Chapter 5- Enzymes State Standard Standard 1.b. – Enzymes
... A farm worker accidentally was splashed with a powerful insecticide. A few minutes later, he went into convulsion, stopped breathing, and died. The insecticide was a competitive inhibitor of an enzyme important in the function of the nervous system. 6. Describe the relationship between the structure ...
... A farm worker accidentally was splashed with a powerful insecticide. A few minutes later, he went into convulsion, stopped breathing, and died. The insecticide was a competitive inhibitor of an enzyme important in the function of the nervous system. 6. Describe the relationship between the structure ...
Unit 1 PPT 3 (2biii-iv Binding and conformation)
... • End product inhibition occurs when the final product of a cascade of enzyme reactions interacts with an allosteric site of the first enzyme in the cascade to inhibit it and thus the production of the end product. • This is an example of negative feedback. • End product inhibition animation ...
... • End product inhibition occurs when the final product of a cascade of enzyme reactions interacts with an allosteric site of the first enzyme in the cascade to inhibit it and thus the production of the end product. • This is an example of negative feedback. • End product inhibition animation ...
Enzymes
... There are numerous ways in which enzymes can be inhibited. For example, heat can denature an enzyme, or change its structure, making it unable to bind to a substrate. Enzymes can also be denatured by acidic environments. Many chemical substances interfere with the activity of enzymes by binding to t ...
... There are numerous ways in which enzymes can be inhibited. For example, heat can denature an enzyme, or change its structure, making it unable to bind to a substrate. Enzymes can also be denatured by acidic environments. Many chemical substances interfere with the activity of enzymes by binding to t ...
enzyme
... • Tay-Sachs disease = lack an enzyme necessary for breaking down certain fatty substances in brain and nerve cells • Fabry Disease = A chemical in the body which would normally be broken down builds up and causes damage, mainly to the heart, kidneys and brain •Lysosomal Storage Disorder (i.e Gaucher ...
... • Tay-Sachs disease = lack an enzyme necessary for breaking down certain fatty substances in brain and nerve cells • Fabry Disease = A chemical in the body which would normally be broken down builds up and causes damage, mainly to the heart, kidneys and brain •Lysosomal Storage Disorder (i.e Gaucher ...
... acir alone and in combination with other natural ingredients an weight loss . The study was conducted under controlled circumstances on 60 moderately obese subjects . The findings afte ; 8 weeks of HCA supplemertation were that appetite, Body Mass Index, total cholesterol, low- density lipoproteins, ...
CRYSTAL 24 Abstract Submission Form
... series of mutant proteins that have enhanced activity towards the non-physiological substrates, -naphthyl acetate and p-nitrophenyl acetate. In terms of steady state kinetics, the mutations caused a drop in the Km for the hydrolysis reaction with these two substrates. For the best mutant, there was ...
... series of mutant proteins that have enhanced activity towards the non-physiological substrates, -naphthyl acetate and p-nitrophenyl acetate. In terms of steady state kinetics, the mutations caused a drop in the Km for the hydrolysis reaction with these two substrates. For the best mutant, there was ...
2. Enzyme activity - Lectures For UG-5
... When the enzyme initially introduced to the reactants and the excess substrate is steadily combining with available enzyme, the reaction rate rises. After the enzyme is saturated, the rates of product formation, release of enzyme ,and recombination with more substrate proceed linearly. 6to8 minutes ...
... When the enzyme initially introduced to the reactants and the excess substrate is steadily combining with available enzyme, the reaction rate rises. After the enzyme is saturated, the rates of product formation, release of enzyme ,and recombination with more substrate proceed linearly. 6to8 minutes ...
Enzyclean® IV Multiple Enzyme - Micro
... Enzyclean® IV Multiple Enzyme Detergent is specially formulated for use as a presoak or manual detergent and for use in ultrasonic washers, automatic washing equipment and evacuators. The protease, lipase, amylase and cellulase enzymes in Enzyclean® IV break down organic and inorganic soils, residue ...
... Enzyclean® IV Multiple Enzyme Detergent is specially formulated for use as a presoak or manual detergent and for use in ultrasonic washers, automatic washing equipment and evacuators. The protease, lipase, amylase and cellulase enzymes in Enzyclean® IV break down organic and inorganic soils, residue ...
enzymes - MrsGorukhomework
... enzymes. Many enzymes have Allosteric sites – not active sites- molecules fit into these sites and either activate or inhibit the enzyme by slightly changing the shape. Eg. As the product builds up, the product will non-competitively inhibit the enzyme. This whole type of metabolic pathway, where th ...
... enzymes. Many enzymes have Allosteric sites – not active sites- molecules fit into these sites and either activate or inhibit the enzyme by slightly changing the shape. Eg. As the product builds up, the product will non-competitively inhibit the enzyme. This whole type of metabolic pathway, where th ...
Enzymes - TeacherWeb
... • Proteins (ex: enzymes) are made up of DIFFERENT amino acids sequences (orders) • Each amino acid has different functional groups (R groups) • Different R groups in active site allow enzyme to bind different substrates ...
... • Proteins (ex: enzymes) are made up of DIFFERENT amino acids sequences (orders) • Each amino acid has different functional groups (R groups) • Different R groups in active site allow enzyme to bind different substrates ...
Enzyme
... Reversible inhibitors: The effect is temporary. The inhibiting effect can be eliminated if the reversible inhibitor is removed. Irreversible inhibitors: This kind of inhibitor disrupts the bonds of the polypeptides which form the enzyme. Therefore the shape of the active site is altered permanently ...
... Reversible inhibitors: The effect is temporary. The inhibiting effect can be eliminated if the reversible inhibitor is removed. Irreversible inhibitors: This kind of inhibitor disrupts the bonds of the polypeptides which form the enzyme. Therefore the shape of the active site is altered permanently ...
can
... • Neuraminidase is attached to the viral surface by a single hydrophobic sequence of 29 amino acids • The enzyme can be easily mutated. There are two main types corresponding to influenza A and B. • However, the active site is located in a deep pocket and the 18 amino acids making up the active site ...
... • Neuraminidase is attached to the viral surface by a single hydrophobic sequence of 29 amino acids • The enzyme can be easily mutated. There are two main types corresponding to influenza A and B. • However, the active site is located in a deep pocket and the 18 amino acids making up the active site ...
Altering enzyme activities using chemical modification Claire Louise
... advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twenty proteogenic amino acids. By using chemical modification we have produced a protein containing a non-natural amino acid at hi ...
... advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twenty proteogenic amino acids. By using chemical modification we have produced a protein containing a non-natural amino acid at hi ...
3 - IBperiod5
... allosteric regulation- regulatory molecules bind on the enzyme and change its shape either activating it, or inactivating it. An allosteric enzyme is made of more than one polypeptide chain. There are two non-competitive sites. One non-competitive site activates the enzyme, the other non-competitive ...
... allosteric regulation- regulatory molecules bind on the enzyme and change its shape either activating it, or inactivating it. An allosteric enzyme is made of more than one polypeptide chain. There are two non-competitive sites. One non-competitive site activates the enzyme, the other non-competitive ...
Enzymes
... microenvironment for a specific reaction. Enzymes may even bind covalently to substrates in an intermediate step before returning to normal. ...
... microenvironment for a specific reaction. Enzymes may even bind covalently to substrates in an intermediate step before returning to normal. ...
Enzyme WebQuest
... Enzymes control cellular reactions. As you remember, reactions that break down substances and release energy are called catabolic reactions. Examples are __________ and _____________. The other types of reactions are called anabolic reactions. These reactions consume (_________) energy. These reacti ...
... Enzymes control cellular reactions. As you remember, reactions that break down substances and release energy are called catabolic reactions. Examples are __________ and _____________. The other types of reactions are called anabolic reactions. These reactions consume (_________) energy. These reacti ...
Enzymes
... In many pathways, the product of the last reaction, attaches to the enzyme that catalyses the first reaction and inhibits that enzyme This is called end-product inhibition The enzyme that is inhibited is an example of an allosteric enzyme This is a type of noncompetitive inhibition that contr ...
... In many pathways, the product of the last reaction, attaches to the enzyme that catalyses the first reaction and inhibits that enzyme This is called end-product inhibition The enzyme that is inhibited is an example of an allosteric enzyme This is a type of noncompetitive inhibition that contr ...
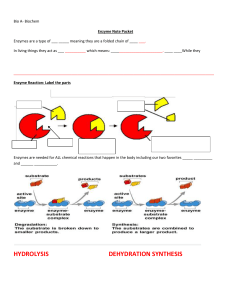
Bio A- Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of ___
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
Enzyme Review - Explore Biology
... is increased gradually from 10°C to 30°C. Explain your answer. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 22. What ...
... is increased gradually from 10°C to 30°C. Explain your answer. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 22. What ...
Name: Date: Per: ______ EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... solution (product) is measured at time zero and at five-minute intervals. In this procedure an increase in solution is related to the amount of product formed during the reaction. The experiment is conducted using the three preparations shown in the table below. ...
... solution (product) is measured at time zero and at five-minute intervals. In this procedure an increase in solution is related to the amount of product formed during the reaction. The experiment is conducted using the three preparations shown in the table below. ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction?
... Energy needed to start a reaction Identify the activation energy supplied for the following chemical reactions 1) Building a Fire 2) Turning on a Light 3) Starting a Car ...
... Energy needed to start a reaction Identify the activation energy supplied for the following chemical reactions 1) Building a Fire 2) Turning on a Light 3) Starting a Car ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Option C
... If an organism is starving, protein can be used as a source of energy. Protein is split into amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In e ...
... If an organism is starving, protein can be used as a source of energy. Protein is split into amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In e ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.