Week 21
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
File
... He (third person) might replace Jake (antecedent) she – Jenna it – textbook they – the band I (first person) we You (second person) ...
... He (third person) might replace Jake (antecedent) she – Jenna it – textbook they – the band I (first person) we You (second person) ...
Stage 26 Vocabulary Sheet
... The children went to school in order that they might not be stupid. **Notice how the Imperfect Subjunctive has changed slightly in translation… For now, translate the purpose clause literally, as shown above. LATER you will be able to translate the clause to look more like an Infinitive phrase, and ...
... The children went to school in order that they might not be stupid. **Notice how the Imperfect Subjunctive has changed slightly in translation… For now, translate the purpose clause literally, as shown above. LATER you will be able to translate the clause to look more like an Infinitive phrase, and ...
What comes after verbs? - RIT
... - An adverb phrase may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). - An adverb phrase may be a prepositional phrase or a simple adverb. - An adverb phrase answers WHEN, WHERE, WHY, HOW questions. 3. Period (.) - A period (.) may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). 4. Noun or Adjective - A noun or ...
... - An adverb phrase may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). - An adverb phrase may be a prepositional phrase or a simple adverb. - An adverb phrase answers WHEN, WHERE, WHY, HOW questions. 3. Period (.) - A period (.) may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). 4. Noun or Adjective - A noun or ...
Grammar Lesson 30
... Exercise 5: Underline the verb or verb phrase in each sentence. Then identify the voice of the verb by writing A for Active or P for Passive in the blank. _____1. Clear the deck! _____2. A large storm was brewing over the lake. _____3. The bridge to the castle was guarded by two alligators in armor. ...
... Exercise 5: Underline the verb or verb phrase in each sentence. Then identify the voice of the verb by writing A for Active or P for Passive in the blank. _____1. Clear the deck! _____2. A large storm was brewing over the lake. _____3. The bridge to the castle was guarded by two alligators in armor. ...
Noun: a person, place or thing - Baltimore County Public Schools
... Conjunction: a word that joins together words, phrases and clauses FANBOYS – the conjunctions that join together the two halves of a compound sentence For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so Subordinating Conjunction – the conjunctions that are used in complex sentences After, since, before, while, beca ...
... Conjunction: a word that joins together words, phrases and clauses FANBOYS – the conjunctions that join together the two halves of a compound sentence For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so Subordinating Conjunction – the conjunctions that are used in complex sentences After, since, before, while, beca ...
prepositions
... LATIN I MASTERY LIST This is the information that you should know at the beginning of second year. We will spend a week or so reviewing – but it would be a good idea to go over this material before returning to school. ...
... LATIN I MASTERY LIST This is the information that you should know at the beginning of second year. We will spend a week or so reviewing – but it would be a good idea to go over this material before returning to school. ...
LATIN I MASTERY LIST
... LATIN I MASTERY LIST This is the information that you should know at the beginning of second year. We will spend a week or so reviewing – but it would be a good idea to go over this material before returning to school. ...
... LATIN I MASTERY LIST This is the information that you should know at the beginning of second year. We will spend a week or so reviewing – but it would be a good idea to go over this material before returning to school. ...
Past participles used as adjectives
... same form as the past tense of the verb. However, you can tell the difference because: • The past tense acts as a verb and has a subject “I” = subject I burned my hand. • The past participle acts as an adjective and describes a noun My hand is burned. ...
... same form as the past tense of the verb. However, you can tell the difference because: • The past tense acts as a verb and has a subject “I” = subject I burned my hand. • The past participle acts as an adjective and describes a noun My hand is burned. ...
NOUNS – name persons, places, things, or ideas
... past perfect - shows a past action or condition that ended before another past action EX.: I had never seen the beach before I moved to the coast. future perfect - shows a future action or condition that will have ended before another begins; it refers to the past in the future! EX.: I will have for ...
... past perfect - shows a past action or condition that ended before another past action EX.: I had never seen the beach before I moved to the coast. future perfect - shows a future action or condition that will have ended before another begins; it refers to the past in the future! EX.: I will have for ...
Grammar Boot Camp - Downtown Magnets High School
... “because” is the subordinating conjunction “the student” is the subject “prepared” is the verb “for the exam” completes the dependent clause ...
... “because” is the subordinating conjunction “the student” is the subject “prepared” is the verb “for the exam” completes the dependent clause ...
Grammar Lessons
... it would still be correct, but we don’t usually do that in actual conversation. You could also add the person’s name, if you know it. Again, we don’t always do this. ...
... it would still be correct, but we don’t usually do that in actual conversation. You could also add the person’s name, if you know it. Again, we don’t always do this. ...
Present Perfect
... Provozuje Národní ústav pro vzdělávání, školské poradenské zařízení a zařízení pro další vzdělávání pedagogických pracovníků (NÚV). ...
... Provozuje Národní ústav pro vzdělávání, školské poradenské zařízení a zařízení pro další vzdělávání pedagogických pracovníků (NÚV). ...
The present perfect is formed by combining the auxiliary verb "has
... Notice that we use "ha" to agree with "Juan". We do NOT use "han" to agree with "cuentas." The auxiliary verb is conjugated for the subject of the sentence, not the object. Compare these two examples: Juan ha pagado las cuentas. Juan has paid the bills. Juan y María han viajado a España. Juan and Ma ...
... Notice that we use "ha" to agree with "Juan". We do NOT use "han" to agree with "cuentas." The auxiliary verb is conjugated for the subject of the sentence, not the object. Compare these two examples: Juan ha pagado las cuentas. Juan has paid the bills. Juan y María han viajado a España. Juan and Ma ...
ADVERBIAL MODIFIER - qls
... another. Often used with demonstrative pronouns and adverbs: e.g. They must go to the dean and confess. Such was his plan. The word marking continuity is sometimes placed at the beginning of the sentence, with the verb immediately following: e.g. Next comes the juicy bit of the story. ...
... another. Often used with demonstrative pronouns and adverbs: e.g. They must go to the dean and confess. Such was his plan. The word marking continuity is sometimes placed at the beginning of the sentence, with the verb immediately following: e.g. Next comes the juicy bit of the story. ...
The past participle and the present perfect tense
... the sentence. The past participle, however, does not change according to the subject when it forms part of the perfect tense because it is not a adjective. ...
... the sentence. The past participle, however, does not change according to the subject when it forms part of the perfect tense because it is not a adjective. ...
verb subject object passive nouns verbs nouns adverbs modify verb
... She finished when the teacher got cross. [subordinate clause used as adverbial] ...
... She finished when the teacher got cross. [subordinate clause used as adverbial] ...
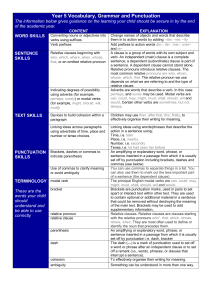
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
Realidades 2 – Capítulo 3B
... the action of the verb (or who’s / what’s being “verbed”). This chapter we will more closely study the first and second person direct object pronouns. These pronouns are used in place of the direct object in order to be less ...
... the action of the verb (or who’s / what’s being “verbed”). This chapter we will more closely study the first and second person direct object pronouns. These pronouns are used in place of the direct object in order to be less ...
Phrases and Clauses
... IV. Dependent clauses have a subject doing a verb, but they have a subordinate conjunction placed in front of the clause. That subordinate conjunction means that the clause can't stand independently by itself and become a complete sentence. Instead, the dependent clause is dependent upon another cla ...
... IV. Dependent clauses have a subject doing a verb, but they have a subordinate conjunction placed in front of the clause. That subordinate conjunction means that the clause can't stand independently by itself and become a complete sentence. Instead, the dependent clause is dependent upon another cla ...
Phrases and Clauses
... IV. Dependent clauses have a subject doing a verb, but they have a subordinate conjunction placed in front of the clause. That subordinate conjunction means that the clause can't stand independently by itself and become a complete sentence. Instead, the dependent clause is dependent upon another cla ...
... IV. Dependent clauses have a subject doing a verb, but they have a subordinate conjunction placed in front of the clause. That subordinate conjunction means that the clause can't stand independently by itself and become a complete sentence. Instead, the dependent clause is dependent upon another cla ...
File - Mrs. Atcheson
... Begins a subordinate clause (has subject and verb, but is dependent) May look for comma before in some cases ...
... Begins a subordinate clause (has subject and verb, but is dependent) May look for comma before in some cases ...