Lecture Summary MicrobialControl(CH5)
... definitions of the terms bacteriostatic and bactericidal will be important in our discussion of the methods of control. Bacteriostatic refers to something that inhibits bacterial growth while the term bactericidal refers to something that kills bacterial cells. And then there are the terms antisepti ...
... definitions of the terms bacteriostatic and bactericidal will be important in our discussion of the methods of control. Bacteriostatic refers to something that inhibits bacterial growth while the term bactericidal refers to something that kills bacterial cells. And then there are the terms antisepti ...
supporting information file s1
... aggregation of abrin and the UV-induced aggregation of -crystallin as assay systems were carried out, but neither the full length enzyme nor the CTD could protect any of the said proteins from aggregation, ruling out a general chaperonic role for the CTD (Fig. S1). Regulatory role-In order to explo ...
... aggregation of abrin and the UV-induced aggregation of -crystallin as assay systems were carried out, but neither the full length enzyme nor the CTD could protect any of the said proteins from aggregation, ruling out a general chaperonic role for the CTD (Fig. S1). Regulatory role-In order to explo ...
ppt
... The dbEST is a division of GenBank that contains sequence data and other information on “singke-pass” cDNA sequences, from a number of organisms. ...
... The dbEST is a division of GenBank that contains sequence data and other information on “singke-pass” cDNA sequences, from a number of organisms. ...
(Submitted) Genetic Synthesis of Periodic Protein Materials M. J.
... assembled and expressed, by the strategy outlined above for the product 3 protein. This construct features the same @-strand sequence, but a turn of two amino acids rather than three. The basic repeat is ...
... assembled and expressed, by the strategy outlined above for the product 3 protein. This construct features the same @-strand sequence, but a turn of two amino acids rather than three. The basic repeat is ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes Types of Proteins Amino Acids
... groups gives a strong structure • Typical of collagen, connective tissue, skin, tendons, and cartilage ...
... groups gives a strong structure • Typical of collagen, connective tissue, skin, tendons, and cartilage ...
Lab23
... Add dye to PCR samples and load as much of each sample as will fit in the well into the good experimental gel: no air bubbles in tip while loading! Be certain power source is set to 70 VOLTS not AMPS Run gels for ~1.5 hrs (have lecture while waiting) Stain and destain gel Interpret results ...
... Add dye to PCR samples and load as much of each sample as will fit in the well into the good experimental gel: no air bubbles in tip while loading! Be certain power source is set to 70 VOLTS not AMPS Run gels for ~1.5 hrs (have lecture while waiting) Stain and destain gel Interpret results ...
Protein Interaction Profiling of the p97 Adaptor UBXD1 Points to a
... saline (PBS)-Tween-20 (PBS-T) (63 mM Na2HPO4, 15.5 mM NaH2PO4, 7.5 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20) and blocked in 5% milk in PBS-T for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies were added at appropriate dilutions in 5% milk in PBS-T and rocked overnight at 4 °C. Following primary antibody, membranes were ...
... saline (PBS)-Tween-20 (PBS-T) (63 mM Na2HPO4, 15.5 mM NaH2PO4, 7.5 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20) and blocked in 5% milk in PBS-T for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies were added at appropriate dilutions in 5% milk in PBS-T and rocked overnight at 4 °C. Following primary antibody, membranes were ...
Deep architectures for protein contact map prediction
... Strands and helices as periodic structures with periods 2 and 7 respectively. ...
... Strands and helices as periodic structures with periods 2 and 7 respectively. ...
L2 Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes
... Cells may contain several, or have a single large one They have two membranes ► An outer membrane ‐ highly permeable ► And a highly convoluted inner membrane ‐ highly permeable ...
... Cells may contain several, or have a single large one They have two membranes ► An outer membrane ‐ highly permeable ► And a highly convoluted inner membrane ‐ highly permeable ...
Max ARM (Anabolic Recovery Matrix) from Max Muscle Sports
... enzymes Akt/mTOR (rapamycin), a protein kinase and the sequential stimulation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70 S6K) through enhanced translation of specific mRNAs. The Akt/mTOR pathway in muscle is upregulated during the hypertrophy (increase in muscle size) phase.† An exciting area in the molecular ...
... enzymes Akt/mTOR (rapamycin), a protein kinase and the sequential stimulation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70 S6K) through enhanced translation of specific mRNAs. The Akt/mTOR pathway in muscle is upregulated during the hypertrophy (increase in muscle size) phase.† An exciting area in the molecular ...
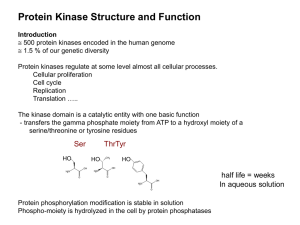
Substrate targeting mechanisms
... Very versatile and pervasive but hard to predict substrate-kinase relationship due to variation in placement and degenerate nature of the motifs Substrates may not look anything like each other except for presence of two short motifs Each kinase can / has evolved tens to hundreds of substrates ...
... Very versatile and pervasive but hard to predict substrate-kinase relationship due to variation in placement and degenerate nature of the motifs Substrates may not look anything like each other except for presence of two short motifs Each kinase can / has evolved tens to hundreds of substrates ...
m5zn_14bea598b5b7901
... Cysteine and Glutamine belong to this group. • Serine, threonine and tyrosine have ‘OH’ group in the side chain • Aspargine and glutamine have amide group (CO-NH) and cysteine has a thiol (-SH) group in the side chain which can be hydrophilic in ...
... Cysteine and Glutamine belong to this group. • Serine, threonine and tyrosine have ‘OH’ group in the side chain • Aspargine and glutamine have amide group (CO-NH) and cysteine has a thiol (-SH) group in the side chain which can be hydrophilic in ...
Computational Pharmacology
... Rotation of the polypeptide chain is permitted around the N-Calpha (angle Phi) and Calpha-C (angle Psi) bonds (except Proline) and the peptide bond (angle omega), which is either trans in most cases (omega=180o) or cis (omega=0o) in rare cases, i.e. at Proline residues. These angles define the backb ...
... Rotation of the polypeptide chain is permitted around the N-Calpha (angle Phi) and Calpha-C (angle Psi) bonds (except Proline) and the peptide bond (angle omega), which is either trans in most cases (omega=180o) or cis (omega=0o) in rare cases, i.e. at Proline residues. These angles define the backb ...
Organic Compounds Powerpoint
... Bonding continues until ultimately you end up with a POLYPEPTIDE (which can have anywhere between 30 to 30,000 amino acids). Another name for a polypeptide is protein. ...
... Bonding continues until ultimately you end up with a POLYPEPTIDE (which can have anywhere between 30 to 30,000 amino acids). Another name for a polypeptide is protein. ...
The bond in the bacteriophage 4x174 gene A protein
... Amino acid analysis or s~uencing of radioactive peptides which can be obtained after cleavage of the A protein-oligo~n~leotide complex with proteolytic enzymes could reveal which of the tyrosine residues in gene A protein are involved in cleavage of and binding to DNA. However, these analyses requir ...
... Amino acid analysis or s~uencing of radioactive peptides which can be obtained after cleavage of the A protein-oligo~n~leotide complex with proteolytic enzymes could reveal which of the tyrosine residues in gene A protein are involved in cleavage of and binding to DNA. However, these analyses requir ...
Class-11
... through the text thoroughly with understanding, it is easy. The were questions like filling tables, matching columns etc. These look easy but you need good solid basics and thinking ability to get through. D.B : The exam had 2 parts theory and practical. The ...
... through the text thoroughly with understanding, it is easy. The were questions like filling tables, matching columns etc. These look easy but you need good solid basics and thinking ability to get through. D.B : The exam had 2 parts theory and practical. The ...
Chapter 1 - Cell Biology Review Extended Response Answers
... h. until a plateau is reached at higher CO2 levels/when another factor is limiting; i. CO2 needed for light independent reactions/Calvin cycle/carboxylation of RuBP/production of glycerate phosphate; If the candidate outlines more than two factors, only mark the first two. Accept the first two point ...
... h. until a plateau is reached at higher CO2 levels/when another factor is limiting; i. CO2 needed for light independent reactions/Calvin cycle/carboxylation of RuBP/production of glycerate phosphate; If the candidate outlines more than two factors, only mark the first two. Accept the first two point ...
Dr. Atiya Abbasi Lecture 04_ IEC_ 16 Jan.ppt
... medium remains constant despite extreme changes in salt concentration or pH thus improving reproducibility and avoiding the need to repack columns. High physical stability and uniformity of particle size facilitate high flow rates, particularly during cleaning or re-equilibration steps, to improve ...
... medium remains constant despite extreme changes in salt concentration or pH thus improving reproducibility and avoiding the need to repack columns. High physical stability and uniformity of particle size facilitate high flow rates, particularly during cleaning or re-equilibration steps, to improve ...
Exam I Review - Iowa State University
... What type of transport protein can move 2 or more different molecules in opposite directions? a. Uniporter b. Antiporter c. Symporter d. Multiporter e. Diporter In the formation of salt, the chlorine atom– a. Gains an electron from sodium b. Becomes a positive ion c. Has one more proton than electro ...
... What type of transport protein can move 2 or more different molecules in opposite directions? a. Uniporter b. Antiporter c. Symporter d. Multiporter e. Diporter In the formation of salt, the chlorine atom– a. Gains an electron from sodium b. Becomes a positive ion c. Has one more proton than electro ...
Guidelines for Abstract Submission
... the dual targeting of the RBP1a (At4g13850), RBP1b (At3g23830), and RPS19 (At5g47320) proteins. Their N-terminal amino acid sequences are relatively conserved, suggesting that they originated by gene duplication after acquisition of the targeting sequence (TS). When the first 39 amino acids of RBP1b ...
... the dual targeting of the RBP1a (At4g13850), RBP1b (At3g23830), and RPS19 (At5g47320) proteins. Their N-terminal amino acid sequences are relatively conserved, suggesting that they originated by gene duplication after acquisition of the targeting sequence (TS). When the first 39 amino acids of RBP1b ...
exon f exon g
... a weighted sum of protein composition over the 20 standard amino acid residue types, where each weight corresponds to the expected change in the score by inserting a specific type of amino acid residue. The weights are estimated from a separate training set of 1,686,320 models generated by MODPIPE. ...
... a weighted sum of protein composition over the 20 standard amino acid residue types, where each weight corresponds to the expected change in the score by inserting a specific type of amino acid residue. The weights are estimated from a separate training set of 1,686,320 models generated by MODPIPE. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Port Washington School District
... acids to the ribosomes where they are eventually assembled into protein chains – Each amino acid is coded for by a different triplet codon on mRNA – tRNA has an anticodon that will pair up with codon on mRNA ...
... acids to the ribosomes where they are eventually assembled into protein chains – Each amino acid is coded for by a different triplet codon on mRNA – tRNA has an anticodon that will pair up with codon on mRNA ...
13 Protein Synthesis Making a Sentence Activity Key
... Follow the instructions below for the three numbers assigned to your group from the sentence code sheet (Page 3). Be sure to fill out the blanks on both pages 1 and 2 as you go. 1. The DNA stays in the nucleus (which is your assigned lab table). The DNA has the sentence code sheet out focusing on th ...
... Follow the instructions below for the three numbers assigned to your group from the sentence code sheet (Page 3). Be sure to fill out the blanks on both pages 1 and 2 as you go. 1. The DNA stays in the nucleus (which is your assigned lab table). The DNA has the sentence code sheet out focusing on th ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.