Sentence Parts Cheat Sheet
... The answer to the “Subject Verb What?” question may not be a direct object. It could be a predicate nominative. A predicate nominative is a noun or a pronoun. It could replace or rename the subject. One is saying that the subject IS that thing. You could even switch the subject and the predicate nom ...
... The answer to the “Subject Verb What?” question may not be a direct object. It could be a predicate nominative. A predicate nominative is a noun or a pronoun. It could replace or rename the subject. One is saying that the subject IS that thing. You could even switch the subject and the predicate nom ...
The national curriculum in England
... An active verb has its usual pattern of subject and object (in contrast with the passive). ...
... An active verb has its usual pattern of subject and object (in contrast with the passive). ...
English_Glossary National Curriculum
... An active verb has its usual pattern of subject and object (in contrast with the passive). ...
... An active verb has its usual pattern of subject and object (in contrast with the passive). ...
the parts of speech
... when they tell us to what extent: Mary ran very quickly. Or Mary is extremely pretty. Or Mary is too skilled at soccer to enjoy being on a losing team. ...
... when they tell us to what extent: Mary ran very quickly. Or Mary is extremely pretty. Or Mary is too skilled at soccer to enjoy being on a losing team. ...
Minimum of English Grammar
... years’, the Present Perfect grammar allows you to talk in the present tense about the ongoing smoking done over the twenty years (in the past). In relation to this same grammar, the Past Perfect then allows you to remove yourself from that same present tense reference point and to speak in totality ...
... years’, the Present Perfect grammar allows you to talk in the present tense about the ongoing smoking done over the twenty years (in the past). In relation to this same grammar, the Past Perfect then allows you to remove yourself from that same present tense reference point and to speak in totality ...
Parts of Speech: How Words Are Used
... Nouns—These are the names of something (people, places, things, ideas). Common nouns are non-specific (girl, city, baseball team) while proper nouns refer to a specific person, place, or thing (Britney Spears, Seattle, New York Yankees). Concrete nouns refer to actual, physical items (pizza, dog, Jo ...
... Nouns—These are the names of something (people, places, things, ideas). Common nouns are non-specific (girl, city, baseball team) while proper nouns refer to a specific person, place, or thing (Britney Spears, Seattle, New York Yankees). Concrete nouns refer to actual, physical items (pizza, dog, Jo ...
Easy to understand Fr 9 Grammar booklet
... The negative of the present tense. If a verb is in the negative then the subject is NOT doing the action. For example—she doesn’t dance. He is not speaking. We are not eating. In French the negative is formed by sandwiching the CONJUGATED verb with ne or n’ and pas. Example: Je ne danse pas. (I don’ ...
... The negative of the present tense. If a verb is in the negative then the subject is NOT doing the action. For example—she doesn’t dance. He is not speaking. We are not eating. In French the negative is formed by sandwiching the CONJUGATED verb with ne or n’ and pas. Example: Je ne danse pas. (I don’ ...
Predicate Adjectives and Predicate Nouns Power Point
... • Earlier we learned that a direct object receives the action of the action verb. • Now we are learning that a predicate noun is linked to the subject by a linking verb. • Remember that linking verbs act like equals signs. The Subject = Predicate Noun ...
... • Earlier we learned that a direct object receives the action of the action verb. • Now we are learning that a predicate noun is linked to the subject by a linking verb. • Remember that linking verbs act like equals signs. The Subject = Predicate Noun ...
LECT 3B
... In a non-finite verb phrase, all verbs are non-finite. There are three types of non-finite verb phrases, the to infinitive, the ing participle, and the -ed participle. Non-finite verb phrases normally do not occur as the verb phrase of an independent sentence. That is, they are always embedded ...
... In a non-finite verb phrase, all verbs are non-finite. There are three types of non-finite verb phrases, the to infinitive, the ing participle, and the -ed participle. Non-finite verb phrases normally do not occur as the verb phrase of an independent sentence. That is, they are always embedded ...
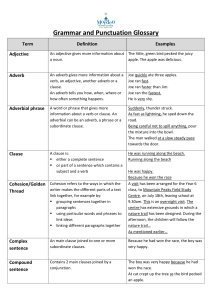
Grammar and Punctuation Glossary
... An adverb gives more information about a verb, an adjective, another adverb or a clause. An adverb tells you how, when, where or how often something happens. ...
... An adverb gives more information about a verb, an adjective, another adverb or a clause. An adverb tells you how, when, where or how often something happens. ...
Transformations
... Intransitive verb is complete in itself even when there is no object. Examples: S IV (where) English language is used in the world today. S IV (where) The Angles came from Engle. S IV (where) Most of the Celtic speakers were pushed into Wales, Cornwall and Scotland. NOTE: The above verbs have no obj ...
... Intransitive verb is complete in itself even when there is no object. Examples: S IV (where) English language is used in the world today. S IV (where) The Angles came from Engle. S IV (where) Most of the Celtic speakers were pushed into Wales, Cornwall and Scotland. NOTE: The above verbs have no obj ...
English Glossary - Pinchbeck East Church of England Primary
... air through the vocal tract, usually using lips, tongue or teeth. Most of the letters of the alphabet ...
... air through the vocal tract, usually using lips, tongue or teeth. Most of the letters of the alphabet ...
English glossary - Goostrey Community Primary School
... air through the vocal tract, usually using lips, tongue or teeth. Most of the letters of the alphabet ...
... air through the vocal tract, usually using lips, tongue or teeth. Most of the letters of the alphabet ...
Brush Strokes
... and down into the water. – Gary Paulsen Examples: Roaring a loud warning screech, the elephant charged the lions. (participle brush stroke phrase) Trailing, tracking, accelerating, the cheetah gained on the injured zebra. (3 participles used together for effect) Write your own example below. _______ ...
... and down into the water. – Gary Paulsen Examples: Roaring a loud warning screech, the elephant charged the lions. (participle brush stroke phrase) Trailing, tracking, accelerating, the cheetah gained on the injured zebra. (3 participles used together for effect) Write your own example below. _______ ...
Catullus 51 - WhippleHill
... d. Horace 2. To whom does ille refer in lines 1 and 2? a. Publius Clodius Pulcher b. Lesbia c. Marcus Caelius Rufus d. Quintus Caecilius Metellus 3. What use of the infinitive can be seen in line 2? a. historical b. indirect statement c. complementary d. objective ...
... d. Horace 2. To whom does ille refer in lines 1 and 2? a. Publius Clodius Pulcher b. Lesbia c. Marcus Caelius Rufus d. Quintus Caecilius Metellus 3. What use of the infinitive can be seen in line 2? a. historical b. indirect statement c. complementary d. objective ...
What is subject-verb agreement?
... An expression of amount may be singular or plural, depending on how it is used. An expression of amount is • singular when the amount is thought of as a unit Three fourths of the pizza ...
... An expression of amount may be singular or plural, depending on how it is used. An expression of amount is • singular when the amount is thought of as a unit Three fourths of the pizza ...
LING 220 LECTURE #12 SYNTAX: THE ANALYSIS OF SENTENCE
... Adjectives → they designate properties or attributes of nouns (small, white) ...
... Adjectives → they designate properties or attributes of nouns (small, white) ...
Abbreviations and Initials
... comma to separate three or more words in a series. Use a comma before the word and, but, or or when two sentences are combined. Use a comma to separate a word used in direct address from a sentence. Use a comma between quotation and the rest of the sentence. ...
... comma to separate three or more words in a series. Use a comma before the word and, but, or or when two sentences are combined. Use a comma to separate a word used in direct address from a sentence. Use a comma between quotation and the rest of the sentence. ...
Using Subject-Verb Agreement
... An expression of amount may be singular or plural, depending on how it is used. An expression of amount is • singular when the amount is thought of as a unit Three fourths of the pizza ...
... An expression of amount may be singular or plural, depending on how it is used. An expression of amount is • singular when the amount is thought of as a unit Three fourths of the pizza ...
GRAMMAR REVIEW
... conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
... conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
grammar review
... conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
... conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
grammar guide - North Salem Central School District
... Hanged, not hung, should be used when referring to executions: convicted killers are hanged; posters are hung. Use have, not of, as an auxiliary verb with could, must, should, would, may, and might. Of is a preposition. Its is a possessive pronoun. It's is a contraction of "it is" or occasionally "i ...
... Hanged, not hung, should be used when referring to executions: convicted killers are hanged; posters are hung. Use have, not of, as an auxiliary verb with could, must, should, would, may, and might. Of is a preposition. Its is a possessive pronoun. It's is a contraction of "it is" or occasionally "i ...