of each. I understand two lows make a high. ...
... I know the structure of protein. I can understand the different functions of protein in the diet. I know the difference between high biological value proteins and low biological value proteins and can list food examples of each. I understand two lows make a high. ...
DNA - BiologyProvidence
... protein, takes place in the cytoplasm The mRNA interacts with a specialized organelle in the rough ER called a ribosome, which “reads” the sequence of mRNA bases Each sequence of three bases, called a codon, codes for one particular amino acid (the building blocks of proteins). tRNA assembles the pr ...
... protein, takes place in the cytoplasm The mRNA interacts with a specialized organelle in the rough ER called a ribosome, which “reads” the sequence of mRNA bases Each sequence of three bases, called a codon, codes for one particular amino acid (the building blocks of proteins). tRNA assembles the pr ...
Control of Gene Expression Control of Gene Expression Regulatory
... the trp repressor protein – trp repressor binds to the operator to block transcription – binding of repressor to the operator requires a corepressor which is tryptophan – low levels of tryptophan prevent the repressor from binding to the operator ...
... the trp repressor protein – trp repressor binds to the operator to block transcription – binding of repressor to the operator requires a corepressor which is tryptophan – low levels of tryptophan prevent the repressor from binding to the operator ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.