IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008.
... carbon of the scissile peptide bond of the substrate. A pair of electrons on the histidine nitrogen has the ability to accept the hydrogen from the serine -OH group, thus coordinating the attack of the peptide bond. The carboxyl group on the aspartic acid in turn forms hydrogen bonds with histidine, ...
... carbon of the scissile peptide bond of the substrate. A pair of electrons on the histidine nitrogen has the ability to accept the hydrogen from the serine -OH group, thus coordinating the attack of the peptide bond. The carboxyl group on the aspartic acid in turn forms hydrogen bonds with histidine, ...
01_Introduction. Structure, properties and biological functions
... •Inhibitor binds as a substrate and is initially processed by the normal catalytic mechanism •It then generates a chemically reactive intermediate that inactivates the enzyme through covalent modification •Suicide because enzyme participates in its own irreversible inhibition ...
... •Inhibitor binds as a substrate and is initially processed by the normal catalytic mechanism •It then generates a chemically reactive intermediate that inactivates the enzyme through covalent modification •Suicide because enzyme participates in its own irreversible inhibition ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY - Georgia Institute of Technology
... GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Phosphate Binding Pi ...
... GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Phosphate Binding Pi ...
BI1
... As soon as possible send the Chief Examiner/Team Leader 10 marked and checked scripts, together with a stamped addressed envelope and your telephone number. Marking may continue once these have been checked and a reply given. It is essential that marked scripts are returned in batches of approximate ...
... As soon as possible send the Chief Examiner/Team Leader 10 marked and checked scripts, together with a stamped addressed envelope and your telephone number. Marking may continue once these have been checked and a reply given. It is essential that marked scripts are returned in batches of approximate ...
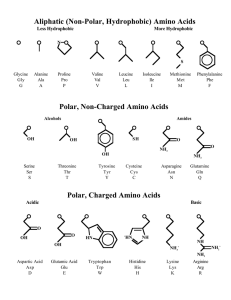
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
THE CENTRAL DOGMA THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... Even the simplest proteins can assume many different conformations. ...
... Even the simplest proteins can assume many different conformations. ...
Enzyme Power Point
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
Enzymes - myndrs.com
... D. Enzymes • Cells contain many different enzymes, each of which catalyzes a different reaction. • They cannot speed up reactions that would not normally occur on their own. • A given enzyme interacts with a set of reactants (called substrates) or occasionally with a few closely related ones. ...
... D. Enzymes • Cells contain many different enzymes, each of which catalyzes a different reaction. • They cannot speed up reactions that would not normally occur on their own. • A given enzyme interacts with a set of reactants (called substrates) or occasionally with a few closely related ones. ...
Unit 1 PPT 3 (2biii-iv Binding and conformation)
... of a protein • Enzymes and proteins are three-dimensional and have a specific shape or conformation. • As a ligand binds to a protein binding site, or a substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site, the conformation of the protein changes. • This change in conformation causes a functional change in th ...
... of a protein • Enzymes and proteins are three-dimensional and have a specific shape or conformation. • As a ligand binds to a protein binding site, or a substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site, the conformation of the protein changes. • This change in conformation causes a functional change in th ...
9. AH Cell Enzymes - charlestonbiology
... Catabolic Reactions • These release energy through the BREAKDOWN of large molecules into smaller units e.g. Cellular Respiration: ATP ADP + Pi • Also known as exothermic reactions ...
... Catabolic Reactions • These release energy through the BREAKDOWN of large molecules into smaller units e.g. Cellular Respiration: ATP ADP + Pi • Also known as exothermic reactions ...
answer - RogueBCHES.com
... a) The _____________ noncovalent binding interaction is used to capture ligand-binding entities in the “affinity capture” technique. b) Two examples of reversible factors that control the catalytic capability of an enzyme are: ______________, ________________ c) A zymogen is a protein that is conver ...
... a) The _____________ noncovalent binding interaction is used to capture ligand-binding entities in the “affinity capture” technique. b) Two examples of reversible factors that control the catalytic capability of an enzyme are: ______________, ________________ c) A zymogen is a protein that is conver ...
C483 Practice Final Exam
... 19. ______ Which of the statements concerning a near-equilibrium reaction is TRUE? A. The concentrations of reactants and products are nearly equal under cellular conditions B. The enzyme catalyzed reaction is most likely regulated. C. The standard free energy of the reaction must be near zero. D. ...
... 19. ______ Which of the statements concerning a near-equilibrium reaction is TRUE? A. The concentrations of reactants and products are nearly equal under cellular conditions B. The enzyme catalyzed reaction is most likely regulated. C. The standard free energy of the reaction must be near zero. D. ...
Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by
... The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. A protein may consist of a single ...
... The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. A protein may consist of a single ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Special inhibition • End product inhibition • E.g. phospofructokinase an enzyme used in production of ATP lots of ATP inhibit it’s production – makes sense really • Enzyme inhibition – inactive precursors e.g. ...
... Special inhibition • End product inhibition • E.g. phospofructokinase an enzyme used in production of ATP lots of ATP inhibit it’s production – makes sense really • Enzyme inhibition – inactive precursors e.g. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... dipeptide_ 22. Two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond is called this. nucleic acids_23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ion_ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. neutral_ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
... dipeptide_ 22. Two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond is called this. nucleic acids_23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ion_ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. neutral_ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.