Practice in IDing Variables
... (8-10% AP Exam) Textbook: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 Overview: Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. There have been significant changes in the theories that psychologists use to explain behavior and mental processes. In addition, the methodology of psychological res ...
... (8-10% AP Exam) Textbook: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 Overview: Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. There have been significant changes in the theories that psychologists use to explain behavior and mental processes. In addition, the methodology of psychological res ...
The History of Psychology
... •First American psychologist •Started psychology at Harvard in 1870s •Opposed Wundt and Titchener’s approach •Author of the first psychology ...
... •First American psychologist •Started psychology at Harvard in 1870s •Opposed Wundt and Titchener’s approach •Author of the first psychology ...
AP Psych Chapter 1 notes
... Showed humans are not above the laws of nature Can be studied like other animals Inspired others to apply the scientific method to our own species paving the way for modern psychology Wundt and Titchener: Structuralism First formal lab – tried to study everything about perception – was a little over ...
... Showed humans are not above the laws of nature Can be studied like other animals Inspired others to apply the scientific method to our own species paving the way for modern psychology Wundt and Titchener: Structuralism First formal lab – tried to study everything about perception – was a little over ...
History and Approaches - Airport Senior High School
... • James proposed a countering point of view called functionalism, in which the way the mind allows us to adapt is stressed. • Functionalism is influenced the modern fields of educational psychology, evolutionary psychology and industrial/organization psychology. ...
... • James proposed a countering point of view called functionalism, in which the way the mind allows us to adapt is stressed. • Functionalism is influenced the modern fields of educational psychology, evolutionary psychology and industrial/organization psychology. ...
The Science of Psychology - Columbus State University
... Behaviorism: Watson & Skinner • Founder - John B. Watson • Goal - Psychologists should study only “observable behaviors” • Watson & Raynor’s (1921) “Little Albert Study” demonstrated that Pavlov’s classical conditioning works in humans • B. F. Skinner - focused on Operant (Instrumental) conditionin ...
... Behaviorism: Watson & Skinner • Founder - John B. Watson • Goal - Psychologists should study only “observable behaviors” • Watson & Raynor’s (1921) “Little Albert Study” demonstrated that Pavlov’s classical conditioning works in humans • B. F. Skinner - focused on Operant (Instrumental) conditionin ...
Unit 2: Vocab List and Objectives
... (8-10% AP Exam) Textbook: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 Overview: Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. There have been significant changes in the theories that psychologists use to explain behavior and mental processes. In addition, the methodology of psychological res ...
... (8-10% AP Exam) Textbook: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 Overview: Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. There have been significant changes in the theories that psychologists use to explain behavior and mental processes. In addition, the methodology of psychological res ...
Scope of Psychology
... one that stresses the role of intellectual discernment while at the same time highlighting his conviction that no amount of discernment is sufficient to account for what we might refer to, for want of a better phrase, as the phenomenology of internal moral conflict. ...
... one that stresses the role of intellectual discernment while at the same time highlighting his conviction that no amount of discernment is sufficient to account for what we might refer to, for want of a better phrase, as the phenomenology of internal moral conflict. ...
Early Roots in Philosophy
... Functionalsim (Analyze the function of consciousness, not its structure. how does consciousness help us to adapt to a changing environment?) Using Charles Darwin’s (1809 – 1882) theory of Natural Selection, James proposed that the mind must serve some important purpose related to the survival of th ...
... Functionalsim (Analyze the function of consciousness, not its structure. how does consciousness help us to adapt to a changing environment?) Using Charles Darwin’s (1809 – 1882) theory of Natural Selection, James proposed that the mind must serve some important purpose related to the survival of th ...
History and Approaches History Hippocrates
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Recognize how philosophical perspectives shaped the development of psychological thought. • Describe and compare different theoretical approaches in ...
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Recognize how philosophical perspectives shaped the development of psychological thought. • Describe and compare different theoretical approaches in ...
General Psychology Introduction
... B. Significant people: Hypocrites, Aristotle, Descarte, John Lock, Benjamin Rush, & Charles Darwin C. Wilhelm Wundt considered "Father of Psychology" 1. 1st to set up a psychology research laboratory in Leipiz, Germany in 1879. 2. 1st to publish in a reputable scientific journal. 3. Structuralism - ...
... B. Significant people: Hypocrites, Aristotle, Descarte, John Lock, Benjamin Rush, & Charles Darwin C. Wilhelm Wundt considered "Father of Psychology" 1. 1st to set up a psychology research laboratory in Leipiz, Germany in 1879. 2. 1st to publish in a reputable scientific journal. 3. Structuralism - ...
Chapter
... • The light rays are bent, refracted and focused by the lens. The lens' job is to make sure the rays come to a sharp focus on the retina. The resulting image on the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical impulses which are then transmitted through the ...
... • The light rays are bent, refracted and focused by the lens. The lens' job is to make sure the rays come to a sharp focus on the retina. The resulting image on the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical impulses which are then transmitted through the ...
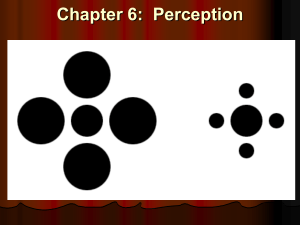
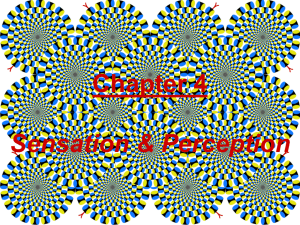
Perception
... Perceptual Illusions Illusions provide good examples in understanding how perception is organized. Studying faulty perception is as important as studying other perceptual phenomena. ...
... Perceptual Illusions Illusions provide good examples in understanding how perception is organized. Studying faulty perception is as important as studying other perceptual phenomena. ...
Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Module 1 – The Story of Psychology What
... 6. Sociocultural perspective - focuses on the relationship between social behavior and culture. 7. Evolutionary perspective - focuses on the biological bases of universal mental characteristics ...
... 6. Sociocultural perspective - focuses on the relationship between social behavior and culture. 7. Evolutionary perspective - focuses on the biological bases of universal mental characteristics ...
psychology - History of - 2013
... form of cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) & was first expounded by Ellis in the mid 1950s; development continued until his death in 2007. ...
... form of cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) & was first expounded by Ellis in the mid 1950s; development continued until his death in 2007. ...
Psychology 111
... Emphasis on adaptation Conceptually related to Evolutionary theory Wm. James ...
... Emphasis on adaptation Conceptually related to Evolutionary theory Wm. James ...
Intro to Psychology
... experience • Structuralism would be a building block for other psychological systems ...
... experience • Structuralism would be a building block for other psychological systems ...
Important Psychologists
... Observed stimuli and response, adopted Pavlov’s concept of conditioning Intelligence testing First to advance the Gestalt viewpoint, thought it was a mistake to break psychological experiences down into smaller pieces to analyze Whorf’s linguistic determinism – we think in terms of our culture and t ...
... Observed stimuli and response, adopted Pavlov’s concept of conditioning Intelligence testing First to advance the Gestalt viewpoint, thought it was a mistake to break psychological experiences down into smaller pieces to analyze Whorf’s linguistic determinism – we think in terms of our culture and t ...
Alfred Adler
... Austrian psychologist whose work was related to the Gestalt school In 1958 he published The Psychology of Interpersonal Relations, which systematized and expanded upon his creation of balance theory and attribution theory Gestalt Theory German: Gestalt - "essence or shape of an entity's comple ...
... Austrian psychologist whose work was related to the Gestalt school In 1958 he published The Psychology of Interpersonal Relations, which systematized and expanded upon his creation of balance theory and attribution theory Gestalt Theory German: Gestalt - "essence or shape of an entity's comple ...
Design Theory
... experiences that influence their perception of images. • We have seen that meaningfulness can help determine which area we see as figure. • If something has meaning to someone, it normally "jumps out" at them, and is more noticeable ...
... experiences that influence their perception of images. • We have seen that meaningfulness can help determine which area we see as figure. • If something has meaning to someone, it normally "jumps out" at them, and is more noticeable ...