What`s nature`s most abundant and most ubiquitous protein
... • The most abundant protein: RuBisCo* • How so? It’s the enzyme with the highest copy number in ecosystems (or with highest total mass). • Is it the most ubiquitous? No! It’s almost only in photosynthetic organisms. • Is its gene the most abundant? No! Most genomes lack it. ...
... • The most abundant protein: RuBisCo* • How so? It’s the enzyme with the highest copy number in ecosystems (or with highest total mass). • Is it the most ubiquitous? No! It’s almost only in photosynthetic organisms. • Is its gene the most abundant? No! Most genomes lack it. ...
Proteins - RMC Science Home
... together by a peptide bond. Contain hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen The main function of proteins is to build and maintain tissues. Can also be used for energy but ONLY if carbohydrate and fat stores are depleated. ...
... together by a peptide bond. Contain hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen The main function of proteins is to build and maintain tissues. Can also be used for energy but ONLY if carbohydrate and fat stores are depleated. ...
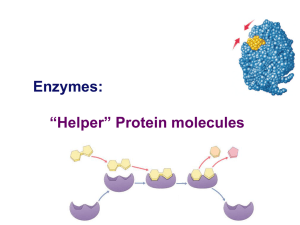
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction Must be the right shape for the job Enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction Must be the right shape for the job Enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
MACRONUTRIENT FOUNDATIONS
... Protein is STRUCTURE • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism ...
... Protein is STRUCTURE • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism ...
3. Proteins Classification (2017)
... denature proteins, such as heating or high concentrations of urea ...
... denature proteins, such as heating or high concentrations of urea ...
Protein microarrays
... teins, they confer enhanced site-specific attachment and oriented immobilization of capture proteins by binding to reactive groups of organic thin films. Table 1 outlines various tags used for protein capture. An affinity or epitope tag is usually an intact protein, a polypeptide or polyamino acid ( ...
... teins, they confer enhanced site-specific attachment and oriented immobilization of capture proteins by binding to reactive groups of organic thin films. Table 1 outlines various tags used for protein capture. An affinity or epitope tag is usually an intact protein, a polypeptide or polyamino acid ( ...
Marvelous Macromolecules - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... individual; they vary more among unrelated individuals in the same species; and vary even more in different ...
... individual; they vary more among unrelated individuals in the same species; and vary even more in different ...
CHM 103 Lecture 36 S07
... Optimum pH Values Most Enzymes in • the body have an optimum pH of about 7.4. • certain organs, enzymes operate at lower and higher optimum pH values. ...
... Optimum pH Values Most Enzymes in • the body have an optimum pH of about 7.4. • certain organs, enzymes operate at lower and higher optimum pH values. ...
A study was designed to examine the effectiveness of low voltage
... ranging between 320 and 350 kg were used. Fourteen were subjected to ES with 80V, 10 minutes post-slaughter for 30 seconds and 14 were unstimulated (NES) as control. The pH and temperature were monitored every hour for the first 10 hours and subsequently at 24 hours. Carcasses were chilled at 2˚C fo ...
... ranging between 320 and 350 kg were used. Fourteen were subjected to ES with 80V, 10 minutes post-slaughter for 30 seconds and 14 were unstimulated (NES) as control. The pH and temperature were monitored every hour for the first 10 hours and subsequently at 24 hours. Carcasses were chilled at 2˚C fo ...
chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... Link together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain Only 20 amino acids ...
... Link together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain Only 20 amino acids ...
Repressilator
... One possible solution: weaker promoters ( < Ktransc ) + strong repressors ( high promoter affinity ) ...
... One possible solution: weaker promoters ( < Ktransc ) + strong repressors ( high promoter affinity ) ...
CHAPTER 4 FREE ENERGY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA
... This procedure may be reversed to study the binding of ligands to proteins such as O2 to Hb or Mb by placing the protein without ligands into a buffer solution in the cellophane bag and then immersing the bag into a similar buffer solution that contains the ligand (say O2) of known concentration. ...
... This procedure may be reversed to study the binding of ligands to proteins such as O2 to Hb or Mb by placing the protein without ligands into a buffer solution in the cellophane bag and then immersing the bag into a similar buffer solution that contains the ligand (say O2) of known concentration. ...
Biochemistry
... • (a) The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide strand. • (b) Hydrogen bonds that form with nearby amino acids coil and fold the polypeptide into α-helices and β-pleated sheets; these constitute the polypeptide’s secondary structure. • (c) The polypeptide ...
... • (a) The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide strand. • (b) Hydrogen bonds that form with nearby amino acids coil and fold the polypeptide into α-helices and β-pleated sheets; these constitute the polypeptide’s secondary structure. • (c) The polypeptide ...
CELB30090 Advanced Cell Biology Prof. Jeremy C
... discovered by Camillo Golgi (Italian biologist, b. 1843) ‐ inventor of new types of staining procedures that he hoped might reveal the organization of nerve cells within the central nervous system applied a silver nitrate‐based stain for several days to cerebellum nerve cells and saw darkly stain ...
... discovered by Camillo Golgi (Italian biologist, b. 1843) ‐ inventor of new types of staining procedures that he hoped might reveal the organization of nerve cells within the central nervous system applied a silver nitrate‐based stain for several days to cerebellum nerve cells and saw darkly stain ...
BrevdueNord.dk PRACTICAL FEEDING FOR PERFORMANCE By
... wing during the race. Regular handling of the bird will give the fancier a guide. Most birds will become race fit with fat levels in the diet around 10-15%. 2. Amino acid balance – As mentioned earlier, amino acids are substances that “clump” together to make proteins. For this reasons they are ofte ...
... wing during the race. Regular handling of the bird will give the fancier a guide. Most birds will become race fit with fat levels in the diet around 10-15%. 2. Amino acid balance – As mentioned earlier, amino acids are substances that “clump” together to make proteins. For this reasons they are ofte ...
Figure 6 The RAD51 ATP-binding site
... pGAT3, a member of the pGAT series of expression vectors that allow production of the target gene fused to a double amino-terminal tag consisting of a six histidine sequence followed by the glutathioneS-transferase protein 35. The BRC4 - RAD51 fusion protein was overexpressed in E. coli strain BL21( ...
... pGAT3, a member of the pGAT series of expression vectors that allow production of the target gene fused to a double amino-terminal tag consisting of a six histidine sequence followed by the glutathioneS-transferase protein 35. The BRC4 - RAD51 fusion protein was overexpressed in E. coli strain BL21( ...
Review Sheet
... devoted to new material than to old material. Also remember that the phrasing, format, and/or specific facts needed to answer the quiz questions may be quite different than what is covered below. I suggest that you study for the quiz as follows: first read over your entire set of lecture/lab/discuss ...
... devoted to new material than to old material. Also remember that the phrasing, format, and/or specific facts needed to answer the quiz questions may be quite different than what is covered below. I suggest that you study for the quiz as follows: first read over your entire set of lecture/lab/discuss ...
carbohydrate, protein and fat.
... Fats coat the flour particles and prevent them from absorbing water. This reduces the formation of gluten development, which would cause the dough to become elastic. Fats such as pure vegetable fats or lard are suitable for shortening because of their low water content. There are distinctive colours ...
... Fats coat the flour particles and prevent them from absorbing water. This reduces the formation of gluten development, which would cause the dough to become elastic. Fats such as pure vegetable fats or lard are suitable for shortening because of their low water content. There are distinctive colours ...
Go-ChIP-Grade™ Purified anti-Histone H3 (C-terminus
... IgG3, κ Isotype Control Antibody (clone MG335), or C) competitor's ChIP-grade Purified anti-Histone H3 Antibody and D) equal amount of matched Isotype Control Antibody as recommended by the manufacturer. The enriched DNA was purified and quantified by real-time qPCR using primers targeting human GAP ...
... IgG3, κ Isotype Control Antibody (clone MG335), or C) competitor's ChIP-grade Purified anti-Histone H3 Antibody and D) equal amount of matched Isotype Control Antibody as recommended by the manufacturer. The enriched DNA was purified and quantified by real-time qPCR using primers targeting human GAP ...
1. Name the two major divisions of metabolism, and
... Breaking starch down into monosaccharides, etc. ...
... Breaking starch down into monosaccharides, etc. ...
CHEM 260 | ELEMENTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY L/L
... - Predict enzyme actions, kinetics, inhibition, and regulation - Classify and name carbohydrates, describe functions, (chemical reactions) (anomeric carbon) - Illustrate steps of glycolysis, name enzymes and possible end products - Classify lipids, name different lipids and identify lipid functions ...
... - Predict enzyme actions, kinetics, inhibition, and regulation - Classify and name carbohydrates, describe functions, (chemical reactions) (anomeric carbon) - Illustrate steps of glycolysis, name enzymes and possible end products - Classify lipids, name different lipids and identify lipid functions ...
Wellness- lesson 03- Proteins
... used for in the body including creating hormones, enzymes, DNA determines how to combine amino acids to build antibodies, and cell components as well as maintaining fluid specific proteins. Every single cell has the capacity to balance. Proteins can also function instruct the body to build the infin ...
... used for in the body including creating hormones, enzymes, DNA determines how to combine amino acids to build antibodies, and cell components as well as maintaining fluid specific proteins. Every single cell has the capacity to balance. Proteins can also function instruct the body to build the infin ...
PDF file
... grinder, the homogenates were centrifuged at 25,000 ×g for 30 min at 4ºC. The supernatant was centrifuged at 150,000 ×g for 2 h at 4ºC and the resulting supernatant (S150) was used as a source of enzymes. Glucosylation of glycogenin Glucose incorporation into glycogenin was measured as described by ...
... grinder, the homogenates were centrifuged at 25,000 ×g for 30 min at 4ºC. The supernatant was centrifuged at 150,000 ×g for 2 h at 4ºC and the resulting supernatant (S150) was used as a source of enzymes. Glucosylation of glycogenin Glucose incorporation into glycogenin was measured as described by ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.