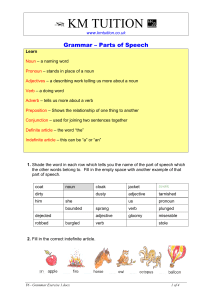
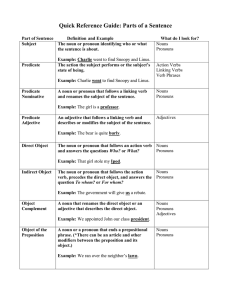
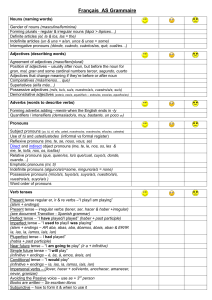
Parts Of Speech
... Verb -Action – what the noun or pronoun does = running, walking, sitting, talking, and more… -Being – is, are, was, were, am, be, been -Auxillary (Helping) Verbs – would, could, should, can, may, might, will, and more Adjective – describes a noun -“red” car, “slow” horse, “young” student, “old” teac ...
... Verb -Action – what the noun or pronoun does = running, walking, sitting, talking, and more… -Being – is, are, was, were, am, be, been -Auxillary (Helping) Verbs – would, could, should, can, may, might, will, and more Adjective – describes a noun -“red” car, “slow” horse, “young” student, “old” teac ...
Repaso: C4G2 Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct objects 1.
... 2. RP can go just before the cong. verb or it can be attached to the end of the a present particple or inf. ex: Esa jugadora_____está vendando la mano. Las otras jugadoras están calentándo____. La entrenadora va a poner____ un abrigo. 3. RP is attached to the end of the verb in ________command. It i ...
... 2. RP can go just before the cong. verb or it can be attached to the end of the a present particple or inf. ex: Esa jugadora_____está vendando la mano. Las otras jugadoras están calentándo____. La entrenadora va a poner____ un abrigo. 3. RP is attached to the end of the verb in ________command. It i ...
A noun is the word we use to identify a person, place, object or idea
... to any of the above, whereas proper nouns refer to any particular person, place, object or idea. Examples of common nouns: boy, shop, table, dream Examples of proper nouns: Sally, London, Channel Tunnel ...
... to any of the above, whereas proper nouns refer to any particular person, place, object or idea. Examples of common nouns: boy, shop, table, dream Examples of proper nouns: Sally, London, Channel Tunnel ...
Present Participle
... The present participle can also be used after verbs of the senses if we do not want to emphasise that the action was completed. (see Infinitive or Ing-Form) feel, find, hear, listen to, notice, see, smell, watch Did you see him dancing? ...
... The present participle can also be used after verbs of the senses if we do not want to emphasise that the action was completed. (see Infinitive or Ing-Form) feel, find, hear, listen to, notice, see, smell, watch Did you see him dancing? ...
NOUNS-VERBS-ADJECTIVES
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
Verb Tense Exercises
... second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
... second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
Verb Study Guide Quiz Date: ______ Most verbs show action, but
... EXAMPLE: John marched down the hall. ( marched= action verb) Martha hoped that her mom would return soon. ( hoped = mental verb) Helping Verbs: Some verbs are helped along the way with helping verbs. EX: Sally is trying to read her book. ( verb= is trying/ is= helping verb) ...
... EXAMPLE: John marched down the hall. ( marched= action verb) Martha hoped that her mom would return soon. ( hoped = mental verb) Helping Verbs: Some verbs are helped along the way with helping verbs. EX: Sally is trying to read her book. ( verb= is trying/ is= helping verb) ...
Heading Glossary of grammatical terms
... ■ clause A clause is a group of words which includes a subject and a verb. It may or may not constitute a complete sentence. I am leaving. (one clause – one sentence) I am leaving when I’ve finished. (two clauses – one sentence) ■ comparative (see adjective) ■ conjugation/conjugate A conjugation ...
... ■ clause A clause is a group of words which includes a subject and a verb. It may or may not constitute a complete sentence. I am leaving. (one clause – one sentence) I am leaving when I’ve finished. (two clauses – one sentence) ■ comparative (see adjective) ■ conjugation/conjugate A conjugation ...
Noun Study Guide
... Common adjectives = describe a nonspecific noun Examples: damaged shed, shiny star Proper adjectives = describe a specific noun, so it is capitalized Examples: American flag, English book ...
... Common adjectives = describe a nonspecific noun Examples: damaged shed, shiny star Proper adjectives = describe a specific noun, so it is capitalized Examples: American flag, English book ...
Part 2 Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...
Document
... 3. ADJECTIVE- describes (modifies) a noun or pronoun Answers questions- Which one? What kind? How many? (ie. large, red shiny, delicious) 4. VERB- an action word, or a state of being Verbs that express state of being, or can be used as linking verbs, or can be used as helpers with action verbs (yell ...
... 3. ADJECTIVE- describes (modifies) a noun or pronoun Answers questions- Which one? What kind? How many? (ie. large, red shiny, delicious) 4. VERB- an action word, or a state of being Verbs that express state of being, or can be used as linking verbs, or can be used as helpers with action verbs (yell ...
Chapter 45
... – Formed from the present stem (just like imperfect, present, and future tense indicative verbs) – The noun modified is doing the action (active) at the same time (present) as the main verb – Translated “verbing” ...
... – Formed from the present stem (just like imperfect, present, and future tense indicative verbs) – The noun modified is doing the action (active) at the same time (present) as the main verb – Translated “verbing” ...
Chapter 2 Parts of Speech
... • Being verbs: is, as, were, are, am • Helping verbs are used with main verbs to form other tenses to form verb phrases: had sung, will be singing ...
... • Being verbs: is, as, were, are, am • Helping verbs are used with main verbs to form other tenses to form verb phrases: had sung, will be singing ...
One finds in French a number of nouns with a
... One finds in French a number of nouns with a -ion suffix which are formally and semantically related to adjectives, e.g. abjection related to abject, or (in)correction related to (in)correct. As the examples show, however, two cases must be distinguished. In the case represented by abjection, the ad ...
... One finds in French a number of nouns with a -ion suffix which are formally and semantically related to adjectives, e.g. abjection related to abject, or (in)correction related to (in)correct. As the examples show, however, two cases must be distinguished. In the case represented by abjection, the ad ...
Parts of Speech Overview - BMC
... may precede nouns, or they may appear after a form of the reflexive verb to be (am, are, is, was, etc.). Examples: ...
... may precede nouns, or they may appear after a form of the reflexive verb to be (am, are, is, was, etc.). Examples: ...
Infinitives The gerunds
... The infinitive is the base form of the verb. It is sometimes preceded by the marker to and then it is called the to-infinitive. Remember that that ‘to’ is a not a part of the infinitive and the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘ ...
... The infinitive is the base form of the verb. It is sometimes preceded by the marker to and then it is called the to-infinitive. Remember that that ‘to’ is a not a part of the infinitive and the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘ ...
Grammar Point: Definite and indefinite articles
... How do you know which verb to use? Hints: • tener is sometimes followed by “que” and another not-conjugated verb • tener can also be followed by something that someone “had” or “didn’t have” such as time, money, stamps, gas, etc. • poder is often followed by another not-conjugated verb meaning “cou ...
... How do you know which verb to use? Hints: • tener is sometimes followed by “que” and another not-conjugated verb • tener can also be followed by something that someone “had” or “didn’t have” such as time, money, stamps, gas, etc. • poder is often followed by another not-conjugated verb meaning “cou ...
a quick english grammar review
... o Vocative: used in direct address (In English, case is indicated by word order, a preposition preceding the word, a possessive form, or inflection of the word) ...
... o Vocative: used in direct address (In English, case is indicated by word order, a preposition preceding the word, a possessive form, or inflection of the word) ...
Action Verb: Tells what the subject does. • Jeremy likes to run
... • That was the worst storm ever. Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. • (verb) The snail moved slowly. • (adjective) The horse was already gigantic. • (adverb) The kingdom was far away. ...
... • That was the worst storm ever. Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. • (verb) The snail moved slowly. • (adjective) The horse was already gigantic. • (adverb) The kingdom was far away. ...
Study Guide for Grammar Test 2
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
The Eight Parts of Speech Poem
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
Français AS Grammaire
... Français AS Grammaire Nouns (naming words) Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, ...
... Français AS Grammaire Nouns (naming words) Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, ...
Gerunds
... Participles are adjectives that look like verbs. They usually end in ing or ed, but can also have irregular forms. Ex. Walking in the rain, the traveler searched for shelter. ...
... Participles are adjectives that look like verbs. They usually end in ing or ed, but can also have irregular forms. Ex. Walking in the rain, the traveler searched for shelter. ...