03_Lecture_Presentation
... 3.11 Proteins are made from amino acids linked by peptide bonds Proteins are – involved in nearly every dynamic function in your body and – very diverse, with tens of thousands of different proteins, each with a specific structure and function, in the human body. ...
... 3.11 Proteins are made from amino acids linked by peptide bonds Proteins are – involved in nearly every dynamic function in your body and – very diverse, with tens of thousands of different proteins, each with a specific structure and function, in the human body. ...
The Transition from Stiff to Compliant Materials in Squid Beaks
... from the hard, stiff tip to the soft, compliant base. When detached from the buccal mass, each Humboldt squid beak exhibits clearly visible gradients in pigmentation, ranging from translucent along the wing edge to black at the beak tip (Fig. 1, B and C). The pigmentation gradient appears to be clos ...
... from the hard, stiff tip to the soft, compliant base. When detached from the buccal mass, each Humboldt squid beak exhibits clearly visible gradients in pigmentation, ranging from translucent along the wing edge to black at the beak tip (Fig. 1, B and C). The pigmentation gradient appears to be clos ...
Limits of adaptation to high dietary protein intakes
... not suf®cient criterion. In addition there is the need to determine the extent to which the demand for a critical range of functions has been satis®ed. For the system as a whole the demand side is determined by the pattern and rate of protein synthesis and the utilisation of amino acids for other me ...
... not suf®cient criterion. In addition there is the need to determine the extent to which the demand for a critical range of functions has been satis®ed. For the system as a whole the demand side is determined by the pattern and rate of protein synthesis and the utilisation of amino acids for other me ...
Module Outline
... 12. Explain why cells cannot be smaller than a certain minimum size or larger than a certain maximum size. Explain the surface-to-volume ratio and discuss the implications for cell size. 13. Explain what is meant by cell fractionation and its use in biology. 14. Describe the structural organization ...
... 12. Explain why cells cannot be smaller than a certain minimum size or larger than a certain maximum size. Explain the surface-to-volume ratio and discuss the implications for cell size. 13. Explain what is meant by cell fractionation and its use in biology. 14. Describe the structural organization ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-300 L)
... 4. On what structural level of the enzyme (primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary) does the enzyme-substrate interaction depend? The substrate binds to the enzyme in the activation centers. These are specific three-dimensional sites and thus they depend on the protein tertiary and quaternary str ...
... 4. On what structural level of the enzyme (primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary) does the enzyme-substrate interaction depend? The substrate binds to the enzyme in the activation centers. These are specific three-dimensional sites and thus they depend on the protein tertiary and quaternary str ...
called Oxidative phosphorylation.
... F1 ATPase (or ATP synthase) system. In the next few lectures we will discuss the followings; • The mitochondrial structure • Electron transport from NADH and FADH2 to O2 a. Thermodynomics of Electron transport b. Sequence of electron transport • Oxidative phosphorylation a. Chemiosmotic theory b. AT ...
... F1 ATPase (or ATP synthase) system. In the next few lectures we will discuss the followings; • The mitochondrial structure • Electron transport from NADH and FADH2 to O2 a. Thermodynomics of Electron transport b. Sequence of electron transport • Oxidative phosphorylation a. Chemiosmotic theory b. AT ...
Document
... The use of a basal diet deficient in the test AA The basal diet contains adequate levels of nutrients other than the test AA The use of at least 4 graded levels of the test AA Adequate duration of the experiment in relation to the response criterion An adequate statistical model to describe the resp ...
... The use of a basal diet deficient in the test AA The basal diet contains adequate levels of nutrients other than the test AA The use of at least 4 graded levels of the test AA Adequate duration of the experiment in relation to the response criterion An adequate statistical model to describe the resp ...
Homology among (βα) 8 Barrels: Implications for the Evolution of
... a superfamily have a probable common evolutionary origin. Most recently, Thornton and co-workers have analyzed TIM barrels from a structural viewpoint, classifying nine families on the basis of hydrogen bond patterns and residue packing in the interior of the barrel (Nagano et al., 1999). In this st ...
... a superfamily have a probable common evolutionary origin. Most recently, Thornton and co-workers have analyzed TIM barrels from a structural viewpoint, classifying nine families on the basis of hydrogen bond patterns and residue packing in the interior of the barrel (Nagano et al., 1999). In this st ...
Nutrient Profile of Renal Specific Formula
... Dr. Kelly obtained both his Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) and Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Nutrition from University College Cork, Ireland. As a Postdoctoral Fellow at The Florida State University, Dr. Kelly received an American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Young Investigator Award for his ...
... Dr. Kelly obtained both his Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) and Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Nutrition from University College Cork, Ireland. As a Postdoctoral Fellow at The Florida State University, Dr. Kelly received an American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Young Investigator Award for his ...
protien notes - davis.k12.ut.us
... Protein PROTEIN 1. Proteins provide _________ calories per gram. 2. The main function of protein is to ___________________________________________________. If carbohydrates and fat are not available, your body will use protein. Is this a good thing? _______ 3. You must eat protein _______________ ...
... Protein PROTEIN 1. Proteins provide _________ calories per gram. 2. The main function of protein is to ___________________________________________________. If carbohydrates and fat are not available, your body will use protein. Is this a good thing? _______ 3. You must eat protein _______________ ...
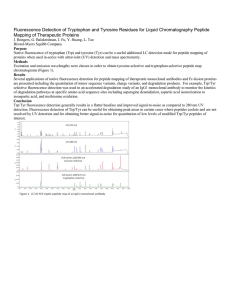
Fluorescence Detection of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues for
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
spin-system assignments
... there won’t be very many unique amino acid residues in a protein, however. but there will be many unique dipeptide sequences but in order to use this fact, we need to be able to connect adjacent residues. ...
... there won’t be very many unique amino acid residues in a protein, however. but there will be many unique dipeptide sequences but in order to use this fact, we need to be able to connect adjacent residues. ...
Unit 1.1 Building Blocks of Life The student knows the significance of
... The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms. The student is expected to: ...
... The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms. The student is expected to: ...
NH 2
... - the resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. The four-atom functional group -C(=O)NH- is called an amide group or (in the context of proteins) a peptide group. - living organisms employ enzymes to form peptide bonds. eg. during translation process. - W ...
... - the resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. The four-atom functional group -C(=O)NH- is called an amide group or (in the context of proteins) a peptide group. - living organisms employ enzymes to form peptide bonds. eg. during translation process. - W ...
Isolation and Characterization of Plastidic Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
... Plant cells contain plastids, organelles dedicated to performing specific biochemical processes including photosynthesis, starch and oil biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis in oil seeds occurs in one type of plastid termed the leucoplast. Anabolic metabolism in leucoplasts includes the production ...
... Plant cells contain plastids, organelles dedicated to performing specific biochemical processes including photosynthesis, starch and oil biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis in oil seeds occurs in one type of plastid termed the leucoplast. Anabolic metabolism in leucoplasts includes the production ...
CET MODEL TEST PAPER -4
... 3. They can develop into any tissue in the body. 4. They can be used to treat infectious diseases. 24. The term” restriction” in restriction endonuclease refers to 1. Breaking phosphodiester bond in DNA by enzyme. 2. Preventing multiplication of bacteriophage in bacteria. 3. Cutting DNA at spec ...
... 3. They can develop into any tissue in the body. 4. They can be used to treat infectious diseases. 24. The term” restriction” in restriction endonuclease refers to 1. Breaking phosphodiester bond in DNA by enzyme. 2. Preventing multiplication of bacteriophage in bacteria. 3. Cutting DNA at spec ...
Corn Bt11 x MIR162 x TC1507 x GA21
... The six proteins (Cry1Ab, PAT, Vip3Aa20, Cry1F, PMI and EPSPS) show no homology to any known mammalian allergen or toxin. There is no evidence suggesting that the six proteins will interact to form (some) new allergen or toxin since each has distinct mode of action and are not likely to interact. Al ...
... The six proteins (Cry1Ab, PAT, Vip3Aa20, Cry1F, PMI and EPSPS) show no homology to any known mammalian allergen or toxin. There is no evidence suggesting that the six proteins will interact to form (some) new allergen or toxin since each has distinct mode of action and are not likely to interact. Al ...
Chapter 6 Pichia pastoris
... (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris), mammalian cells, amphibian oocytes (Xenopus laevis), insect cells and bacteria (Escherichia coli). Plant cells are useful as hosts if mutants are available (Holton et al., 1993), but in many cases the distinction from resident activities may present a ...
... (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris), mammalian cells, amphibian oocytes (Xenopus laevis), insect cells and bacteria (Escherichia coli). Plant cells are useful as hosts if mutants are available (Holton et al., 1993), but in many cases the distinction from resident activities may present a ...
Translation text
... - ribosome will eventually reach the stop codon in A binding site which has no corresponding amino acid - tRNA carrying pp chain stays on P site until protein called a release factor binds to A site recognize that the ribosome has stopped and release the polypeptide chain - the ribosome will break d ...
... - ribosome will eventually reach the stop codon in A binding site which has no corresponding amino acid - tRNA carrying pp chain stays on P site until protein called a release factor binds to A site recognize that the ribosome has stopped and release the polypeptide chain - the ribosome will break d ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.