Adverbs and adverbial phrases
... EVEN: used for showing that you are saying something that is SURPRISING. ...
... EVEN: used for showing that you are saying something that is SURPRISING. ...
Types of Sentences
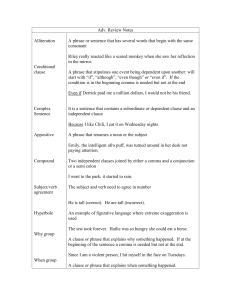
... 2. a COMPOUND sentence has two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction or conjunctive adverb, or separated by a semi colon: We went to the Thunderwolves’ hockey game last night, and we met up with our old neighbours from Westfort. We went to a hockey game; needless to say, my team lost. ...
... 2. a COMPOUND sentence has two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction or conjunctive adverb, or separated by a semi colon: We went to the Thunderwolves’ hockey game last night, and we met up with our old neighbours from Westfort. We went to a hockey game; needless to say, my team lost. ...
(Actually, articles are adjectives and not a different
... Article: There are only three articles--the, a , an (Actually, articles are adjectives and not a different part of speech) ...
... Article: There are only three articles--the, a , an (Actually, articles are adjectives and not a different part of speech) ...
NOUN
... Jack - he, him girl - she, her tree - it My favorite tree is in our front yard; it provides shade for many. ...
... Jack - he, him girl - she, her tree - it My favorite tree is in our front yard; it provides shade for many. ...
AE1
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb by making its meaning more specific. Adverbs modify by answering the questions “when”, “where”, “how”. ...
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb by making its meaning more specific. Adverbs modify by answering the questions “when”, “where”, “how”. ...
Basic Diagramming Dialogue
... subject complement (predicate adjective, predicate nominative, or predicate pronoun), not a direct object. If the sentence has a linking verb, place its complement after the verb, separated by a line that slants toward the subject. 8. After writing the subject, verb, and any direct object(s) or subj ...
... subject complement (predicate adjective, predicate nominative, or predicate pronoun), not a direct object. If the sentence has a linking verb, place its complement after the verb, separated by a line that slants toward the subject. 8. After writing the subject, verb, and any direct object(s) or subj ...
File - Renaissance middle school
... Subject and verb agreement and predicate. The subject identifies who or what is the focus with the verb showing its action. The predicate tells the reader what the subject is doing or what it is like. Punctuation (i.e. period (.), question mark (?), colon (:), semi-colon (;), Contraction means ...
... Subject and verb agreement and predicate. The subject identifies who or what is the focus with the verb showing its action. The predicate tells the reader what the subject is doing or what it is like. Punctuation (i.e. period (.), question mark (?), colon (:), semi-colon (;), Contraction means ...
Adv
... A phrase that stipulates one event being dependent upon another: will start with “if”, “although”, “even though” or “even if”. If the condition is in the beginning comma is needed but not at the end Even if Derrick paid me a million dollars, I would not be his friend. ...
... A phrase that stipulates one event being dependent upon another: will start with “if”, “although”, “even though” or “even if”. If the condition is in the beginning comma is needed but not at the end Even if Derrick paid me a million dollars, I would not be his friend. ...
Parts of Speech Table
... Determiners (a, the, every, this, that) modify and determine the kind of reference a noun or noun group has. ...
... Determiners (a, the, every, this, that) modify and determine the kind of reference a noun or noun group has. ...
the parts of speech
... plan into action. [Putting their plan into action is the direct object of the verb avoid. Plan is the direct object of the gerund putting. ...
... plan into action. [Putting their plan into action is the direct object of the verb avoid. Plan is the direct object of the gerund putting. ...
partsofspeech3
... subject of a sentence with more information about that subject. That bowtie looks dorky on you. He was sad that particular morning. ...
... subject of a sentence with more information about that subject. That bowtie looks dorky on you. He was sad that particular morning. ...
Grammar
... To determine whether a verb is being used as a linking or an action verb, use: am, are, or is for the verb. If the sentence makes sense with the substitution, the original verb is a linking verb. ...
... To determine whether a verb is being used as a linking or an action verb, use: am, are, or is for the verb. If the sentence makes sense with the substitution, the original verb is a linking verb. ...
condensed grammar review
... Which one? The, this, these, either, her, my How many? Two, several, many, few, every, seventh ...
... Which one? The, this, these, either, her, my How many? Two, several, many, few, every, seventh ...
French 12
... In French, il is similarly used as a dummy subject: il pleut. There are other idioms with the dummy subject, however, that English does not share. You have encountered one of them already: il y a. ...
... In French, il is similarly used as a dummy subject: il pleut. There are other idioms with the dummy subject, however, that English does not share. You have encountered one of them already: il y a. ...
The 8 Parts of Speech
... **Auxiliary verbs (helping verbs) combine with other verbs to create verb phrases o Include forms of be, do, and have o Also include can, could, may, must, shall, should, will, and would ...
... **Auxiliary verbs (helping verbs) combine with other verbs to create verb phrases o Include forms of be, do, and have o Also include can, could, may, must, shall, should, will, and would ...
Verb complexities
... We insist that he do the job properly. The committee proposes that she be appointed treasurer immediately It is essential that we be informed of your plan. The past subjunctive is sometimes called the were subjunctive, since were is the only subjunctive form that is distinct from the indicative past ...
... We insist that he do the job properly. The committee proposes that she be appointed treasurer immediately It is essential that we be informed of your plan. The past subjunctive is sometimes called the were subjunctive, since were is the only subjunctive form that is distinct from the indicative past ...
Verbs are usually defined as "action" words or "doing" words. The
... The plane arrived. The intransitive verb, arrived, takes no direct object. If we add modifiers to this arrived verb, these modifiers ARE NOT DIRECT OBJECTS: The plane from Los Angeles arrived LATER THAN USUAL. Later than usual modifies arrived, but it is NOT the object of arrived. To repeat: We have ...
... The plane arrived. The intransitive verb, arrived, takes no direct object. If we add modifiers to this arrived verb, these modifiers ARE NOT DIRECT OBJECTS: The plane from Los Angeles arrived LATER THAN USUAL. Later than usual modifies arrived, but it is NOT the object of arrived. To repeat: We have ...
Parts of Speech
... Objects of prepositions can be nouns, pronouns, gerunds, and clauses. o Prepositions do not always have modifiers (to him, with her). o The subject and verb of a sentence will never be found in a prepositional phrase. o Complements will never be found in a ...
... Objects of prepositions can be nouns, pronouns, gerunds, and clauses. o Prepositions do not always have modifiers (to him, with her). o The subject and verb of a sentence will never be found in a prepositional phrase. o Complements will never be found in a ...
Parts of Speech Overview
... There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb plus a helping verb. She turned the key and opened the door. Jackson was studying when I saw him last. ...
... There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb plus a helping verb. She turned the key and opened the door. Jackson was studying when I saw him last. ...
1. Grammar and Sentence Structure Order of presentation
... Action verb Their function in a sentence: Subject Predicate Sentence Expanders: Adjectives Adverbs Prepositions Prepositional phrase with punctuation. *When a prepositional phrase is at the beginning of a sentence use a comma with three or more words. With two words or less it is optional. Example: ...
... Action verb Their function in a sentence: Subject Predicate Sentence Expanders: Adjectives Adverbs Prepositions Prepositional phrase with punctuation. *When a prepositional phrase is at the beginning of a sentence use a comma with three or more words. With two words or less it is optional. Example: ...
Grammar Review
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
File
... S To test: S usually we can insert a preposition and the sentence will make sense (its like having an imaginary prepositional phrase that functions as an adverb or time or place) ...
... S To test: S usually we can insert a preposition and the sentence will make sense (its like having an imaginary prepositional phrase that functions as an adverb or time or place) ...
LABEL ALL NOUNS LABEL ALL ARTICLES LABEL ALL
... Proper Nouns begin with a capital letter & can be more than one word. ...
... Proper Nouns begin with a capital letter & can be more than one word. ...
Lecture 3
... - consists of a preposition (to, for, from, of, by, with) and the following noun or pronoun. a. PO after the preposition to A. When we want to emphasize Oi: They lent it to Jane, not to John. B. When Oi is expressed by means of inter./rel. pronouns: To whom did you promise it? C. When Od is expresse ...
... - consists of a preposition (to, for, from, of, by, with) and the following noun or pronoun. a. PO after the preposition to A. When we want to emphasize Oi: They lent it to Jane, not to John. B. When Oi is expressed by means of inter./rel. pronouns: To whom did you promise it? C. When Od is expresse ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.