3 Amino acids and crude protein - DLG
... • gaseous losses of N from faeces and urine • result often representative only for short periods of time or weight • feed intake pre-determined ...
... • gaseous losses of N from faeces and urine • result often representative only for short periods of time or weight • feed intake pre-determined ...
08A-MembraneStructure
... for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. ...
... for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. ...
08A-MembraneStructure
... for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. ...
... for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. ...
Oncoprotein metastasis: an expanded topography
... course of cancer disease altogether and, at the same time, reciprocating in oncology the (serum therapy or, respectively, passive immunization) treatment strategy that Victor Babes and Emil von Behring successfully introduced for the treatment of various infectious diseases more than a century ago. ...
... course of cancer disease altogether and, at the same time, reciprocating in oncology the (serum therapy or, respectively, passive immunization) treatment strategy that Victor Babes and Emil von Behring successfully introduced for the treatment of various infectious diseases more than a century ago. ...
ijbbaug
... centchroman. Antiserum raised against centchroman derivative (6a) was found to be most specific, showing <4% crossreactivity with a putative metabolite, 7-desmethyl centchroman (2b). This antiserum, when used in solid phase EIA format, exhibited sensitivity of 250 pg/ml, total assay variance of CV<1 ...
... centchroman. Antiserum raised against centchroman derivative (6a) was found to be most specific, showing <4% crossreactivity with a putative metabolite, 7-desmethyl centchroman (2b). This antiserum, when used in solid phase EIA format, exhibited sensitivity of 250 pg/ml, total assay variance of CV<1 ...
Simultaneous digital counting of DNA, RNA, and Protein
... FIGURE 4: (A) Workflow of multiplexed RNA and protein analysis.(B) Correlation of RNA and protein measurements between the universal cell capture and centrifugation methods. 50,000 PBMCs (universal cell capture) or 500,000 PBMCs (centrifugation method) were used. (C) Correlation between CD3E and CD2 ...
... FIGURE 4: (A) Workflow of multiplexed RNA and protein analysis.(B) Correlation of RNA and protein measurements between the universal cell capture and centrifugation methods. 50,000 PBMCs (universal cell capture) or 500,000 PBMCs (centrifugation method) were used. (C) Correlation between CD3E and CD2 ...
Introducing: TGGE
... In contrast to conventional electrophoresis, in TGGE the migration length does NOT only depend on running time, but rather on the temperature gradient. Extended running times do not necessarily lead to a better separation of bands Instead, the temperature gradient should be ...
... In contrast to conventional electrophoresis, in TGGE the migration length does NOT only depend on running time, but rather on the temperature gradient. Extended running times do not necessarily lead to a better separation of bands Instead, the temperature gradient should be ...
Differences in Total Mitochondrial Proteins and
... reduction of a polypeptide with an approximate molecular out in the presence of cycloheximide, an inhibitor of cytoweight of 36,000 in tumor mitochondria (dashed arrow). Other differences can be detected between tumor and host plasmic but not mitochondrial protein synthesis (11). There fore cytoplas ...
... reduction of a polypeptide with an approximate molecular out in the presence of cycloheximide, an inhibitor of cytoweight of 36,000 in tumor mitochondria (dashed arrow). Other differences can be detected between tumor and host plasmic but not mitochondrial protein synthesis (11). There fore cytoplas ...
Protein Structure - FAU College of Engineering
... Tertiary Structure describes the shapes which form when the secondary spirals of the protein chain further fold up on themselves. ...
... Tertiary Structure describes the shapes which form when the secondary spirals of the protein chain further fold up on themselves. ...
Bioinformatics - Health and Science Pipeline Initiative
... Isolating this group by comparing the hundreds of thousands of genes in each of many genomes would be very impractical. Looking at the proteomes of the cells associated with the disease is much more efficient. ...
... Isolating this group by comparing the hundreds of thousands of genes in each of many genomes would be very impractical. Looking at the proteomes of the cells associated with the disease is much more efficient. ...
Nutritional biochemistry
... 4- Sodium and potassium balance: Na+ and K+ ions are very important for the normal functioning of many cells. Na ions are concentrated outside the cells (extra cellular) and K ions are concentrated inside the cells (intracellular). Protein maintains their concentration outside and inside the cells. ...
... 4- Sodium and potassium balance: Na+ and K+ ions are very important for the normal functioning of many cells. Na ions are concentrated outside the cells (extra cellular) and K ions are concentrated inside the cells (intracellular). Protein maintains their concentration outside and inside the cells. ...
A General Target Selection Method for Crystallographic Proteomics
... Target selection methods take advantage of the data generated by structural genomics projects to identify correlations between protein attributes (determined by sequence analysis) and its success or failure through the expression-purificationcrystallization process. This is then used to extract rule ...
... Target selection methods take advantage of the data generated by structural genomics projects to identify correlations between protein attributes (determined by sequence analysis) and its success or failure through the expression-purificationcrystallization process. This is then used to extract rule ...
Bio 263/F94/T3 V2 - Millersville University
... 44. A molecule is known to bind to calcium ions released into the cytoplasm of a cell causing it to be activated. It then is able to trigger a number of intracellular activities. Of what protein family is this protein likely to be a member? ...
... 44. A molecule is known to bind to calcium ions released into the cytoplasm of a cell causing it to be activated. It then is able to trigger a number of intracellular activities. Of what protein family is this protein likely to be a member? ...
Amino acids
... carbon and hydrogen; energyrich • Functional Groups - Groups of molecules that have definite chemical properties they retain ...
... carbon and hydrogen; energyrich • Functional Groups - Groups of molecules that have definite chemical properties they retain ...
슬라이드 1
... 1. Direct conjugation of drugs or therapeutic proteins to macromolecules such as polymers and proteins. ...
... 1. Direct conjugation of drugs or therapeutic proteins to macromolecules such as polymers and proteins. ...
protein review 2 - Ms. Hart WHS Science
... • Alterations in pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other environmental factors can cause a protein to unravel • This loss of a protein’s native structure is called denaturation • A denatured protein is biologically inactive ...
... • Alterations in pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other environmental factors can cause a protein to unravel • This loss of a protein’s native structure is called denaturation • A denatured protein is biologically inactive ...
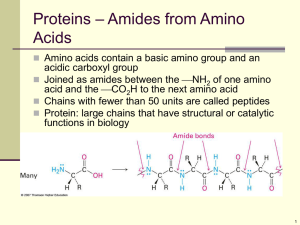
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
... their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
a) Water is a good solvent – all molecules in a living things are
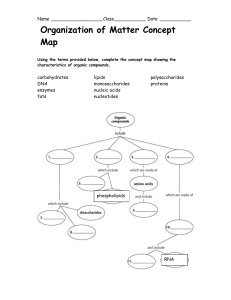
... link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monomers in the chain. 2.1.2. The monomers for different types of polymers are: monosaccharides ...
... link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monomers in the chain. 2.1.2. The monomers for different types of polymers are: monosaccharides ...
Protein-Protein Interactions
... Forces that mediate protein-protein interactions include electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, the van der Waals attraction and hydrophobic effects. The average protein-protein interface is not less polar or more hydrophobic than the surface remaining in contact with the solvent. Water is usua ...
... Forces that mediate protein-protein interactions include electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, the van der Waals attraction and hydrophobic effects. The average protein-protein interface is not less polar or more hydrophobic than the surface remaining in contact with the solvent. Water is usua ...
Chapter 14 Nutrition Nutrients A nutrient is a component of food that
... (i.e. legumes, nuts, grains, etc…) and need to be combined with another incomplete protein to provide all of the essential amino acids to be used in the body Amino acids cannot be stored in the body thus small amounts (2 meat servings) need to be ingested on a daily basis Can proteins be harmful ...
... (i.e. legumes, nuts, grains, etc…) and need to be combined with another incomplete protein to provide all of the essential amino acids to be used in the body Amino acids cannot be stored in the body thus small amounts (2 meat servings) need to be ingested on a daily basis Can proteins be harmful ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.