The Perfect Tense in Spanish
... whether it is regular using the list(above) print it out and learn it , then check in your head ! • The past participle NEVER changes in the perfect tense. When It is used in other ways , as an adjective ,it does agree with the noun, like all adjectives. • DON’T SPLIT THE HABER from its PAST PARTICI ...
... whether it is regular using the list(above) print it out and learn it , then check in your head ! • The past participle NEVER changes in the perfect tense. When It is used in other ways , as an adjective ,it does agree with the noun, like all adjectives. • DON’T SPLIT THE HABER from its PAST PARTICI ...
File
... • Coordinating Conjunctions may join single words, or they may join groups of words, but they must always join similar elements such as subject+subject, verb phrase+verb phrase, or sentence+sentence. When a coordinating conjunction is used to join elements, the element becomes a compound element. o ...
... • Coordinating Conjunctions may join single words, or they may join groups of words, but they must always join similar elements such as subject+subject, verb phrase+verb phrase, or sentence+sentence. When a coordinating conjunction is used to join elements, the element becomes a compound element. o ...
Guess What - Amy Benjamin
... together (without being a sentence). There are noun phrases and verb phrases. Once we have both a noun and a verb, then we have a clause. A clause is a group of words that may or may not be a complete sentence. If a clause can stand alone as a sentence, then we call it an independent clause. (If a c ...
... together (without being a sentence). There are noun phrases and verb phrases. Once we have both a noun and a verb, then we have a clause. A clause is a group of words that may or may not be a complete sentence. If a clause can stand alone as a sentence, then we call it an independent clause. (If a c ...
Document - Eldwick Primary School
... Bears live in Canada. Should I eat these seeds? Take these seeds away. The dog chased the cat. What a good friend you are! Sit in your chair. When the dust settled, they saw the devastation. Don’t, shouldn’t ...
... Bears live in Canada. Should I eat these seeds? Take these seeds away. The dog chased the cat. What a good friend you are! Sit in your chair. When the dust settled, they saw the devastation. Don’t, shouldn’t ...
LG506/LG606 Glossary of terms
... do-support: insertion of the auxiliary do in constructions which require an auxiliary for syntactic reasons: e.g. Did he leave?, Yes, he did, He did not leave (p14) ECM (Exceptional Case-marking): assignment of accusative case to the subject of an infinitive by a transitive verb in the higher clause ...
... do-support: insertion of the auxiliary do in constructions which require an auxiliary for syntactic reasons: e.g. Did he leave?, Yes, he did, He did not leave (p14) ECM (Exceptional Case-marking): assignment of accusative case to the subject of an infinitive by a transitive verb in the higher clause ...
Some technical terms for sentences
... some other word in a phrase or sentence. (e.g. to, in, about, above, around, among, off, on, by under, from, over, near, during.) Clause: a group of words which has both a subject and a predicate Types: Independent (main): makes a complete statement and can stand alone as a sentence. e.g. I took my ...
... some other word in a phrase or sentence. (e.g. to, in, about, above, around, among, off, on, by under, from, over, near, during.) Clause: a group of words which has both a subject and a predicate Types: Independent (main): makes a complete statement and can stand alone as a sentence. e.g. I took my ...
Grammar for english
... • Describing problems with the past participles as adjectives and with need+gerund, need+passive, infinitive, and keep + gerund • Passive in the present continuous and present perfect • Prepositions of caus ...
... • Describing problems with the past participles as adjectives and with need+gerund, need+passive, infinitive, and keep + gerund • Passive in the present continuous and present perfect • Prepositions of caus ...
Participles - Stjohns
... “must be built, must be fortified” * again, remember that with 3rd-io and 4th conjugation verbs, you need to drop the entire infinitive ending, add -ie-, then add the adjective ending ...
... “must be built, must be fortified” * again, remember that with 3rd-io and 4th conjugation verbs, you need to drop the entire infinitive ending, add -ie-, then add the adjective ending ...
collective noun
... Linking – link two parts of a sentence Test: substitute am, are, or is for the verb; if the sentence with the new verb still makes sense, then the original verb is a linking verb I smelled the rain. (action) The rain smelled fresh. (linking) ...
... Linking – link two parts of a sentence Test: substitute am, are, or is for the verb; if the sentence with the new verb still makes sense, then the original verb is a linking verb I smelled the rain. (action) The rain smelled fresh. (linking) ...
- ESL101.com
... The second module focuses on nouns and other nominal. Like verbs, nouns are key players in any sentence. We will focus mainly on the functions of nouns in sentences (subjects, objects, complements, adjectives) in order to gain a fuller understanding of their flexibility beyond a more simplistic view ...
... The second module focuses on nouns and other nominal. Like verbs, nouns are key players in any sentence. We will focus mainly on the functions of nouns in sentences (subjects, objects, complements, adjectives) in order to gain a fuller understanding of their flexibility beyond a more simplistic view ...
Daily Grammar Practice (DGP) Notes
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
What are verbs? Source: www.englishgrammar.org Read the
... person or a thing. They say what a person or a thing does. These words are called verbs. Now read the following sentences. We have two hands and two legs. She is a good girl. Here the verbs have and is show what a person has or is. These words are also called verbs. Thus we have seen that a verb is ...
... person or a thing. They say what a person or a thing does. These words are called verbs. Now read the following sentences. We have two hands and two legs. She is a good girl. Here the verbs have and is show what a person has or is. These words are also called verbs. Thus we have seen that a verb is ...
PowerPoint on some of the main ideas in English 1H.
... then-than- Then indicates a specific time or particular period of time, than indicated comparison between two things accept-except- Accept active verb showing something being given or taken and except is a preposition similar to “but” Affect- effect- Affect is active verb that asks how one thi ...
... then-than- Then indicates a specific time or particular period of time, than indicated comparison between two things accept-except- Accept active verb showing something being given or taken and except is a preposition similar to “but” Affect- effect- Affect is active verb that asks how one thi ...
Preterite Tense –er and –ir Verbs
... To form the preterite of the verb comer in the nosotros form, take off the -er and you are left with the stem of the verb (com-). Now add the ending –imos for nosotros. comer com + imos comimos nosotros comimos we ate Let’s look at all the comer conjugations in the preterite tense: comí comimos ...
... To form the preterite of the verb comer in the nosotros form, take off the -er and you are left with the stem of the verb (com-). Now add the ending –imos for nosotros. comer com + imos comimos nosotros comimos we ate Let’s look at all the comer conjugations in the preterite tense: comí comimos ...
The Sentence
... It is different from a phrase in that a phrase does not include BOTH a subject and a verb relationship. Is every sentence a clause? ...
... It is different from a phrase in that a phrase does not include BOTH a subject and a verb relationship. Is every sentence a clause? ...
Name - Campus Post It
... The most frequently used linking verb is to be. Other commonly used linking verbs are become, seem, look, feel, get, and appear. TRY IT - Look through one of your writing selections to find an example of a sentence that uses a linking verb. Copy it in the space below drawing a line from the verb to ...
... The most frequently used linking verb is to be. Other commonly used linking verbs are become, seem, look, feel, get, and appear. TRY IT - Look through one of your writing selections to find an example of a sentence that uses a linking verb. Copy it in the space below drawing a line from the verb to ...
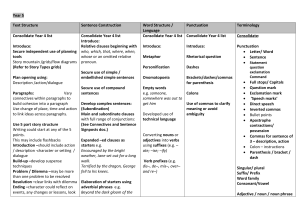
Year 5 Text Structure Sentence Construction Word Structure
... e.g. lengthening or shortening sentence for meaning and /or effect Moving sentence chunks (how, when, where) around for different effects e.g. The siren echoed loudly ….through the lonely streets ….at midnight Use of rhetorical questions Stage directions in speech (speech + verb + action) e.g. “Stop ...
... e.g. lengthening or shortening sentence for meaning and /or effect Moving sentence chunks (how, when, where) around for different effects e.g. The siren echoed loudly ….through the lonely streets ….at midnight Use of rhetorical questions Stage directions in speech (speech + verb + action) e.g. “Stop ...
1A Parts of Speech
... [Interrogative adjective: “What books have you read?” “What kind of fruit is that?”] 5. Adverb [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ...
... [Interrogative adjective: “What books have you read?” “What kind of fruit is that?”] 5. Adverb [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ...
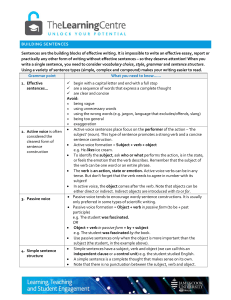
Building sentences
... e.g. She rides to work, and he catches the bus. (This could easily be broken into two sentences: She rides to work. He catches the bus). • In a complex sentence, simple sentences (independent clauses or control units) are combined with dependent clauses or a support unit. • Dependent clauses or supp ...
... e.g. She rides to work, and he catches the bus. (This could easily be broken into two sentences: She rides to work. He catches the bus). • In a complex sentence, simple sentences (independent clauses or control units) are combined with dependent clauses or a support unit. • Dependent clauses or supp ...
Grammar
... Prepositions are words that link a noun or a pronoun to another word in the sentence. Prepositions are used to show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence. A noun ALWAYS follows a preposition ...
... Prepositions are words that link a noun or a pronoun to another word in the sentence. Prepositions are used to show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence. A noun ALWAYS follows a preposition ...
Unit 3: Phrases
... WHAT IS A PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE? A GROUP of words beginning with a preposition and ending with a noun or pronoun It RELATES to some other word in the sentence. Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of that object ...
... WHAT IS A PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE? A GROUP of words beginning with a preposition and ending with a noun or pronoun It RELATES to some other word in the sentence. Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of that object ...
Verbals
... Past participles are formed by adding either –ed, -d-, -t, -en, or –n to the plain form of the verb. Others may be formed as irregular ...
... Past participles are formed by adding either –ed, -d-, -t, -en, or –n to the plain form of the verb. Others may be formed as irregular ...