OPTICAL LINK OF THE ATLAS PIXEL DETECTOR
... of data bits (logic level 0), the resulting signal is a 20 MHz square wave. Data bits are encoded as an extra transition at beam-crossing clock trailing edges. The amplitude of the current from the PIN diode is expected to be in the range of 40-1000 µA. The 40 MHz clock recovered by the DORIC is req ...
... of data bits (logic level 0), the resulting signal is a 20 MHz square wave. Data bits are encoded as an extra transition at beam-crossing clock trailing edges. The amplitude of the current from the PIN diode is expected to be in the range of 40-1000 µA. The 40 MHz clock recovered by the DORIC is req ...
debug0
... Know what to expect at each stage Inputs on SSI and MSI logic can be grounded for short time Don't connect unused inputs directly to +5 V CMOS or some TTL Output present then goes away after input probed Open input Learn to recognize proper output levels TTL - 0.4 - 3.5 CMOS - 0.0 - 4.8 If any failu ...
... Know what to expect at each stage Inputs on SSI and MSI logic can be grounded for short time Don't connect unused inputs directly to +5 V CMOS or some TTL Output present then goes away after input probed Open input Learn to recognize proper output levels TTL - 0.4 - 3.5 CMOS - 0.0 - 4.8 If any failu ...
Spur-Reduction Frequency Synthesizer Exploiting Randomly
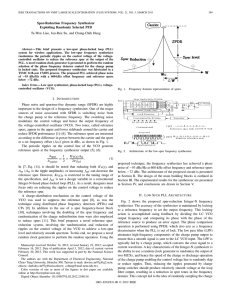
... noise of −93 dBc/Hz at 600-kHz offset frequency and reference spurs below −72 dBc. The architecture of the proposed circuit is presented in Section II. The design of the main building blocks is outlined in Section III. The experimental results for the synthesizer are presented in Section IV, and con ...
... noise of −93 dBc/Hz at 600-kHz offset frequency and reference spurs below −72 dBc. The architecture of the proposed circuit is presented in Section II. The design of the main building blocks is outlined in Section III. The experimental results for the synthesizer are presented in Section IV, and con ...
Pulse Width Modulation Amplifiers
... supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infr ...
... supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infr ...
Circuit Note - Analog Devices
... The interposer circuit relies upon two ADN4651 600 Mbps LVDS isolators to isolate the LVDS interface to the AD7960. As shown in Figure 1, two LVDS clocks are sent from the Spartan 6 FPGA to the AD7960; the 5 MHz sample clock (CNV±) and a 300 MHz reference clock (CLK±). The AD7960 uses the 300 MHz re ...
... The interposer circuit relies upon two ADN4651 600 Mbps LVDS isolators to isolate the LVDS interface to the AD7960. As shown in Figure 1, two LVDS clocks are sent from the Spartan 6 FPGA to the AD7960; the 5 MHz sample clock (CNV±) and a 300 MHz reference clock (CLK±). The AD7960 uses the 300 MHz re ...
A/D Converter Specifications (Cont.)
... Has a up/down counter controlled by the comparator. If the input signal is higher or lower than the output of the D/A converter, the counter counts up or down, respectively. May quickly converge to the correct digital value when the signal is not changing rapidly. May have to count through its full ...
... Has a up/down counter controlled by the comparator. If the input signal is higher or lower than the output of the D/A converter, the counter counts up or down, respectively. May quickly converge to the correct digital value when the signal is not changing rapidly. May have to count through its full ...
WEEKLY PROGRESS REPORT Student: Rizal Maulana 102521603
... Figure 1 shows the pinout of the NI-USB 6008. Analog input signal names are listed as single-ended analog input name, AI x, and then differential analog input name, (AI x+/-). Refer to Table 2 for a detailed description of each signal. ...
... Figure 1 shows the pinout of the NI-USB 6008. Analog input signal names are listed as single-ended analog input name, AI x, and then differential analog input name, (AI x+/-). Refer to Table 2 for a detailed description of each signal. ...
DS1020 Programmable 8-Bit Silicon Delay Line • FEATURES
... Maximum flexibility is obtained when the eight parallel programming bits are set using computer-generated data. When the data setup (tDSE) and data hold (tDHE) requirements are observed, the enable pin can be used to latch data supplied on an 8-bit bus. Enable must be held at a logic 1 if it is not ...
... Maximum flexibility is obtained when the eight parallel programming bits are set using computer-generated data. When the data setup (tDSE) and data hold (tDHE) requirements are observed, the enable pin can be used to latch data supplied on an 8-bit bus. Enable must be held at a logic 1 if it is not ...
Time-to-digital converter

In electronic instrumentation and signal processing, a time to digital converter (abbreviated TDC) is a device for recognizing events and providing a digital representation of the time they occurred. For example, a TDC might output the time of arrival for each incoming pulse. Some applications wish to measure the time interval between two events rather than some notion of an absolute time.In electronics time-to-digital converters (TDCs) or time digitizers are devices commonly used to measure a time interval and convert it into digital (binary) output. In some cases interpolating TDCs are also called time counters (TCs).TDCs are used in many different applications, where the time interval between two signal pulses (start and stop pulse) should be determined. Measurement is started and stopped, when either the rising or the falling edge of a signal pulse crosses a set threshold. These requirements are fulfilled in many physical experiments, like time-of-flight and lifetime measurements in atomic and high energy physics, experiments that involve laser ranging and electronic research involving the testing of integrated circuits and high-speed data transfer.