Parts of Speech
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
Verbals
... • Introductory participles are followed by a comma. • If the participle is nonessential, it is followed by a comma. ...
... • Introductory participles are followed by a comma. • If the participle is nonessential, it is followed by a comma. ...
For projection use only. Printing is prohibited by copyright law.
... • transitive verb (vt): takes a direct object (We love English.) • intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (Please sit down.) • All linking verbs are intransitive. ...
... • transitive verb (vt): takes a direct object (We love English.) • intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (Please sit down.) • All linking verbs are intransitive. ...
Document
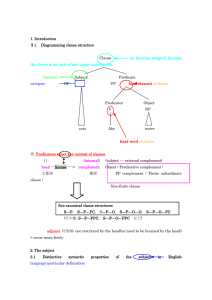
... (b) case of the pronoun in subject: nominative (cf. accusative of objects) (c) verb agreement (d) subject-auxiliary inversion 2.2 Traditional errors in defining the subject: related to their inappropriateness at language-particular level (a) subject is not alway the actor (b) subject is not alway th ...
... (b) case of the pronoun in subject: nominative (cf. accusative of objects) (c) verb agreement (d) subject-auxiliary inversion 2.2 Traditional errors in defining the subject: related to their inappropriateness at language-particular level (a) subject is not alway the actor (b) subject is not alway th ...
doc - English Banana
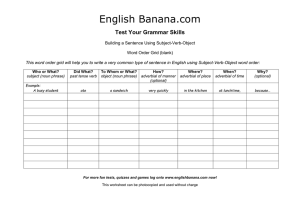
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
Grammar Review
... **If it’s an action verb…do you have a direct? indirect object? **If it’s a linking verb…do you have a predicate adj? pred. noun? (if no pa or pn, it’s a being verb) ...
... **If it’s an action verb…do you have a direct? indirect object? **If it’s a linking verb…do you have a predicate adj? pred. noun? (if no pa or pn, it’s a being verb) ...
Grammar - InRisk - University of British Columbia
... It is tempting to suggest that grammar is of secondary importance in technical writing. Perhaps the equations, figures, tables, and numbers speak for themselves. The contrary is true: grammar contributes strongly to the clarity, quality, and repute of a paper. Although this may seem unfair to academ ...
... It is tempting to suggest that grammar is of secondary importance in technical writing. Perhaps the equations, figures, tables, and numbers speak for themselves. The contrary is true: grammar contributes strongly to the clarity, quality, and repute of a paper. Although this may seem unfair to academ ...
ENC0027 “Cheat Sheet” for Grammar, Spelling, and Punctuation I
... A word that connects independent clauses or connects an independent clause to a phrase or dependent clause. ...
... A word that connects independent clauses or connects an independent clause to a phrase or dependent clause. ...
2014 Grammar progress appendix 1
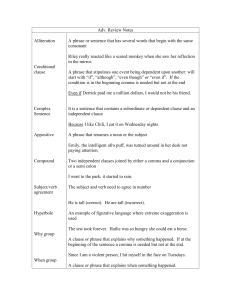
... • to use relative clauses to add extra information(who, which, where, whose, why) e.g. The sailor, who has been at sea for six months, was glad to be home. ...
... • to use relative clauses to add extra information(who, which, where, whose, why) e.g. The sailor, who has been at sea for six months, was glad to be home. ...
Adv
... Two independent clauses joined by either a comma and a conjunction or a semi colon I went to the park; it started to rain. ...
... Two independent clauses joined by either a comma and a conjunction or a semi colon I went to the park; it started to rain. ...
Irregular verbs lesson plan
... time I went to pet her. I got it some water and food and decided I would just watch it. It ate and drank everything I put down for it. This was one hungry little cat! ...
... time I went to pet her. I got it some water and food and decided I would just watch it. It ate and drank everything I put down for it. This was one hungry little cat! ...
Clause Toolbox Clause Toolbox A clause is a group of related
... The second clause describes what happened as a result of the action described in the first clause. “She completed her novel” is an independent clause because it can stand-alone. Types of Dependent (Subordinate) Clause Adjective Clauses - dependent clauses that modify nouns and pronouns (just as adje ...
... The second clause describes what happened as a result of the action described in the first clause. “She completed her novel” is an independent clause because it can stand-alone. Types of Dependent (Subordinate) Clause Adjective Clauses - dependent clauses that modify nouns and pronouns (just as adje ...
Sample
... first word and after the last word. If you only have one clause, it must be independent. Write “ind cl” above the sentence. A sentence made up of just one independent clause is called a simple sentence, and the sentence just declares a fact, so it’s a simple/declarative. Write S/dec off to the side ...
... first word and after the last word. If you only have one clause, it must be independent. Write “ind cl” above the sentence. A sentence made up of just one independent clause is called a simple sentence, and the sentence just declares a fact, so it’s a simple/declarative. Write S/dec off to the side ...
Present Perfect and Pluperfect
... The past perfect (also called the pluperfect and, in Spanish, the pluscuamperfecto), remember, is the past of the past and translates with “had” in English. ALL perfect tenses get a helping verb and a past participle: present perfect past perfect future perfect conditional perfect ...
... The past perfect (also called the pluperfect and, in Spanish, the pluscuamperfecto), remember, is the past of the past and translates with “had” in English. ALL perfect tenses get a helping verb and a past participle: present perfect past perfect future perfect conditional perfect ...
Present Perfect and Pluperfect
... The past perfect (also called the pluperfect and, in Spanish, the pluscuamperfecto), remember, is the past of the past and translates with “had” in English. ALL perfect tenses get a helping verb and a past participle: present perfect past perfect future perfect conditional perfect ...
... The past perfect (also called the pluperfect and, in Spanish, the pluscuamperfecto), remember, is the past of the past and translates with “had” in English. ALL perfect tenses get a helping verb and a past participle: present perfect past perfect future perfect conditional perfect ...
Participles - George Brown College
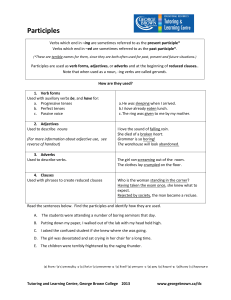
... Verbs which end in –ing are sometimes referred to as the present participle* Verbs which end in –ed are sometimes referred to as the past participle*. (*These are terrible names for them, since they are both often used for past, present and future situations.) ...
... Verbs which end in –ing are sometimes referred to as the present participle* Verbs which end in –ed are sometimes referred to as the past participle*. (*These are terrible names for them, since they are both often used for past, present and future situations.) ...
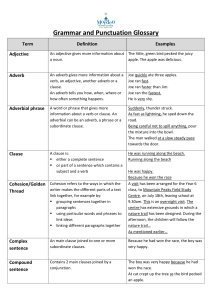
Grammar and Punctuation Glossary
... occasionally brackets. After a dash there may be a list or subordinate clause. A determiner goes in front of a noun and its adjectives to help to tell you which person or thing the sentence is about, or how much or how many of them there are. A hyphen is used to join two or more words that should be ...
... occasionally brackets. After a dash there may be a list or subordinate clause. A determiner goes in front of a noun and its adjectives to help to tell you which person or thing the sentence is about, or how much or how many of them there are. A hyphen is used to join two or more words that should be ...
the free PDF resource
... A word or phrase that usually comes after the verb can appear at the beginning of a sentence. This is called fronting. Fronted adverbials appear before the verb e.g. After the match, we had a party. Words with different meanings which look exactly the same when written and sound exactly the same whe ...
... A word or phrase that usually comes after the verb can appear at the beginning of a sentence. This is called fronting. Fronted adverbials appear before the verb e.g. After the match, we had a party. Words with different meanings which look exactly the same when written and sound exactly the same whe ...
DGP Tuesday Notes - Sentence Parts and Phrases
... 1. Simple Subject (S): the “who” or “what” of the verb. Must be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or infinitive. Can NEVER be a prepositional phrase. There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an “understood you”: Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) Example: The d ...
... 1. Simple Subject (S): the “who” or “what” of the verb. Must be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or infinitive. Can NEVER be a prepositional phrase. There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an “understood you”: Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) Example: The d ...
GRAMMAR SKILLS QUESTIONNAIRE
... 32. The structure of sentences often depends on the genre of writing (fiction, recipes, editorials, news reports). ...
... 32. The structure of sentences often depends on the genre of writing (fiction, recipes, editorials, news reports). ...
Sentence Patterns - Tidewater Community College
... Fax: 757-427-0327 http://www.tcc.edu/writing December 18, 2006 ...
... Fax: 757-427-0327 http://www.tcc.edu/writing December 18, 2006 ...
Practice Set #l--Diagram the following sentences looking
... C. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases. Prepositional phrases are frequently used to modify the subjects and verbs of sentences. A prepositional phrase must contain (a) a preposition, (b) the object of the preposition, and (c) any modifiers of the object. To diagram a prepositional phrase, the preposi ...
... C. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases. Prepositional phrases are frequently used to modify the subjects and verbs of sentences. A prepositional phrase must contain (a) a preposition, (b) the object of the preposition, and (c) any modifiers of the object. To diagram a prepositional phrase, the preposi ...
File
... A pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is used as a noun. Through the use of pronouns, one may avoid repeating name words: Mary has lost her book. The box has lost its handle. Ruth saw the boys and talked to them. VERBS A verb is a word used to express action, being, or stat ...
... A pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is used as a noun. Through the use of pronouns, one may avoid repeating name words: Mary has lost her book. The box has lost its handle. Ruth saw the boys and talked to them. VERBS A verb is a word used to express action, being, or stat ...
Word Classes - Elstow School
... more about a noun or pronoun. They give the reader a clearer picture of what is being described. Mr Fox had a long, bushy tail and gleaming eyes. He wore an old, scruffy jacket. She did not have any food left. ...
... more about a noun or pronoun. They give the reader a clearer picture of what is being described. Mr Fox had a long, bushy tail and gleaming eyes. He wore an old, scruffy jacket. She did not have any food left. ...