Unit 3: Chapter 6
... f. Factors that Effect Enzyme Activity i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and n ...
... f. Factors that Effect Enzyme Activity i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and n ...
chapter 8 notes - 8.4 and 8.5 - APBio09-10
... Organic cofactors are called coenzymes i. Vitamins act as coenzymes or help form coenzymes 4. Enzyme Inhibitors a. If an inhibitors attaches itself with covalent bonds, inhibition is usually irreversible b. Most inhibitors bind via weak bonds and ARE reversible c. Competitive Inhibitors i. Resemble ...
... Organic cofactors are called coenzymes i. Vitamins act as coenzymes or help form coenzymes 4. Enzyme Inhibitors a. If an inhibitors attaches itself with covalent bonds, inhibition is usually irreversible b. Most inhibitors bind via weak bonds and ARE reversible c. Competitive Inhibitors i. Resemble ...
Enzyme - Madison Public Schools
... • More accurate model of enzyme action – 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate – substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit • “conformational change” • bring chemical groups in position to catalyze reaction ...
... • More accurate model of enzyme action – 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate – substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit • “conformational change” • bring chemical groups in position to catalyze reaction ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
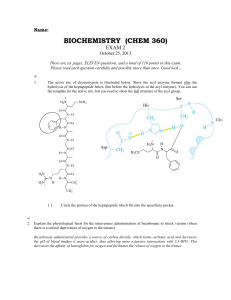
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
Lecture Resource ()
... In the PLP-dependent reactions, the bond cleaved in the first step of the reaction depends on the conformation of the amino acid that the enzyme binds ...
... In the PLP-dependent reactions, the bond cleaved in the first step of the reaction depends on the conformation of the amino acid that the enzyme binds ...
Enzymes are specific? - The BioUpdate Foundation
... biological catalyst), typically a protein, is isolated and found to be responsible for that activity. This protein is not tested for any other activities and thus it enters the literature as having only one function. The literature is full of hundreds, if not thousands, of examples of enzymes which ...
... biological catalyst), typically a protein, is isolated and found to be responsible for that activity. This protein is not tested for any other activities and thus it enters the literature as having only one function. The literature is full of hundreds, if not thousands, of examples of enzymes which ...
Chem452_Quiz_2
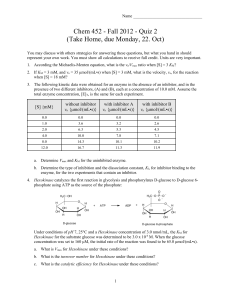
... (Take Home, due Monday, 22. Oct) You may discuss with others strategies for answering these questions, but what you hand in should represent your own work. You must show all calculations to receive full credit. Units are very important. 1. According the Michaelis-Menten equation, what is the vo/Vmax ...
... (Take Home, due Monday, 22. Oct) You may discuss with others strategies for answering these questions, but what you hand in should represent your own work. You must show all calculations to receive full credit. Units are very important. 1. According the Michaelis-Menten equation, what is the vo/Vmax ...
Organic vs. Inorganic
... things undergo thousands of chemical reactions as part of the life process ...
... things undergo thousands of chemical reactions as part of the life process ...
Bio H - Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of
... Some chemical reactions are spontaneous, and require no additional energy. But many require at least a small amount of activation energy. Chemical reactions release energy which means that the _________________________ have more energy than ________________________. These are called ________________ ...
... Some chemical reactions are spontaneous, and require no additional energy. But many require at least a small amount of activation energy. Chemical reactions release energy which means that the _________________________ have more energy than ________________________. These are called ________________ ...
Enzymes
... – Definition: The sum total of all biochemical activity that takes place in a living organism • Catabolic Metabolism – break down – AB = A & B ...
... – Definition: The sum total of all biochemical activity that takes place in a living organism • Catabolic Metabolism – break down – AB = A & B ...
Unit 1 Review
... 1. For each of the following patient scenarios, say what vitamin the patient is most likely lacking. A) A child has been diagnosed with Rickets, a disease that prevents proper bone formation. B) A mother accidentally cuts her finger while cutting onions for dinner. However, her cut does not stop ble ...
... 1. For each of the following patient scenarios, say what vitamin the patient is most likely lacking. A) A child has been diagnosed with Rickets, a disease that prevents proper bone formation. B) A mother accidentally cuts her finger while cutting onions for dinner. However, her cut does not stop ble ...
chemical reactions
... Most genetic disorders are due to a deficiency in enzyme function. This archival photo shows three children with the enzyme deficiency that causes phenylketonuria. ...
... Most genetic disorders are due to a deficiency in enzyme function. This archival photo shows three children with the enzyme deficiency that causes phenylketonuria. ...
Chapter 5 – Homework
... ½ pt – All are made by the same reaction, dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction. 2. Identify what function group monosaccharides have in abundance. Describe what properties this functional group give these molecules. 1 pt total ½ pt – they have multiple hydroxyl groups ½ pt – the molecules ...
... ½ pt – All are made by the same reaction, dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction. 2. Identify what function group monosaccharides have in abundance. Describe what properties this functional group give these molecules. 1 pt total ½ pt – they have multiple hydroxyl groups ½ pt – the molecules ...
General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis and Maud
... In noncompetitive inhibition, which also is reversible, the inhibitor and substrate can bind simultaneously to an enzyme molecule at different binding sites . A noncompetitive inhibitor acts by decreasing the turnover number rather than by diminishing the proportion of enzyme molecules that are boun ...
... In noncompetitive inhibition, which also is reversible, the inhibitor and substrate can bind simultaneously to an enzyme molecule at different binding sites . A noncompetitive inhibitor acts by decreasing the turnover number rather than by diminishing the proportion of enzyme molecules that are boun ...
CHAPTER-II ENZYMES
... Strychnine binds to an alternate site that reduces the affinity of the glycine receptor for glycine, resulting in convulsions due to lessened inhibition by the glycine. In competitive inhibition the maximal rate of the reaction is not changed, but higher substrate concentrations are required to rea ...
... Strychnine binds to an alternate site that reduces the affinity of the glycine receptor for glycine, resulting in convulsions due to lessened inhibition by the glycine. In competitive inhibition the maximal rate of the reaction is not changed, but higher substrate concentrations are required to rea ...
enzymes - charlestonbiology
... substrate to be able to function Substrate concentration: At low concentrations, the reaction rate is low - too few substrates to fill the active sites Increasing concentration, more active sites filled - increasing rate of reaction Eventually all active sites are filled ...
... substrate to be able to function Substrate concentration: At low concentrations, the reaction rate is low - too few substrates to fill the active sites Increasing concentration, more active sites filled - increasing rate of reaction Eventually all active sites are filled ...
Ch7 Enzymes II: Coenzymes, Regulation, Abzymes, and Ribozymes
... – M and H are made from two separate genes, are similar in amino acid sequence but can be separated by electrophoresis. – M4 in skeletal muscle – H4 in heart muscle – Mixture of five possible forms (M4, M3H, M2H2, MH3, H4) in ...
... – M and H are made from two separate genes, are similar in amino acid sequence but can be separated by electrophoresis. – M4 in skeletal muscle – H4 in heart muscle – Mixture of five possible forms (M4, M3H, M2H2, MH3, H4) in ...
Enzyme Activity
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
Lecture #2 – Review of Protein Chemistry, Enzyme Specificity
... In this case, the R group looks nothing like a peptide, yet the enzyme is still active. The product here is an intermediate in the production of a pharmaceutical compound that was investigated for the treatment of benign prostate enlargement. This example raises two issues about enzyme specificity. ...
... In this case, the R group looks nothing like a peptide, yet the enzyme is still active. The product here is an intermediate in the production of a pharmaceutical compound that was investigated for the treatment of benign prostate enlargement. This example raises two issues about enzyme specificity. ...
Mic 428 Lecture 11
... Enzyme B is also synthesized constitutively but its activity can be inhibited. The synthesis of the product of gene C can be prevented by control at the level of translation. The synthesis of the product of gene D can be prevented by control at the level of transcription. ...
... Enzyme B is also synthesized constitutively but its activity can be inhibited. The synthesis of the product of gene C can be prevented by control at the level of translation. The synthesis of the product of gene D can be prevented by control at the level of transcription. ...
Covalent Inhibition
... Note that the apparent pKa derived from inspection of kinetic data may be significantly different than the actual pKa of the sidechain. More sophisticated analysis is required to obtain an accurate estimation of the pKa in the enzyme. ...
... Note that the apparent pKa derived from inspection of kinetic data may be significantly different than the actual pKa of the sidechain. More sophisticated analysis is required to obtain an accurate estimation of the pKa in the enzyme. ...
Class3 POGIL Enzyme Mechanics Worksheet
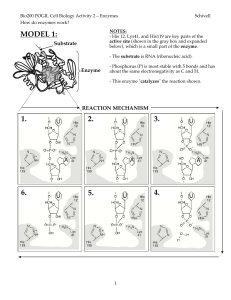
... 12. How does reaction speed change when the active site is changed? _____________________ 13. a. Is the relative position of a specific R-group within an active site important? _________ b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and ...
... 12. How does reaction speed change when the active site is changed? _____________________ 13. a. Is the relative position of a specific R-group within an active site important? _________ b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.