File
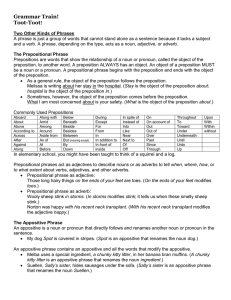
... A phrase is just a group of words that cannot stand alone as a sentence because it lacks a subject and a verb. A phrase, depending on the type, acts as a noun, adjective, or adverb. The Prepositional Phrase Prepositions are words that show the relationship of a noun or pronoun, called the object of ...
... A phrase is just a group of words that cannot stand alone as a sentence because it lacks a subject and a verb. A phrase, depending on the type, acts as a noun, adjective, or adverb. The Prepositional Phrase Prepositions are words that show the relationship of a noun or pronoun, called the object of ...
En mi tiempo libre PRESENT TENSE
... What is the present tense? We use it to describe actions which are happening now or which are true at the moment or in general. Hablo español I speak Spanish ...
... What is the present tense? We use it to describe actions which are happening now or which are true at the moment or in general. Hablo español I speak Spanish ...
Types of Verbals
... Definition: A participle is a verb form that functions as an adjective. A participle phrase consists of a participle along with its modifiers and complements. Like other adjectives, participles and participle phrases modify nouns and pronouns. Example: A tired hiker woke a sleeping bear. When alone, ...
... Definition: A participle is a verb form that functions as an adjective. A participle phrase consists of a participle along with its modifiers and complements. Like other adjectives, participles and participle phrases modify nouns and pronouns. Example: A tired hiker woke a sleeping bear. When alone, ...
the passive voice - Aula Virtual Maristas Mediterránea
... ACTIVE: SUBJECT + VERB+ OBJECT. The object of the verb in the active sentence becomes the subject in the passive sentence. The subject of the active sentence becomes the agent in the passive sentence. PASSIVE : OBJECT + VERB + SUBJECT: by agent when necessary) ...
... ACTIVE: SUBJECT + VERB+ OBJECT. The object of the verb in the active sentence becomes the subject in the passive sentence. The subject of the active sentence becomes the agent in the passive sentence. PASSIVE : OBJECT + VERB + SUBJECT: by agent when necessary) ...
Verbs Powerpoint
... 2. My grandfather (sits, sets) by a stream during fishing season. Page 111 2. Jenny is (laying, lying) in the sun without a hat. 3. That lady always (sits, sets) in the sun without a hat.) ...
... 2. My grandfather (sits, sets) by a stream during fishing season. Page 111 2. Jenny is (laying, lying) in the sun without a hat. 3. That lady always (sits, sets) in the sun without a hat.) ...
TYPES OF PHRASES
... For example. The girl with blue eyes bought a beautiful chair. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE. A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition, object of preposition(noun or pronoun) and may also consist of other modifiers. e.g. on a table, near a wall, in the room, at the door, under a tree A prepositional ...
... For example. The girl with blue eyes bought a beautiful chair. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE. A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition, object of preposition(noun or pronoun) and may also consist of other modifiers. e.g. on a table, near a wall, in the room, at the door, under a tree A prepositional ...
GREEK MYTHOLOGY
... Should indicates that the speaker feels compelled to walk home, but does not necessarily wish to ...
... Should indicates that the speaker feels compelled to walk home, but does not necessarily wish to ...
Proficiency Powerpoint Game Review
... Pronouns are used to replace nouns. Which of the following words is not a pronoun? I Me ...
... Pronouns are used to replace nouns. Which of the following words is not a pronoun? I Me ...
Academic Resource Center - Wheeling Jesuit University
... fragments, but try reading only one of the italicized clauses. Here is one way to repair the fragments: Last Friday, my husband and I drove to the shore. Several weeks ago, we had been invited to spend the weekend with the Laurences, our neighbors who spend most weekends at their house on the beach. ...
... fragments, but try reading only one of the italicized clauses. Here is one way to repair the fragments: Last Friday, my husband and I drove to the shore. Several weeks ago, we had been invited to spend the weekend with the Laurences, our neighbors who spend most weekends at their house on the beach. ...
ing is a gerund - ELT Concourse home
... Easy so far, but there’s a snag as there commonly is when trying to make grammar simple. The truth of the matter is that there is a cline from pure gerund at one end of the spectrum and pure participle at the other. Like this: ...
... Easy so far, but there’s a snag as there commonly is when trying to make grammar simple. The truth of the matter is that there is a cline from pure gerund at one end of the spectrum and pure participle at the other. Like this: ...
Understanding Verbs I - Camilla`s English Page
... regular verbs, the past tense and past participle forms are both formed by adding –ed. However, they can always be distinguished by their different uses. If an –ed form is acting as a verb by itself, it is a past tense verb; if it has a helping verb or is acting in some other way, it is a participle ...
... regular verbs, the past tense and past participle forms are both formed by adding –ed. However, they can always be distinguished by their different uses. If an –ed form is acting as a verb by itself, it is a past tense verb; if it has a helping verb or is acting in some other way, it is a participle ...
Whom or what - Pratt Perfection!
... Right click on this screen and choose to view this as a full screen presentation. This presentation is timed so you will only need to click on the left mouse button when it is time to move to the next slide. At the end of the presentation return to the main Grammar page. ...
... Right click on this screen and choose to view this as a full screen presentation. This presentation is timed so you will only need to click on the left mouse button when it is time to move to the next slide. At the end of the presentation return to the main Grammar page. ...
We performed awesome!
... NOUN = person, place, idea, or thing Common – general name Ex: car Proper – name of a particular person, place, or thing Ex: Honda Concrete – a thing that can be experienced thru one of the 5 senses Ex: ice cream Abstract – idea, feeling, or quality Ex: happiness Collective – names a gro ...
... NOUN = person, place, idea, or thing Common – general name Ex: car Proper – name of a particular person, place, or thing Ex: Honda Concrete – a thing that can be experienced thru one of the 5 senses Ex: ice cream Abstract – idea, feeling, or quality Ex: happiness Collective – names a gro ...
Grammar Glossary, Autumn 2016
... The children played in the playground. The children were playing in the playground. ...
... The children played in the playground. The children were playing in the playground. ...
Description of Editing Symbols
... especially careful not to use indefinite demonstrative pronouns (this, that, they, their, it, its ) in place of the nouns and/or details necessary to maintain clarity vt error or awkwardness in verb tense ...
... especially careful not to use indefinite demonstrative pronouns (this, that, they, their, it, its ) in place of the nouns and/or details necessary to maintain clarity vt error or awkwardness in verb tense ...
Prepositions Notes - LanguageArts-NHS
... Another example is “outside of” when “outside” by itself would do just fine. You should say, “He's outside the door,” not, “He's outside of the door.” Another example is “where are you at”. “Where are you?” would communicate the same sentiment the same. ...
... Another example is “outside of” when “outside” by itself would do just fine. You should say, “He's outside the door,” not, “He's outside of the door.” Another example is “where are you at”. “Where are you?” would communicate the same sentiment the same. ...
A Brief Guide to Megablunders
... Pronoun agreement means that the pronoun must agree with its antecedent and vice versa. • Example #1: Each cowboy and his horse drank their fill at the desert oasis. o Explanation: As we learned with SV agreement, each is a singular noun subject, so the sentence should be viewed like this: Each (cow ...
... Pronoun agreement means that the pronoun must agree with its antecedent and vice versa. • Example #1: Each cowboy and his horse drank their fill at the desert oasis. o Explanation: As we learned with SV agreement, each is a singular noun subject, so the sentence should be viewed like this: Each (cow ...
Sentence Variety
... between 2 nouns or a noun and a verb. Now write 3 sentences with prepositional phrases. Ex: Behind the door, you should find a spare key. ...
... between 2 nouns or a noun and a verb. Now write 3 sentences with prepositional phrases. Ex: Behind the door, you should find a spare key. ...
Indirect Object Pronouns
... affected by the verb’s action. It answers the question “to whom/what?” or “for whom/what?” For example: She gives the man the book. Who gives? - she - subject. Gives what? - book - direct object. To whom? - man - indirect object. ...
... affected by the verb’s action. It answers the question “to whom/what?” or “for whom/what?” For example: She gives the man the book. Who gives? - she - subject. Gives what? - book - direct object. To whom? - man - indirect object. ...
Lecture 5. Verbs and Verb Phrases I
... to (ability), have to or be obliged to (obligation), be possible /to/that/ (probability), and be /allowed/permitted/ to (permission) (e.g. Jag har kunnat köra bil sedan jag fyllde 17 vs. I have been able to drive a car since I turned 17). Marginal modals (dare, need, used to, ought to) can be used e ...
... to (ability), have to or be obliged to (obligation), be possible /to/that/ (probability), and be /allowed/permitted/ to (permission) (e.g. Jag har kunnat köra bil sedan jag fyllde 17 vs. I have been able to drive a car since I turned 17). Marginal modals (dare, need, used to, ought to) can be used e ...
VERB TENSES
... Used to indicate a decision about the future taken at the moment of speaking. I think I’ll (I will) go out on the weekend. I think I won’t (I will not) go out on the weekend. Will you follow me? Yes, I will./No, I won’t. ...
... Used to indicate a decision about the future taken at the moment of speaking. I think I’ll (I will) go out on the weekend. I think I won’t (I will not) go out on the weekend. Will you follow me? Yes, I will./No, I won’t. ...
iii. syntax analysis - Computer Engineering
... The words that are directly affected by the subject are the direct complements. In general the direct complements are used without preposition and directly connected to predicates. The verbs that can take direct complements are transitive verbs. The indirect complements show the action is done for w ...
... The words that are directly affected by the subject are the direct complements. In general the direct complements are used without preposition and directly connected to predicates. The verbs that can take direct complements are transitive verbs. The indirect complements show the action is done for w ...
File - Mrs. Graves` Website
... – This is one of the books that are required for class. – (The relative pronoun that requires the plural verb are because its antecedent, books, is plural) ...
... – This is one of the books that are required for class. – (The relative pronoun that requires the plural verb are because its antecedent, books, is plural) ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.























